- C++菜鸟教程 - 从入门到精通 第二节
DreamByte
c++
一.上节课的补充(数据类型)1.前言继上节课,我们主要讲解了输入,输出和运算符,我们现在来补充一下数据类型的知识上节课遗漏了这个知识点,非常的抱歉顺便说一下,博主要上高中了,更新会慢,2-4周更新一次对了,正好赶上中秋节,小编跟大家说一句:中秋节快乐!2.int类型上节课,我们其实只用了int类型int类型,是整数类型,它们存贮的是整数,不能存小数(浮点数)定义变量的方式很简单inta;//定义一
- Spring MVC 全面指南:从入门到精通的详细解析
一杯梅子酱
技术栈学习springmvcjava
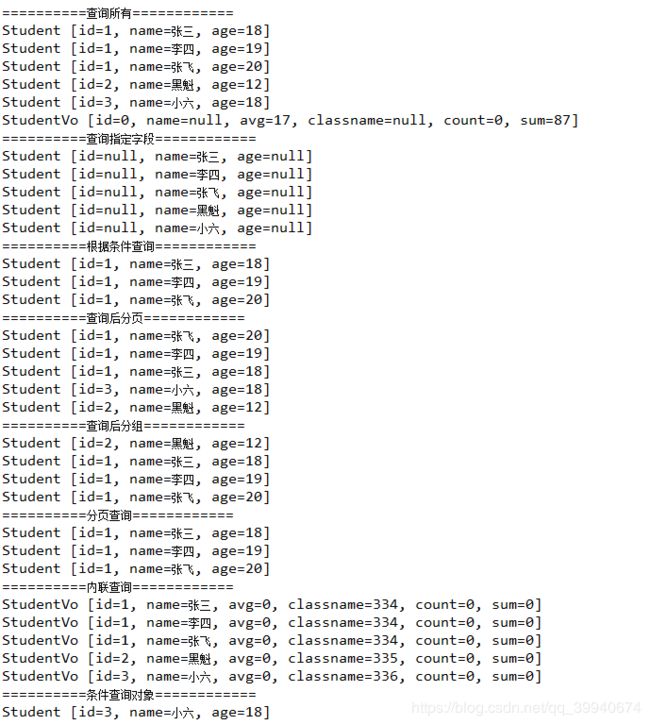
引言:SpringMVC,作为Spring框架的一个重要模块,为构建Web应用提供了强大的功能和灵活性。无论是初学者还是有一定经验的开发者,掌握SpringMVC都将显著提升你的Web开发技能。本文旨在为初学者提供一个全面且易于理解的学习路径,通过详细的知识点分析和实际案例,帮助你快速上手SpringMVC,让学习过程既深刻又高效。一、SpringMVC简介1.1什么是SpringMVC?Spri
- mysql学习教程,从入门到精通,TOP 和MySQL LIMIT 子句(15)
知识分享小能手
大数据数据库MySQLmysql学习oracle数据库开发语言adb大数据
1、TOP和MySQLLIMIT子句内容在SQL中,不同的数据库系统对于限制查询结果的数量有不同的实现方式。TOP关键字主要用于SQLServer和Access数据库中,而LIMIT子句则主要用于MySQL、PostgreSQL(通过LIMIT/OFFSET语法)、SQLite等数据库中。下面将分别详细介绍这两个功能的语法、语句以及案例。1.1、TOP子句(SQLServer和Access)1.1
- Jooq 框架介绍及其核心要点
木南曌
Javajava
一、引言Jooq(JavaPersistenceforRelationalDatabases)是一个强大的类型安全的SQL查询构建器和ORM(Object-RelationalMapping)框架,专为Java和Kotlin设计。它为开发者提供了一种优雅的方式来编写SQL代码,同时还能享受到静态类型检查带来的好处。本文将详细介绍Jooq的核心功能,并通过一系列的代码示例来展示如何使用Jooq。二、
- shell 笔记_s1=abc,s2=def,[-z‘‘‘]&;&;echo‘$s1‘ echo‘$s2‘的输出是什么
2024云技术
运维linux面试
最全的Linux教程,Linux从入门到精通======================linux从入门到精通(第2版)Linux系统移植Linux驱动开发入门与实战LINUX系统移植第2版Linux开源网络全栈详解从DPDK到OpenFlow第一份《Linux从入门到精通》466页====================内容简介====本书是获得了很多读者好评的Linux经典畅销书**《Linu
- python毕业设计作品:python闲置物品二手交易平台系统设计与实现毕业设计源代码(Django框架)
黄菊华老师
毕设资料python二手交易平台系统
博主介绍:黄菊华老师《Vue.js入门与商城开发实战》《微信小程序商城开发》图书作者,CSDN博客专家,在线教育专家,CSDN钻石讲师;专注大学生毕业设计教育和辅导。所有项目都配有从入门到精通的基础知识视频课程,学习后应对毕业设计答辩。项目配有对应开发文档、开题报告、任务书、PPT、论文模版等项目都录了发布和功能操作演示视频;项目的界面和功能都可以定制,包安装运行!!!如果需要联系我,可以在CSD
- 目标检测YOLO系列从入门到精通技术详解100篇-【目标检测】工业相机
格图素书
数码相机目标检测人工智能
目录知识储备深度相机1TOF2双目视觉3结构光4智能门锁应用5手机应用算法原理相机的成像与标定模型相机标定的实施·标定过程的算法实施相机标定的扩展CCD工业相机、镜头倍率及相关参数计算方法知识储备深度相机1TOF1.1Kinectv2Kinectv2是Microsoft在2014年发售的,如图1-1所示。相比于Kinectv1在硬件和软件上作出了很大的进化,且在深度测量的系统和非系统误差方面表现出
- Vue3+TypeScript从入门到精通系列之:类多态
快乐骑行^_^
日常分享专栏typescriptVue3类多态
Vue3+TypeScript从入门到精通系列之:类多态一、TypeScript类多态代码二、TypeScript的类多态转化为JS代码三、查看js输出一、TypeScript类多态代码(()=>{//多态:父类型的引用指向了子类型的对象,不同类型的对象针对相同的方法,产生了不同的行为//定义一个父类classAnimal{name:stringconstructor(name:string){t
- Autosar MCAL从入门到精通系列讲解--总目录
常学常思
Autosar--MCAL从入门到精通嵌入式硬件mcu单片机Autosar
前言欢迎大家一起来学习Autosar,作为一个小白,在最开始的时候也是一脸茫然,不知道如何去学习,如何下手。在这里,我将记录我所有Autosar学习的过程,问题点,以及分享我的代码供大家参考。最终能让大家快速上手。Mcal:可以去官网下载一、EB1.EBtresos创建工程2.EB生成代码编译---makefile二、TricoreMcal实战系列(EB)这里的博客之前都是用S32DS来配置的,在
- python从入门到精通:函数
人间无解
python开发语言数据结构数据库mysql
目录1、函数介绍2、函数的定义3、函数的传入参数4、函数的返回值5、函数说明文档6、函数的嵌套调用7、变量的作用域1、函数介绍函数是组织好的,可重复使用的,用来实现特定功能的代码段。name="zhangsan";length=len(name);print(length)之所以可以随时调用len()(实现统计长度)函数,是因为,它是python内置的函数(提前写好的)。不使用len()函数如何实
- QT之QML从入门到精通(第二章)
only-lucky
qt开发语言
本章介绍QML部件(component)和加载(Loader)的基本使用引言importQtQuick2.12importQtQuick.Window2.12importQtQuick.Controls2.12Window{visible:truewidth:640height:480title:qsTr("HelloWorld")Component.onCompleted:{console.lo
- 2020-12-05
幸福大黑鸭
IT1.LeetCode:存在重复元素Java编写2020-12-05(217.存在重复元素)2.《Java从入门到精通》明日科技:P331~335阅读记xmind笔记,并自己实现实例。知识点之前确实都学过,但还是再系统复习一下吧。3.《Semantic-awareWorkflowConstructionandAnalysisforDistributedDataAnalyticsSystems》:
- chatgpt赋能python:用Python读取雷达数据-从入门到精通(教程)
a1sssssb
ChatGptchatgptpython开发语言计算机
用Python读取雷达数据-从入门到精通(教程)雷达数据是指通过雷达信号采集的气象、地质等信息,广泛应用于气象、军事、航空、航天等领域。Python是一种快速、简洁、易用的编程语言,并且提供了大量用于科学计算和数据分析的库和工具。在本文中,我们将介绍如何使用Python读取雷达数据。什么是雷达数据雷达数据是指通过雷达信号采集的数据,可以是气象信息(例如降水量、风速等)、地质信息(例如地形、地貌等)
- ARM专栏目录
代码改变世界ctw
ARMarm开发智能电视
Arm发布CortexX925、A725、A520,Armv9.2架构【目录】Armv8/Armv9付费专栏中华人民共和国密码行业标准-各类标准文档下载一文帮你梳理ARM基础概念ARMVSX86处理器构架一文读懂arm架构-从入门到精通armv8/armv9MMU深度学习多核多cluster多系统之间缓存一致性概述cache的基本概念原理扫盲SMMU学习这一篇就够了[mmu/cache]-ARMM
- 基于开源CrashRpt与微软开源Detours技术深度改造的异常捕获库分享
dvlinker
C/C++实战专栏异常捕获开源异常捕获库CrashRptCrashPaddump文件Windbg
目录1、异常捕获模块概述2、为什么需要异常捕获模块?3、在有些异常的场景下是没有生成dump文件的4、开源异常捕获库CrashRpt介绍5、对开源库CrashRpt的改进C++软件异常排查从入门到精通系列教程(专栏文章列表,欢迎订阅,持续更新...)https://blog.csdn.net/chenlycly/article/details/125529931
- 点云从入门到精通技术详解100篇-点云特征学习模型及其在配准中的应用
格图素书
学习
目录前言应用前景国内外研究现状点云特征提取算法研究现状点云配准算法研究现状相关理论基础2.1深度学习2.1.1深度学习概述2.1.2自编码器2.1.3稀疏编码2.1.4受限玻尔兹曼机2.2多层感知机2.2.1多层感知机概述2.2.2感知器与多层感知机2.2.3多层感知机的训练2.3点云配准方法2.3.1无点对应关系的点云配准方法2.3.2基于对应关系的点云配准方法2.4评价指标2.4.1点云配准评
- Linux进程间通信方式之管道(pipe)_
前端老侯
运维linux面试
最全的Linux教程,Linux从入门到精通======================linux从入门到精通(第2版)Linux系统移植Linux驱动开发入门与实战LINUX系统移植第2版Linux开源网络全栈详解从DPDK到OpenFlow第一份《Linux从入门到精通》466页====================内容简介====本书是获得了很多读者好评的Linux经典畅销书**《Linu
- 从入门到精通:TEMU商家如何利用自养号测评打造爆款
陈哥测评BWM9992
跨境电商TEMUTEMU测评测评自养号环境搭建
TEMU平台以其独特的魅力和无限潜力,吸引着众多商家竞相入驻。然而,面对激烈的市场竞争,如何快速提高销量,成为摆在每位商家面前的重大课题。本文将深入剖析一种高效且具策略性的方法——精细化自养号测评,帮助TEMU商家在竞争中脱颖而出,实现销量的飞跃。自养号测评的价值自养号测评,是一种通过精心管理买家账号,模拟真实购物体验,并输出高质量评价的方法。它不仅能够直接促进产品曝光和销售转化,还能在消费者心中
- 推荐书籍:FFmpeg从入门到精通
微创光电技术团队
音视频
本书是一本介绍FFmpeg的实战技术指南,全书共10章,分为两个部分。第一部分部分(第1~7章)为FFmpeg的命令行使用篇,介绍了FFmpeg的基础组成部分、FFmpeg工具使用、FFmpeg的封装操作、FFmpeg的转码操作、FFmpeg的流媒体操作、FFmpeg的滤镜操作、FFmpeg的设备操作。第二部分(第8~10章)为FFmpeg的API使用篇,介绍了FFmpeg封装部分的API使用操作
- Python列表全解析:从入门到精通
Bro_cat
Pythonpython开发语言
Python中的列表(List)是一种功能强大且灵活的数据结构,是编程中不可或缺的工具之一。今天将给大家介绍Python列表的基本概念、操作方法、特性、与数组的差异以及常用函数的使用,帮助你从入门到精通。一、列表的基本概念列表是Python中一种有序、可变的数据集合,能够存储多个元素,这些元素可以是任何数据类型。列表使用方括号[]定义,元素之间用逗号,分隔。例如:my_list=[1,2,3,'a
- Flutter 从入门到精通的全方位指北
老三不说话、
flutter
一、Flutter简介Flutter是由谷歌开发的一款跨平台移动应用开发框架。它使用Dart语言,通过一套代码能够同时为iOS和Android等平台构建高质量的原生应用界面。Flutter的特点众多。在性能方面,它拥有出色的渲染能力,能够实现流畅的用户体验。其UI设计灵活多样,提供丰富的自定义选项,让开发者可以轻松打造出独特且美观的界面。同时,Flutter支持热重载功能,极大地提高了开发效率,开
- jooq时间查询语句
朱杰jjj
jooq
最近新用jooq来编程发现中国网站上能给的资料少之又少,直接用时间查询竟然不行,后来整理好长一段时间解决publicListgetfuture(Integerpage){Integerstart=page*20;Datea=newDate();Timestampts=newTimestamp(a.getTime());returncreate().selectFrom(MEETINGS).wher
- javacv从入门到精通——第三章:基本使用
ayou_llf
javacvjavaopencv语音识别音视频视频编解码
了解javacv的基本结构JavaCV的基本结构如下:JavaCV核心类:JavaCV核心类是JavaCV库的核心,它包括了JavaCV的所有功能和特性,可以用来进行计算机视觉和人工智能任务的开发和实现。JavaCV核心类的主要功能包括:视频捕获、视频编解码、图像处理、人脸检测、特征提取等。基本数据类型:JavaCV库支持多种基本数据类型,包括整数、浮点数、布尔类型等,这些基本数据类型是进行计算机
- 2020-12-17
幸福大黑鸭
IT1.LeetCode:各位相加Java编写2020-12-17(258.各位相加)2.《Java从入门到精通》明日科技:P391~395阅读记xmind笔记,并自己实现实例。知识点之前确实都学过,但还是再系统复习一下吧。3.《Semantic-awareWorkflowConstructionandAnalysisforDistributedDataAnalyticsSystems》:精读关键
- Python算法模糊匹配:FuzzyWuzzy深度剖析,从入门到精通,解决你所有需要匹配的需求
长风清留扬
Python人工智能算法python算法大数据网络dba
在数据科学与机器学习的广阔领域中,处理不精确或模糊的数据是一项至关重要的技能。想象一下,当你面对的是一堆拼写错误、缩写、或是格式不一的文本数据时,如何高效地从中提取有价值的信息?这正是FuzzyWuzzy——Python中一个强大的模糊字符串匹配库,能够大展身手的地方。本文将为你全面介绍FuzzyWuzzy——Python中一个强大的通过算法模糊字符串匹配库,全网最全最新,一看就会,接下来带你走进
- C#编程技术指南:从入门到精通的全面教程
猿享天开
学懂C#-高级编程技术精讲c#开发语言C#编程技术指南
无论你是编程新手,还是想要深化.NET技能的开发者,本文都将为你提供一条清晰的学习路径,从C#基础到高级特性,每一站都配有详尽解析和实用示例,旨在帮助你建立坚实的知识体系,并激发你对C#及.NET生态的热情。目录第一部分:C#基础——构建你的第一个程序1.环境搭建2.第一个C#程序3.变量、数据类型与控制流1)变量2)数据类型3)控制流4)条件判断(if语句)5)循环(for语句)6)循环(whi
- R 语言学习教程,从入门到精通,Java 中操作 R(27)
知识分享小能手
学习心得体会数据分析大数据r语言学习java开发语言numpy大数据数据分析
1、Java中操作R首先,在R中安装软件包“Rserve”。如果你使用的是RGui可视化界面,在菜单栏的程序包-安装程序包里可以完成这个步骤。如果你使用的是纯粹的RConsole,可以使用以下命令:install.packages("Rserve",repos="https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/CRAN/")当Reserve安装完成之后,在R的根目录下会有一个library
- C++菜鸟教程 - 从入门到精通 第一节
DreamByte
C++菜鸟教程c++开发语言
一.C++简介C++是一种编程语言,它是由BjarneStroustrup于1979年在贝尔实验室开始设计开发的。C++进一步扩充和完善了C语言,是一种面向对象的程序设计语言。C++可运行于多种平台上,如Windows、MAC操作系统以及UNIX的各种版本。C++是一种静态类型的、编译式的、通用的、大小写敏感的、不规则的编程语言,支持过程化编程、面向对象编程和泛型编程。C++被认为是一种中级语言,
- Chapter 28 继承
Heaven645
Python从入门到精通pythonpycharm面向对象继承复写
欢迎大家订阅【Python从入门到精通】专栏,一起探索Python的无限可能!文章目录前言一、基础语法二、复写前言在面向对象编程中,继承是一个重要的概念,它允许我们创建新的类(子类),以获得现有类(父类)的特性和行为。本文详细讲解了Python中的继承特性,介绍了如何通过继承来有效地扩展和复用代码。本篇文章参考:黑马程序员一、基础语法在Python中,继承(Inheritance)是一种面向对象编
- Qt Phonon多媒体框架详解及简单实例分享
dvlinker
C/C++实战专栏qtPhonon多媒体框架
目录1、Phonon简介2、Phonon基本类2.1、VideoPlayer类2.2、MediaObject类2.3、Phonon::createPath()2.4、AudioOutput类2.5、VideoWidgetClass2.6、SeekSlider类2.7、VolumeSlider类3、Phonon完整使用实例4、总结C++软件异常排查从入门到精通系列教程(专栏文章列表,欢迎订阅,持续更
- 算法 单链的创建与删除
换个号韩国红果果
c算法
先创建结构体
struct student {
int data;
//int tag;//标记这是第几个
struct student *next;
};
// addone 用于将一个数插入已从小到大排好序的链中
struct student *addone(struct student *h,int x){
if(h==NULL) //??????
- 《大型网站系统与Java中间件实践》第2章读后感
白糖_
java中间件
断断续续花了两天时间试读了《大型网站系统与Java中间件实践》的第2章,这章总述了从一个小型单机构建的网站发展到大型网站的演化过程---整个过程会遇到很多困难,但每一个屏障都会有解决方案,最终就是依靠这些个解决方案汇聚到一起组成了一个健壮稳定高效的大型系统。
看完整章内容,
- zeus持久层spring事务单元测试
deng520159
javaDAOspringjdbc
今天把zeus事务单元测试放出来,让大家指出他的毛病,
1.ZeusTransactionTest.java 单元测试
package com.dengliang.zeus.webdemo.test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.junit.Test;
import
- Rss 订阅 开发
周凡杨
htmlxml订阅rss规范
RSS是 Really Simple Syndication的缩写(对rss2.0而言,是这三个词的缩写,对rss1.0而言则是RDF Site Summary的缩写,1.0与2.0走的是两个体系)。
RSS
- 分页查询实现
g21121
分页查询
在查询列表时我们常常会用到分页,分页的好处就是减少数据交换,每次查询一定数量减少数据库压力等等。
按实现形式分前台分页和服务器分页:
前台分页就是一次查询出所有记录,在页面中用js进行虚拟分页,这种形式在数据量较小时优势比较明显,一次加载就不必再访问服务器了,但当数据量较大时会对页面造成压力,传输速度也会大幅下降。
服务器分页就是每次请求相同数量记录,按一定规则排序,每次取一定序号直接的数据
- spring jms异步消息处理
510888780
jms
spring JMS对于异步消息处理基本上只需配置下就能进行高效的处理。其核心就是消息侦听器容器,常用的类就是DefaultMessageListenerContainer。该容器可配置侦听器的并发数量,以及配合MessageListenerAdapter使用消息驱动POJO进行消息处理。且消息驱动POJO是放入TaskExecutor中进行处理,进一步提高性能,减少侦听器的阻塞。具体配置如下:
- highCharts柱状图
布衣凌宇
hightCharts柱图
第一步:导入 exporting.js,grid.js,highcharts.js;第二步:写controller
@Controller@RequestMapping(value="${adminPath}/statistick")public class StatistickController { private UserServi
- 我的spring学习笔记2-IoC(反向控制 依赖注入)
aijuans
springmvcSpring 教程spring3 教程Spring 入门
IoC(反向控制 依赖注入)这是Spring提出来了,这也是Spring一大特色。这里我不用多说,我们看Spring教程就可以了解。当然我们不用Spring也可以用IoC,下面我将介绍不用Spring的IoC。
IoC不是框架,她是java的技术,如今大多数轻量级的容器都会用到IoC技术。这里我就用一个例子来说明:
如:程序中有 Mysql.calss 、Oracle.class 、SqlSe
- TLS java简单实现
antlove
javasslkeystoretlssecure
1. SSLServer.java
package ssl;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.security.KeyStore;
import
- Zip解压压缩文件
百合不是茶
Zip格式解压Zip流的使用文件解压
ZIP文件的解压缩实质上就是从输入流中读取数据。Java.util.zip包提供了类ZipInputStream来读取ZIP文件,下面的代码段创建了一个输入流来读取ZIP格式的文件;
ZipInputStream in = new ZipInputStream(new FileInputStream(zipFileName));
&n
- underscore.js 学习(一)
bijian1013
JavaScriptunderscore
工作中需要用到underscore.js,发现这是一个包括了很多基本功能函数的js库,里面有很多实用的函数。而且它没有扩展 javascript的原生对象。主要涉及对Collection、Object、Array、Function的操作。 学
- java jvm常用命令工具——jstatd命令(Java Statistics Monitoring Daemon)
bijian1013
javajvmjstatd
1.介绍
jstatd是一个基于RMI(Remove Method Invocation)的服务程序,它用于监控基于HotSpot的JVM中资源的创建及销毁,并且提供了一个远程接口允许远程的监控工具连接到本地的JVM执行命令。
jstatd是基于RMI的,所以在运行jstatd的服务
- 【Spring框架三】Spring常用注解之Transactional
bit1129
transactional
Spring可以通过注解@Transactional来为业务逻辑层的方法(调用DAO完成持久化动作)添加事务能力,如下是@Transactional注解的定义:
/*
* Copyright 2002-2010 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version
- 我(程序员)的前进方向
bitray
程序员
作为一个普通的程序员,我一直游走在java语言中,java也确实让我有了很多的体会.不过随着学习的深入,java语言的新技术产生的越来越多,从最初期的javase,我逐渐开始转变到ssh,ssi,这种主流的码农,.过了几天为了解决新问题,webservice的大旗也被我祭出来了,又过了些日子jms架构的activemq也开始必须学习了.再后来开始了一系列技术学习,osgi,restful.....
- nginx lua开发经验总结
ronin47
使用nginx lua已经两三个月了,项目接开发完毕了,这几天准备上线并且跟高德地图对接。回顾下来lua在项目中占得必中还是比较大的,跟PHP的占比差不多持平了,因此在开发中遇到一些问题备忘一下 1:content_by_lua中代码容量有限制,一般不要写太多代码,正常编写代码一般在100行左右(具体容量没有细心测哈哈,在4kb左右),如果超出了则重启nginx的时候会报 too long pa
- java-66-用递归颠倒一个栈。例如输入栈{1,2,3,4,5},1在栈顶。颠倒之后的栈为{5,4,3,2,1},5处在栈顶
bylijinnan
java
import java.util.Stack;
public class ReverseStackRecursive {
/**
* Q 66.颠倒栈。
* 题目:用递归颠倒一个栈。例如输入栈{1,2,3,4,5},1在栈顶。
* 颠倒之后的栈为{5,4,3,2,1},5处在栈顶。
*1. Pop the top element
*2. Revers
- 正确理解Linux内存占用过高的问题
cfyme
linux
Linux开机后,使用top命令查看,4G物理内存发现已使用的多大3.2G,占用率高达80%以上:
Mem: 3889836k total, 3341868k used, 547968k free, 286044k buffers
Swap: 6127608k total,&nb
- [JWFD开源工作流]当前流程引擎设计的一个急需解决的问题
comsci
工作流
当我们的流程引擎进入IRC阶段的时候,当循环反馈模型出现之后,每次循环都会导致一大堆节点内存数据残留在系统内存中,循环的次数越多,这些残留数据将导致系统内存溢出,并使得引擎崩溃。。。。。。
而解决办法就是利用汇编语言或者其它系统编程语言,在引擎运行时,把这些残留数据清除掉。
- 自定义类的equals函数
dai_lm
equals
仅作笔记使用
public class VectorQueue {
private final Vector<VectorItem> queue;
private class VectorItem {
private final Object item;
private final int quantity;
public VectorI
- Linux下安装R语言
datageek
R语言 linux
命令如下:sudo gedit /etc/apt/sources.list1、deb http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/CRAN/bin/linux/ubuntu/ precise/ 2、deb http://dk.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu hardy universesudo apt-key adv --keyserver ke
- 如何修改mysql 并发数(连接数)最大值
dcj3sjt126com
mysql
MySQL的连接数最大值跟MySQL没关系,主要看系统和业务逻辑了
方法一:进入MYSQL安装目录 打开MYSQL配置文件 my.ini 或 my.cnf查找 max_connections=100 修改为 max_connections=1000 服务里重起MYSQL即可
方法二:MySQL的最大连接数默认是100客户端登录:mysql -uusername -ppass
- 单一功能原则
dcj3sjt126com
面向对象的程序设计软件设计编程原则
单一功能原则[
编辑]
SOLID 原则
单一功能原则
开闭原则
Liskov代换原则
接口隔离原则
依赖反转原则
查
论
编
在面向对象编程领域中,单一功能原则(Single responsibility principle)规定每个类都应该有
- POJO、VO和JavaBean区别和联系
fanmingxing
VOPOJOjavabean
POJO和JavaBean是我们常见的两个关键字,一般容易混淆,POJO全称是Plain Ordinary Java Object / Plain Old Java Object,中文可以翻译成:普通Java类,具有一部分getter/setter方法的那种类就可以称作POJO,但是JavaBean则比POJO复杂很多,JavaBean是一种组件技术,就好像你做了一个扳子,而这个扳子会在很多地方被
- SpringSecurity3.X--LDAP:AD配置
hanqunfeng
SpringSecurity
前面介绍过基于本地数据库验证的方式,参考http://hanqunfeng.iteye.com/blog/1155226,这里说一下如何修改为使用AD进行身份验证【只对用户名和密码进行验证,权限依旧存储在本地数据库中】。
将配置文件中的如下部分删除:
<!-- 认证管理器,使用自定义的UserDetailsService,并对密码采用md5加密-->
- mac mysql 修改密码
IXHONG
mysql
$ sudo /usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqld_safe –user=root & //启动MySQL(也可以通过偏好设置面板来启动)$ sudo /usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqladmin -uroot password yourpassword //设置MySQL密码(注意,这是第一次MySQL密码为空的时候的设置命令,如果是修改密码,还需在-
- 设计模式--抽象工厂模式
kerryg
设计模式
抽象工厂模式:
工厂模式有一个问题就是,类的创建依赖于工厂类,也就是说,如果想要拓展程序,必须对工厂类进行修改,这违背了闭包原则。我们采用抽象工厂模式,创建多个工厂类,这样一旦需要增加新的功能,直接增加新的工厂类就可以了,不需要修改之前的代码。
总结:这个模式的好处就是,如果想增加一个功能,就需要做一个实现类,
- 评"高中女生军训期跳楼”
nannan408
首先,先抛出我的观点,各位看官少点砖头。那就是,中国的差异化教育必须做起来。
孔圣人有云:有教无类。不同类型的人,都应该有对应的教育方法。目前中国的一体化教育,不知道已经扼杀了多少创造性人才。我们出不了爱迪生,出不了爱因斯坦,很大原因,是我们的培养思路错了,我们是第一要“顺从”。如果不顺从,我们的学校,就会用各种方法,罚站,罚写作业,各种罚。军
- scala如何读取和写入文件内容?
qindongliang1922
javajvmscala
直接看如下代码:
package file
import java.io.RandomAccessFile
import java.nio.charset.Charset
import scala.io.Source
import scala.reflect.io.{File, Path}
/**
* Created by qindongliang on 2015/
- C语言算法之百元买百鸡
qiufeihu
c算法
中国古代数学家张丘建在他的《算经》中提出了一个著名的“百钱买百鸡问题”,鸡翁一,值钱五,鸡母一,值钱三,鸡雏三,值钱一,百钱买百鸡,问翁,母,雏各几何?
代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int cock,hen,chick; /*定义变量为基本整型*/
for(coc
- Hadoop集群安全性:Hadoop中Namenode单点故障的解决方案及详细介绍AvatarNode
wyz2009107220
NameNode
正如大家所知,NameNode在Hadoop系统中存在单点故障问题,这个对于标榜高可用性的Hadoop来说一直是个软肋。本文讨论一下为了解决这个问题而存在的几个solution。
1. Secondary NameNode
原理:Secondary NN会定期的从NN中读取editlog,与自己存储的Image进行合并形成新的metadata image
优点:Hadoop较早的版本都自带,