Linux eth0, eth1, ..., eth%d 的生成
一直很好奇,Linux下的eth0, eth1,eth2等是如何生成的~
特别函数:
__dev_get_by_name
通过 eth1 这样的名字,找 struct net_device
分三个步骤:
1. 创建 struct net_device 类型的变量 XA ;
2. 将创建的变量 XA 通过 register_netdevice 函数进行注册;
3. ifconfig ethx up,有了这最后一步,才能在 ifconfig 命令的输出中看到增加的 ethx;
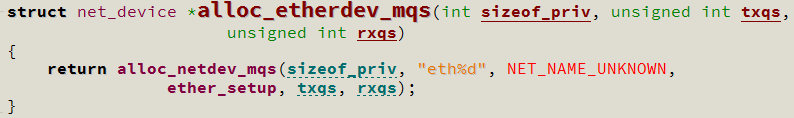
1. 从 alloc_etherdev 开始分析,其实 alloc_etherdev 是一个宏:
alloc_etherdev --> alloc_etherdev_mq --> alloc_etherdev_mqs
最后调用的 alloc_etherdev_mqs 才是一个函数,而这个函数又调用了 alloc_netdev_mqs 函数,具体的操作都是在这个函数中完成的,因此:
alloc_etherdev --> alloc_etherdev_mq --> alloc_etherdev_mqs --> alloc_netdev_mqs
/**
* alloc_etherdev_mqs - Allocates and sets up an Ethernet device
* @sizeof_priv: Size of additional driver-private structure to be allocated
* for this Ethernet device
* @txqs: The number of TX queues this device has.
* @rxqs: The number of RX queues this device has.
*
* Fill in the fields of the device structure with Ethernet-generic
* values. Basically does everything except registering the device.
*
* Constructs a new net device, complete with a private data area of
* size (sizeof_priv). A 32-byte (not bit) alignment is enforced for
* this private data area.
*/
struct net_device *alloc_etherdev_mqs(int sizeof_priv, unsigned int txqs,
unsigned int rxqs)
{
return alloc_netdev_mqs(sizeof_priv, "eth%d", NET_NAME_UNKNOWN,
ether_setup, txqs, rxqs);
}
/**
* alloc_netdev_mqs - allocate network device
* @sizeof_priv: size of private data to allocate space for
* @name: device name format string
* @name_assign_type: origin of device name
* @setup: callback to initialize device
* @txqs: the number of TX subqueues to allocate
* @rxqs: the number of RX subqueues to allocate
*
* Allocates a struct net_device with private data area for driver use
* and performs basic initialization. Also allocates subqueue structs
* for each queue on the device.
*/
struct net_device *alloc_netdev_mqs(int sizeof_priv, const char *name,
unsigned char name_assign_type,
void (*setup)(struct net_device *),
unsigned int txqs, unsigned int rxqs)
{
struct net_device *dev;
size_t alloc_size;
struct net_device *p;
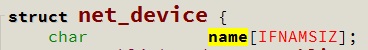
BUG_ON(strlen(name) >= sizeof(dev->name));
if (txqs < 1) {
pr_err("alloc_netdev: Unable to allocate device with zero queues\n");
return NULL;
}
#ifdef CONFIG_SYSFS
if (rxqs < 1) {
pr_err("alloc_netdev: Unable to allocate device with zero RX queues\n");
return NULL;
}
#endif
alloc_size = sizeof(struct net_device);
if (sizeof_priv) {
/* ensure 32-byte alignment of private area */
alloc_size = ALIGN(alloc_size, NETDEV_ALIGN);
alloc_size += sizeof_priv;
}
/* ensure 32-byte alignment of whole construct */
alloc_size += NETDEV_ALIGN - 1;
// 分配 struct net_device 变量空间,在下一步中调用 PTR_ALIGN 宏进行对齐
p = kvzalloc(alloc_size, GFP_KERNEL | __GFP_RETRY_MAYFAIL);
if (!p)
return NULL;
// dev 的值,就是最后 alloc_etherdev 返回的指向 struct net_device 变量/空间的指针
dev = PTR_ALIGN(p, NETDEV_ALIGN);
dev->padded = (char *)dev - (char *)p;
dev->pcpu_refcnt = alloc_percpu(int);
if (!dev->pcpu_refcnt)
goto free_dev;
if (dev_addr_init(dev))
goto free_pcpu;
dev_mc_init(dev);
dev_uc_init(dev);
dev_net_set(dev, &init_net);
dev->gso_max_size = GSO_MAX_SIZE;
dev->gso_max_segs = GSO_MAX_SEGS;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->napi_list);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->unreg_list);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->close_list);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->link_watch_list);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->adj_list.upper);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->adj_list.lower);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->ptype_all);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->ptype_specific);
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_SCHED
hash_init(dev->qdisc_hash);
#endif
dev->priv_flags = IFF_XMIT_DST_RELEASE | IFF_XMIT_DST_RELEASE_PERM;
// 这个 setup,是一个函数指针,由 alloc_etherdev_mqs 调用时传递过来的, alloc_etherdev_mqs 调用时,传递
// 过来的函数是:void ether_setup(struct net_device *dev)
setup(dev);
if (!dev->tx_queue_len) {
dev->priv_flags |= IFF_NO_QUEUE;
dev->tx_queue_len = DEFAULT_TX_QUEUE_LEN;
}
dev->num_tx_queues = txqs;
dev->real_num_tx_queues = txqs;
if (netif_alloc_netdev_queues(dev))
goto free_all;
#ifdef CONFIG_SYSFS
dev->num_rx_queues = rxqs;
dev->real_num_rx_queues = rxqs;
if (netif_alloc_rx_queues(dev))
goto free_all;
#endif
strcpy(dev->name, name);
dev->name_assign_type = name_assign_type;
dev->group = INIT_NETDEV_GROUP;
if (!dev->ethtool_ops)
dev->ethtool_ops = &default_ethtool_ops;
nf_hook_ingress_init(dev);
return dev;
free_all:
free_netdev(dev);
return NULL;
free_pcpu:
free_percpu(dev->pcpu_refcnt);
free_dev:
netdev_freemem(dev);
return NULL;
}
对于这两个函数,除了代码中的注释,最重要的就是 alloc_netdev_mqs 的第二个参数 "eth%d" :
在 alloc_netdev_mqs 中,
因此,此时 alloc_etherdev 返回的 net_device 中的数据成员 name 的值为 "eth%d" (不包含双引号)
2. 从 register_netdevice 开始,步骤一种返回的 struct net_device* 值,刚好是 register_netdevice 函数的参数:
/**
* register_netdevice - register a network device
* @dev: device to register
*
* Take a completed network device structure and add it to the kernel
* interfaces. A %NETDEV_REGISTER message is sent to the netdev notifier
* chain. 0 is returned on success. A negative errno code is returned
* on a failure to set up the device, or if the name is a duplicate.
*
* Callers must hold the rtnl semaphore. You may want
* register_netdev() instead of this.
*
* BUGS:
* The locking appears insufficient to guarantee two parallel registers
* will not get the same name.
*/
// 此时, dev->name 的值是 "eth%d", 不包含双引号
int register_netdevice(struct net_device *dev)
{
int ret;
struct net *net = dev_net(dev);
BUG_ON(dev_boot_phase);
ASSERT_RTNL();
might_sleep();
/* When net_device's are persistent, this will be fatal. */
BUG_ON(dev->reg_state != NETREG_UNINITIALIZED);
BUG_ON(!net);
spin_lock_init(&dev->addr_list_lock);
netdev_set_addr_lockdep_class(dev);
ret = dev_get_valid_name(net, dev, dev->name);
if (ret < 0)
goto out;
/* Init, if this function is available */
if (dev->netdev_ops->ndo_init) {
ret = dev->netdev_ops->ndo_init(dev);
if (ret) {
if (ret > 0)
ret = -EIO;
goto out;
}
}
if (((dev->hw_features | dev->features) &
NETIF_F_HW_VLAN_CTAG_FILTER) &&
(!dev->netdev_ops->ndo_vlan_rx_add_vid ||
!dev->netdev_ops->ndo_vlan_rx_kill_vid)) {
netdev_WARN(dev, "Buggy VLAN acceleration in driver!\n");
ret = -EINVAL;
goto err_uninit;
}
ret = -EBUSY;
if (!dev->ifindex)
dev->ifindex = dev_new_index(net);
else if (__dev_get_by_index(net, dev->ifindex))
goto err_uninit;
/* Transfer changeable features to wanted_features and enable
* software offloads (GSO and GRO).
*/
dev->hw_features |= NETIF_F_SOFT_FEATURES;
dev->features |= NETIF_F_SOFT_FEATURES;
if (dev->netdev_ops->ndo_udp_tunnel_add) {
dev->features |= NETIF_F_RX_UDP_TUNNEL_PORT;
dev->hw_features |= NETIF_F_RX_UDP_TUNNEL_PORT;
}
dev->wanted_features = dev->features & dev->hw_features;
if (!(dev->flags & IFF_LOOPBACK))
dev->hw_features |= NETIF_F_NOCACHE_COPY;
/* If IPv4 TCP segmentation offload is supported we should also
* allow the device to enable segmenting the frame with the option
* of ignoring a static IP ID value. This doesn't enable the
* feature itself but allows the user to enable it later.
*/
if (dev->hw_features & NETIF_F_TSO)
dev->hw_features |= NETIF_F_TSO_MANGLEID;
if (dev->vlan_features & NETIF_F_TSO)
dev->vlan_features |= NETIF_F_TSO_MANGLEID;
if (dev->mpls_features & NETIF_F_TSO)
dev->mpls_features |= NETIF_F_TSO_MANGLEID;
if (dev->hw_enc_features & NETIF_F_TSO)
dev->hw_enc_features |= NETIF_F_TSO_MANGLEID;
/* Make NETIF_F_HIGHDMA inheritable to VLAN devices.
*/
dev->vlan_features |= NETIF_F_HIGHDMA;
/* Make NETIF_F_SG inheritable to tunnel devices.
*/
dev->hw_enc_features |= NETIF_F_SG | NETIF_F_GSO_PARTIAL;
/* Make NETIF_F_SG inheritable to MPLS.
*/
dev->mpls_features |= NETIF_F_SG;
ret = call_netdevice_notifiers(NETDEV_POST_INIT, dev);
ret = notifier_to_errno(ret);
if (ret)
goto err_uninit;
ret = netdev_register_kobject(dev);
if (ret)
goto err_uninit;
dev->reg_state = NETREG_REGISTERED;
__netdev_update_features(dev);
/*
* Default initial state at registry is that the
* device is present.
*/
set_bit(__LINK_STATE_PRESENT, &dev->state);
linkwatch_init_dev(dev);
dev_init_scheduler(dev);
dev_hold(dev);
list_netdevice(dev);
add_device_randomness(dev->dev_addr, dev->addr_len);
/* If the device has permanent device address, driver should
* set dev_addr and also addr_assign_type should be set to
* NET_ADDR_PERM (default value).
*/
if (dev->addr_assign_type == NET_ADDR_PERM)
memcpy(dev->perm_addr, dev->dev_addr, dev->addr_len);
/* Notify protocols, that a new device appeared. */
ret = call_netdevice_notifiers(NETDEV_REGISTER, dev);
ret = notifier_to_errno(ret);
if (ret) {
rollback_registered(dev);
dev->reg_state = NETREG_UNREGISTERED;
}
/*
* Prevent userspace races by waiting until the network
* device is fully setup before sending notifications.
*/
if (!dev->rtnl_link_ops ||
dev->rtnl_link_state == RTNL_LINK_INITIALIZED)
rtmsg_ifinfo(RTM_NEWLINK, dev, ~0U, GFP_KERNEL);
out:
return ret;
err_uninit:
if (dev->netdev_ops->ndo_uninit)
dev->netdev_ops->ndo_uninit(dev);
if (dev->priv_destructor)
dev->priv_destructor(dev);
goto out;
}
register_netdevice --> dev_get_valid_name --> dev_alloc_name_ns --> __dev_alloc_name
register_netdevice 函数中调用:
// 此时,dev->name 的值是 “eth%d”
ret = dev_get_valid_name(net, dev, dev->name);
int dev_get_valid_name(struct net *net, struct net_device *dev,
const char *name)
{
BUG_ON(!net);
if (!dev_valid_name(name))
return -EINVAL;
// char *strchr(const char *s, int c);
// The strchr() function returns a pointer to the first occurrence of the character c in the string s.
// 只要 % 在 name 中出现过,则返回值不为 NULL,此处的 name 是 eth%d ,因此返回值不为 NULL
if (strchr(name, '%'))
return dev_alloc_name_ns(net, dev, name);
else if (__dev_get_by_name(net, name))
return -EEXIST;
else if (dev->name != name)
strlcpy(dev->name, name, IFNAMSIZ);
return 0;
}
static int dev_alloc_name_ns(struct net *net,
struct net_device *dev,
const char *name)
{
char buf[IFNAMSIZ];
int ret;
// 此处的 name 是 eth%d , buf 中的内容应该是全 \0 的,但是跟编译器有关系
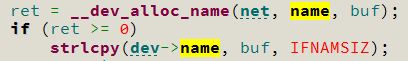
ret = __dev_alloc_name(net, name, buf);
if (ret >= 0)
strlcpy(dev->name, buf, IFNAMSIZ);
return ret;
}
// 主要的操作在 __dev_alloc_name 函数中,一般 PAGE_SIZE 是 4K,因此, net_device 数目最多有 8 * 4K = 32K 个
// 在这个函数中,利用了位图,每一个bit,代表一个 net_device
static int __dev_alloc_name(struct net *net, const char *name, char *buf)
{
int i = 0;
const char *p;
// 通常 PAGE_SIZE 是 4K,因此是 32K
const int max_netdevices = 8*PAGE_SIZE;
unsigned long *inuse;
struct net_device *d;
// IFNAMSIZ 的值 是 16,此处在 前 16 - 1 = 15 个字符中匹配 %
// 因为 net_device 中 name 的定义是: char name[IFNAMSIZ];
p = strnchr(name, IFNAMSIZ-1, '%');
if (p) {
/*
* Verify the string as this thing may have come from
* the user. There must be either one "%d" and no other "%"
* characters.
*/
// % 后必须是 d
if (p[1] != 'd' || strchr(p + 2, '%'))
return -EINVAL;
// 申请一个全是 0 的 page
/* Use one page as a bit array of possible slots */
inuse = (unsigned long *) get_zeroed_page(GFP_ATOMIC);
if (!inuse)
return -ENOMEM;
// 针对 net 空间中已经存在的 net_device,找到每个 net_device 在这个 page 中的 bit 的位置
for_each_netdev(net, d) {
if (!sscanf(d->name, name, &i)) // 特别需要注意 sscanf 函数的用法,此时 d->name 中
// 的值应该是 eth1, eth2这样的,而 name 中是 eth%d,
// 这个函数作用是将 1, 2这样的值,保存到 i 中
continue;
if (i < 0 || i >= max_netdevices)
continue;
/* avoid cases where sscanf is not exact inverse of printf */
// 将 sscanf 分解的 d->name 再重组一遍,进行比较,确定 sscanf 分解的没有错误,
// 才通过 set_bit 将 page 中相应的 bit 值位
snprintf(buf, IFNAMSIZ, name, i); // 重组的内容(字符串) 保存在 buf 中
if (!strncmp(buf, d->name, IFNAMSIZ)) // 如果 buf 与 d->name 中长度 IFNAMSIZ 的内容完全一致,
// 则返回 0
set_bit(i, inuse);
}
// 找到 page 中第一个没有被使用的 bit
i = find_first_zero_bit(inuse, max_netdevices);
free_page((unsigned long) inuse);
}
// 确定 buf 和 name 不是同一个空间,将组成的新名字保存到 buf 中,此时 name 是 eth%d ,
// i 是一个1,2,3这样的数值
if (buf != name)
snprintf(buf, IFNAMSIZ, name, i);
// 通过新组成的名字去找 net_device 设备,确保没有重复的
if (!__dev_get_by_name(net, buf))
return i;
/* It is possible to run out of possible slots
* when the name is long and there isn't enough space left
* for the digits, or if all bits are used.
*/
return -ENFILE;
}
在 static int __dev_alloc_name(struct net *net, const char *name, char *buf) 中组成的名字 ethx,会通过 buf 返回,然后在
dev_alloc_name_ns 函数中保存到步骤一生成的 struct net_device 变量的成员 name 中:
至此, 一个 新的 ethx 这样的名字就生成了。
3. ifconfig ethx up,则在 ifconfig 输出中就能够看到它的相关信息了。