[机器学习-Sklearn]决策树学习与总结 (ID3, C4.5, C5.0, CART)
决策树学习与总结 (ID3, C4.5, C5.0, CART)
- 1. 什么是决策树
- 2. 决策树介绍
- 3. ID3 算法
- 信息熵
- 信息增益
- 缺点
- 4. C4.5算法
- 5. C5.0算法
- 6. CART算法
- 基尼指数 Gini指标
- 7. 连续属性离散化
- 8. 过拟合的解决方案
- 9. 例子1 - 脊椎动物分类
- 10. 例子2
- 1. 准备数据及读取
- 2. 决策树的特征向量化
- 3. 决策树训练
- 4. 决策树可视化
- 5 预测结果
- 6. Module persistence
- 1) 用Python有的pickle对我们训练好的模型保存
- 2) 用joblib’s保持如果你的模型里有大量的 numpy arrays的话
- 7. 自己算验证熵的结果
- 8. 如果你用基尼指数, 也就是CART算法
- 9. 自己算验证基尼指数的结果
- 10. 把数据集全部改成数字不用DictVectorizer做向量化
- 11. 例子 -基于Iris数据集的训练
- 12. 特征的重要性计算
- 可能遇到问题
1. 什么是决策树
决策树是什么,我们来“决策树”这个词进行分词,那么就会是决策/树。大家不妨思考一下,重点是决策还是树呢?其实啊,决策树的关键点在树上。
我们平时写代码的那一串一串的If Else其实就是决策树的思想了。看下面的图是不是觉得很熟悉呢?
2. 决策树介绍
决策树之所以叫决策树,就是因为它的结构是树形状的,如果你之前没了解过树这种数据结构,那么你至少要知道以下几个名词是什么意思。
- 根节点:最顶部的那个节点
- 叶子节点:每条路径最末尾的那个节点,也就是最外层的节点
- 非叶子节点:一些条件的节点,下面会有更多分支,也叫做分支节点
- 分支:也就是分叉
3. ID3 算法
- ID3算法是在每个结点处选取能获得最高信息增益的分支属性进行分裂
- 在每个决策结点处划分分支、选取分支属性的目的是将整个决策树的样本
纯度提升 - 衡量样本集合纯度的指标则是
信息熵
不理解信息熵的可以看这篇博客[机器学习-概念篇]彻底搞懂信息量,熵、相对熵、交叉熵
![[机器学习-Sklearn]决策树学习与总结 (ID3, C4.5, C5.0, CART)_第3张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/b23a4c6ffe9541dfae54dc273ce3ca8f.jpg)
举例来说,如果有一个大小为10的布尔值样本集S,其中有6个真值、4个
假值,那么该布尔型样本分类的熵为:
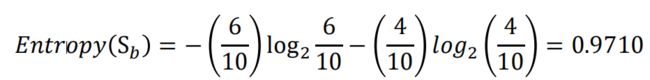
信息增益
- 计算分支属性对于样本集分类好坏程度的度量——信息增益
- 由于分裂后样本集的纯度提高,则样本集的熵降低,熵降低的值即为该分 裂方法的信息增益
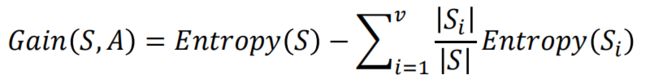
脊椎动物分类训练样本集
![[机器学习-Sklearn]决策树学习与总结 (ID3, C4.5, C5.0, CART)_第4张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/fcdeaab670df4d4cbdd1440b54ef682d.jpg)
共有14个样本,其中8个正例,6个反例,设此样本集为 S,则分裂前的熵值为

脊椎动物训练样本集以“饮食习性”作为分支属性的分裂情况
![[机器学习-Sklearn]决策树学习与总结 (ID3, C4.5, C5.0, CART)_第5张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/1c54dd3b36af4bc68ff1009f427fac2c.jpg)
![[机器学习-Sklearn]决策树学习与总结 (ID3, C4.5, C5.0, CART)_第6张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/cc6ad487f1b24d94860078de44169f77.jpg)
设“饮食习性”属性为Y,由此可以计算得出,作为分支属性进行分裂之后的
信息增益为
![[机器学习-Sklearn]决策树学习与总结 (ID3, C4.5, C5.0, CART)_第7张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/35ca8faa54ae48a18e18b0847c5fbb45.jpg)
同理, 计算可得,以“胎生动物”“水生动物”“会飞”作为分支属性时的信息 增益分别为0.6893、0.0454、0.0454
由此可知“胎生动物”作为分支属性时能获得最大的信息增益,即具有最强的区分样本的能力,所以在此选择使用“胎生动物”作为分支属性对根结点进行划分
由根结点通过计算信息增益选取合适的属性进行分裂,若新生成的结点的分类属性不唯一,则对新生的结点继续进行分裂,不断重复此步骤,直至所有样本属于同 一类,或者达到要求的分类条件为止
缺点
4. C4.5算法
C4.5算法总体思路与ID3类似,都是通过构造决策树进行分类,其区别在于分支的处理,在分支属性的选取上,ID3算法使用信息增益作为度量,而C4.5算法引入了信息增益率作为度量
![[机器学习-Sklearn]决策树学习与总结 (ID3, C4.5, C5.0, CART)_第8张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/71d744fc7cea4bbc847d7a167ef3fb5f.jpg)
由信息增益率公式中可见,当比较大时,信息增益率会明显降低,从而在一定程度上能够解决ID3算法存在的往往选择取值较多的分支属性的问题
在前面例子中,假设选择“饮食习性”作为分支属性,其信息增益率为
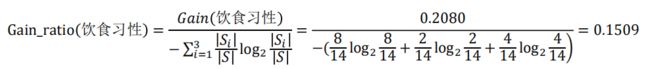
5. C5.0算法
- C5.0算法是Quinlan在C4.5算法的基础上提出的商用改进版本,目的是对含有 大量数据的数据集进行分析
- C5.0算法与C4.5算法相比有以下优势:
– 决策树构建时间要比C4.5算法快上数倍,同时生成的决策树规模也更小,拥有更少的叶子结
点数
– 使用了提升法(boosting),组合多个决策树来做出分类,使准确率大大提高
– 提供可选项由使用者视情况决定,例如是否考虑样本的权重、样本错误分类成本等
6. CART算法
基尼指数 Gini指标
CART算法在分支处理中分支属性的度量指标
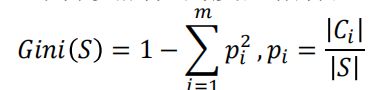
在前面例子中,假设选择“会飞”作为分支属性,其Gini指标为
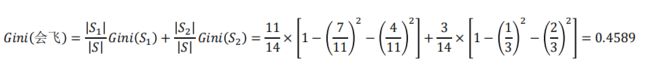
7. 连续属性离散化
如果是连续的数值型是如年龄,我们一般把它离散化,如离散化为幼年,中年,老年
因为你不可能让把每个年龄都分成一个特征,那样会很多,也没必要。
8. 过拟合的解决方案
- 一方面要注意数据训练集的质量,选取具有代表性样本的训练样本集
- 要避免决策树过度增长,通过限制树的深度来减少数据中的噪声对于决策树构建的影响,一般可以采取剪枝的方法
- 剪枝包括预剪枝和后剪枝两类
预剪枝的思路是提前终止决策树的增长,在形成完全拟合训练样本集的决 策树之前就停止树的增长,避免决策树规模过大而产生过拟合
后剪枝策略先让决策树完全生长,之后针对子树进行判断,用叶子结点或者子树中最常用的分支替换子树,以此方式不断改进决策树,直至无法改进为止
9. 例子1 - 脊椎动物分类
脊椎动物分类训练样本集 test.csv 文件, 做了下面的变换
是:0, 否 : 1 ,杂食动物 : omnivorous animal, 肉食动物:carnivorous animals, : 草食动物, herbivore
omnivorous animal, 0, 1, 1, 0
omnivorous animal, 0, 1, 1, 0
carnivorous animals, 0, 1, 1, 0
carnivorous animals, 1, 1, 0, 1
carnivorous animals, 1, 0, 1, 1
carnivorous animals, 1, 1, 1, 1
omnivorous animal, 0, 1, 0, 0
herbivore, 0, 1, 1, 0
omnivorous animal, 1, 1, 0, 1
carnivorous animals, 1, 0, 1, 1
carnivorous animals, 0, 0, 1, 0
carnivorous animals, 1, 1, 1, 0
herbivore, 0, 1, 1, 0
carnivorous animals, 1, 1, 1, 1
代码
import pandas as pd
import sklearn as sklearn
from sklearn.feature_extraction import DictVectorizer
from sklearn import tree
import pydotplus
from sklearn.externals.six import StringIO
# pandas 读取 csv 文件,header = None 表示不将首行作为列
data = pd.read_csv('data/test.csv', header=None)
# 指定列
data.columns = ['Diet Habits', 'viviparous animal', 'Aquatic animals', 'Can fly','mammal']
# sparse=False意思是不产生稀疏矩阵
vec = sklearn.feature_extraction.DictVectorizer(sparse=False)
# 先用 pandas 对每行生成字典,然后进行向量化
feature = data[['Diet Habits', 'viviparous animal', 'Aquatic animals']]
X_train = vec.fit_transform(feature.to_dict(orient='record'))
# 打印各个变量
print('show feature\n', feature)
print('show vector\n', X_train)
print('show vector name\n', vec.get_feature_names())
print('show vector name\n', vec.vocabulary_)
Y_train = data['mammal']
clf = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion='entropy')
clf.fit(X_train, Y_train)
dot_data = StringIO()
tree.export_graphviz(clf,feature_names=vec.get_feature_names(),out_file=dot_data)
graph = pydotplus.graph_from_dot_data(dot_data.getvalue())
graph.write_pdf("test.pdf")
show feature
Diet Habits viviparous animal Aquatic animals
0 omnivorous animal 0 1
1 omnivorous animal 0 1
2 carnivorous animals 0 1
3 carnivorous animals 1 1
4 carnivorous animals 1 0
5 carnivorous animals 1 1
6 omnivorous animal 0 1
7 herbivore 0 1
8 omnivorous animal 1 1
9 carnivorous animals 1 0
10 carnivorous animals 0 0
11 carnivorous animals 1 1
12 herbivore 0 1
13 carnivorous animals 1 1
show vector
[[1. 0. 0. 1. 0.]
[1. 0. 0. 1. 0.]
[1. 1. 0. 0. 0.]
[1. 1. 0. 0. 1.]
[0. 1. 0. 0. 1.]
[1. 1. 0. 0. 1.]
[1. 0. 0. 1. 0.]
[1. 0. 1. 0. 0.]
[1. 0. 0. 1. 1.]
[0. 1. 0. 0. 1.]
[0. 1. 0. 0. 0.]
[1. 1. 0. 0. 1.]
[1. 0. 1. 0. 0.]
[1. 1. 0. 0. 1.]]
show vector name
['Aquatic animals', 'Diet Habits=carnivorous animals', 'Diet Habits=herbivore', 'Diet Habits=omnivorous animal', 'viviparous animal']
show vector name
{'Diet Habits=omnivorous animal': 3, 'viviparous animal': 4, 'Aquatic animals': 0, 'Diet Habits=carnivorous animals': 1, 'Diet Habits=herbivore': 2}
10. 例子2
安装panda 和 scikit-learn 如果你没有安装的话
conda install pandas
conda install scikit-learn
1. 准备数据及读取
| 季节 | 时间已过 8 点 | 风力情况 | 要不要赖床 |
|---|---|---|---|
| spring | no | breeze | yes |
| winter | no | no wind | yes |
| autumn | yes | breeze | yes |
| winter | no | no wind | yes |
| summer | no | breeze | yes |
| winter | yes | breeze | yes |
| winter | no | gale | yes |
| winter | no | no wind | yes |
| spring | yes | no wind | no |
| summer | yes | gale | no |
| summer | no | gale | no |
| autumn | yes | breeze | no |
spring,no,breeze,1
winter,no,no wind,1
autumn,yes,breeze,1
winter,no,no wind,1
summer,no,breeze,1
winter,yes,breeze,1
winter,no,gale,1
winter,no,no wind,1
spring,yes,no wind,0
summer,yes,gale,0
summer,no,gale,0
autumn,yes,breeze,0
2. 决策树的特征向量化
sklearn的DictVectorizer能对字典进行向量化。什么叫向量化呢?比如说你有季节这个属性有[春,夏,秋,冬]四个可选值,那么如果是春季,就可以用[1,0,0,0]表示,夏季就可以用[0,1,0,0]表示。不过在调用DictVectorizer它会将这些属性打乱,不会按照我们的思路来运行,但我们也可以一个方法查看,我们看看代码就明白了
通过DictVectorizer,我们就能够把字符型的数据,转化成0 1的矩阵,方便后面进行运算。额外说一句,这种转换方式其实就是one-hot编码。
import pandas as pd
import sklearn as sklearn
from sklearn.feature_extraction import DictVectorizer
from sklearn import tree
# pandas 读取 csv 文件,header = None 表示不将首行作为列
data = pd.read_csv('data/laic.csv', header=None)
# 指定列
data.columns = ['season', 'after 8', 'wind', 'lay bed']
# sparse=False意思是不产生稀疏矩阵
vec = DictVectorizer(sparse=False)
# 先用 pandas 对每行生成字典,然后进行向量化
feature = data[['season', 'after 8', 'wind']]
X_train = vec.fit_transform(feature.to_dict(orient='record'))
# 打印各个变量
print('show feature\n', feature)
print('show vector\n', X_train)
print('show vector name\n', vec.get_feature_names())
print('show vector name\n', vec.vocabulary_)
执行结果
show feature
season after 8 wind
0 spring no breeze
1 winter no no wind
2 autumn yes breeze
3 winter no no wind
4 summer no breeze
5 winter yes breeze
6 winter no gale
7 winter no no wind
8 spring yes no wind
9 summer yes gale
10 summer no gale
11 autumn yes breeze
show vector
[[1. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0.]
[1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 1.]
[0. 1. 1. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0.]
[1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 1.]
[1. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 1. 0. 0.]
[0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 1. 1. 0. 0.]
[1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 1. 0.]
[1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 1.]
[0. 1. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1.]
[0. 1. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 1. 0.]
[1. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 1. 0.]
[0. 1. 1. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0.]]
show vector name
['after 8=no', 'after 8=yes', 'season=autumn', 'season=spring', 'season=summer', 'season=winter', 'wind=breeze', 'wind=gale', 'wind=no wind']
show vector name
{'season=spring': 3, 'after 8=no': 0, 'wind=breeze': 6, 'season=winter': 5, 'wind=no wind': 8, 'season=autumn': 2, 'after 8=yes': 1, 'season=summer': 4, 'wind=gale': 7}
3. 决策树训练
Y_train = data['lay bed']
clf = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion='entropy')
clf.fit(X_train, Y_train)
4. 决策树可视化
当完成一棵树的训练的时候,我们也可以让它可视化展示出来,不过sklearn没有提供这种功能,它仅仅能够让训练的模型保存到dot文件中。但我们可以借助其他工具让模型可视化,先看保存到dot的代码:
with open("out.dot", 'w') as f :
f = tree.export_graphviz(clf, out_file = f,
feature_names = vec.get_feature_names())
5 预测结果
result = clf.predict([[1., 0., 0. ,1. , 0. , 0. , 1. , 0. , 0.]])
print(result)
[1]
然后可以执行下面命令生成一个out.pdf
dot out.dot -T pdf -o out.pdf
| after 8=no | after 8=yes | season=autumn | season=spring | season=summer | season=winter | wind=breeze | wind=gale | wind=no wind | lay bed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 0. | 0. | 1. | 0. | 0. | 1. | 0. | 0. | 1 |
| 1. | 0. | 0. | 0. | 0. | 1. | 0. | 0. | 1. | 1 |
| 0. | 1. | 1. | 0. | 0. | 0. | 1. | 0. | 0. | 1 |
| 1. | 0. | 0. | 0. | 0. | 1. | 0. | 0. | 1. | 1 |
| 1. | 0. | 0. | 0. | 1. | 0. | 1. | 0. | 0. | 1 |
| 0. | 1. | 0. | 0. | 0. | 1. | 1. | 0. | 0. | 1 |
| 1. | 0. | 0. | 0. | 0. | 1. | 0. | 1. | 0. | 1 |
| 1. | 0. | 0. | 0. | 0. | 1. | 0. | 0. | 1. | 1 |
| 0. | 1. | 0. | 1. | 0. | 0. | 0. | 0. | 1. | 0 |
| 0. | 1. | 0. | 0. | 1. | 0. | 0. | 1. | 0. | 0 |
| 1. | 0. | 0. | 0. | 1. | 0. | 0. | 1. | 0. | 0 |
| 0. | 1. | 1. | 0. | 0. | 0. | 1. | 0. | 0. | 0 |
6. Module persistence
两种方式保持我们的模型
参考Sklearn 官网
1) 用Python有的pickle对我们训练好的模型保存
import pickle
with open('decisive_tree_module.txt', 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(clf, f)
with open('decisive_tree_module.txt', 'rb') as f:
clf2 = pickle.load(f)
#s = pickle.dumps(clf)
#clf2 = pickle.loads(s)
predict2 = clf2.predict([[1., 0., 0. ,1. , 0. , 0. , 1. , 0. , 0.]])
print('Predict result via loading pickle saved module :', predict2)
Predict result via loading pickle saved module : [1]
2) 用joblib’s保持如果你的模型里有大量的 numpy arrays的话
from joblib import dump, load
dump(clf, 'jdecisive_tree_module.joblib')
clf3 = load('jdecisive_tree_module.joblib')
predict3 = clf3.predict([[1., 0., 0. ,1. , 0. , 0. , 1. , 0. , 0.]])
print('Predict result via loading joblib saved module :', predict3)
Predict result via loading joblib saved module : [1]
7. 自己算验证熵的结果
import math
root_node_entropy = -(8/12)*(math.log(8/12, 2)) - (4/12)*(math.log(4/12, 2))
node1_left = (-(3/7)*(math.log(3/7, 2)) - (4/7)*(math.log(4/7,2)))
#node1_right = (-(5/5)*(math.log(5/5, 2)) - (0/5)*(math.log(0/5,2)))
node1_right = (-(5/5)*(0) - 0)
#node2_left = -(3/3)*(math.log(3/3, 2)) - (0/3)*(math.log(0/3, 2))
node2_left = -(3/3)*(0) - 0
node2_right = -(3/4)*(math.log(3/4, 2)) - (1/4)*(math.log(1/4, 2))
print('Entropy of season=winter ', root_node_entropy)
print('Entropy of wind=breeze ', node1_left)
print('Entropy of wind=breeze ', node1_right)
print('Entropy of node2_left', node2_left)
print('Entropy of node2_right', node2_right)
Entropy of season=winter 0.9182958340544896
Entropy of wind=breeze 0.9852281360342516
Entropy of wind=breeze -0.0
Entropy of node2_left -0.0
Entropy of node2_right 0.8112781244591328
8. 如果你用基尼指数, 也就是CART算法
只需要把entropy 改成 gini就可以了
clf = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion='gini')
9. 自己算验证基尼指数的结果
import math
root_node_entropy = 1 -(8 / 12) * (8 / 12) - (4 / 12) *(4 / 12)
node1_left = 1-(3 / 7) * (3 / 7) - (4 / 7) * (4 / 7)
# node1_right = (-(5/5)*(math.log(5/5, 2)) - (0/5)*(math.log(0/5,2)))
node1_right = (-(5 / 5) * (0) - 0)
# node2_left = -(3/3)*(math.log(3/3, 2)) - (0/3)*(math.log(0/3, 2))
node2_left = -(3 / 3) * (0) - 0
node2_right = 1-(3 / 4) * (3 / 4) - (1 / 4) *(1 / 4)
node3_left = -(2 / 2) * (0) - 0
node3_right = 1-(1 / 2) * (1 / 2) - (1 / 2) *(1 / 2)
print('Entropy of season=winter ', root_node_entropy)
print('Entropy of wind=breeze ', node1_left)
print('Entropy of wind=breeze ', node1_right)
print('Entropy of node2_left', node2_left)
print('Entropy of node2_right', node2_right)
print('Entropy of node3_left', node3_left)
print('Entropy of node3_right', node3_right)
Entropy of season=winter 0.4444444444444445
Entropy of wind=breeze 0.489795918367347
Entropy of wind=breeze -0.0
Entropy of node2_left -0.0
Entropy of node2_right 0.375
Entropy of node3_left -0.0
Entropy of node3_right 0.5
10. 把数据集全部改成数字不用DictVectorizer做向量化
spring :1 , summer : 2, spring : 3 , winter : 4
时间已过 8 点-no : 0
时间已过 8 点-yes :1
breeze : 1 , no wind : 2 , gale :3
laic1.csv 文件
1,0,1,1
4,0,2,1
3,1,1,1
4,0,2,1
2,0,1,1
4,1,1,1
4,0,3,1
4,0,2,1
1,1,2,0
2,1,3,0
2,0,3,0
3,1,1,0
代码
import pandas as pd
from sklearn import tree
data = pd.read_csv('data/laic1.csv', header=None)
# 指定列
data.columns = ['season', 'after 8', 'wind', 'lay bed']
X_train = data[['season', 'after 8', 'wind']]
Y_train = data['lay bed']
clf = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion='entropy')
clf.fit(X_train, Y_train)
with open("out1.dot", 'w') as f :
f = tree.export_graphviz(clf, out_file = f,
feature_names =['season', 'after 8', 'wind'])
result = clf.predict([[1,1,1]])
print('Predict result:', result)
Predict result: [0]
11. 例子 -基于Iris数据集的训练
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn import tree
import pydotplus
from sklearn.externals.six import StringIO
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
iris = datasets.load_iris()
# 特征
iris_feature = iris.data
# 分类标签
iris_label = iris.target
iris_target_name=iris['target_names']
feature_names = iris['feature_names']
# 划分
X_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split(iris_feature, iris_label, test_size=0.3, random_state=42)
clf = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion='entropy')
clf.fit(X_train, Y_train)
s = clf.score(X_test, Y_test)
print(s)
0.9777777777777777
12. 特征的重要性计算
数据集如下
![[机器学习-Sklearn]决策树学习与总结 (ID3, C4.5, C5.0, CART)_第13张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/a43474e41bb34069a0863fbf77b21f19.jpg)
构建决策树,使用gini系数作为切割参数,决策数为cart树。生成的树结构如下
![[机器学习-Sklearn]决策树学习与总结 (ID3, C4.5, C5.0, CART)_第14张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/0e4943af643f468ab400acafdc83825b.jpg)
计算个特征的重要性
f1 = 0.497 - 0.3754 + 0.52 + 0.4443 = 4.262
f2 = 0
f3 = 0.45914 - 0.497 - 0.2457 = 1.281
f4 = 0.2457 - 0.4443 + 0.3754 - 0.5*2 = 0.883
这棵树总的不纯减少量为4.262+1.281+0.883=6.426
经过归一化后,各特征的重要性分别如下:
f1_importance = 4.262/6.426=0.663
f2_importance = 0
f3_importance = 1.281/6.426=0.2
f4_importance = 0.883/6.426=0.137
使用代码跑出来的特征重要性如下
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
train_df = pd.DataFrame(
[[1, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[1, 1, 1, 2, 0],
[2, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[3, 2, 1, 1, 1],
[3, 3, 2, 1, 1],
[3, 3, 2, 2, 0],
[2, 3, 2, 2, 1],
[1, 2, 1, 1, 0],
[1, 3, 2, 1, 1],
[3, 2, 2, 1, 1],
[1, 2, 2, 2, 1],
[2, 2, 1, 2, 1],
[2, 1, 2, 1, 1],
[3, 2, 1, 2, 0],
], columns=['f1', 'f2', 'f3', 'f4', 'label'])
X, y = train_df[['f1', 'f2', 'f3', 'f4']].values, train_df['label']
clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion='gini')
clf.fit(X,y)
print(clf.feature_importances_)
# 特征重要性
[0.66296296 0. 0.2 0.13703704]
可能遇到问题
如果你这个graphvis 的问题 (GraphViz’s executables not found), 可以根据下面这个link解决它
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40304090/article/details/88594813
![[机器学习-Sklearn]决策树学习与总结 (ID3, C4.5, C5.0, CART)_第1张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/e8c14e87203f4029b1b32a939b7ec8e7.jpg)
![[机器学习-Sklearn]决策树学习与总结 (ID3, C4.5, C5.0, CART)_第2张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/8cb6edad0d1b40beb85a610818477f7d.jpg)
![[机器学习-Sklearn]决策树学习与总结 (ID3, C4.5, C5.0, CART)_第9张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/8bdd38a87af34f63a24feedd21f55f6b.jpg)
![[机器学习-Sklearn]决策树学习与总结 (ID3, C4.5, C5.0, CART)_第10张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/69659472fae1400b9cd9a140893cd28f.jpg)
![[机器学习-Sklearn]决策树学习与总结 (ID3, C4.5, C5.0, CART)_第11张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/ddba104d3fa24297bed0af06ed0c1c65.jpg)
![[机器学习-Sklearn]决策树学习与总结 (ID3, C4.5, C5.0, CART)_第12张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/94857cff574f4d54897c822f719e8a43.jpg)