【LeetCode】987. Vertical Order Traversal of a Binary Tree 解题报告(C++ & Python)
作者: 负雪明烛
id: fuxuemingzhu
个人博客: http://fuxuemingzhu.cn/
目录
- 题目描述
- 题目大意
- 解题方法
- DFS
- BFS
- 日期
题目地址:https://leetcode.com/problems/vertical-order-traversal-of-a-binary-tree/
题目描述
Given a binary tree, return the vertical order traversal of its nodes values.
For each node at position (X, Y), its left and right children respectively will be at positions (X-1, Y-1) and (X+1, Y-1).
Running a vertical line from X = -infinity to X = +infinity, whenever the vertical line touches some nodes, we report the values of the nodes in order from top to bottom (decreasing Y coordinates).
If two nodes have the same position, then the value of the node that is reported first is the value that is smaller.
Return an list of non-empty reports in order of X coordinate. Every report will have a list of values of nodes.
Example 1:
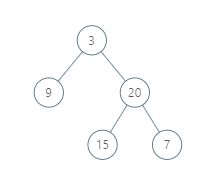
Input: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: [[9],[3,15],[20],[7]]
Explanation:
Without loss of generality, we can assume the root node is at position (0, 0):
Then, the node with value 9 occurs at position (-1, -1);
The nodes with values 3 and 15 occur at positions (0, 0) and (0, -2);
The node with value 20 occurs at position (1, -1);
The node with value 7 occurs at position (2, -2).
Example 2:
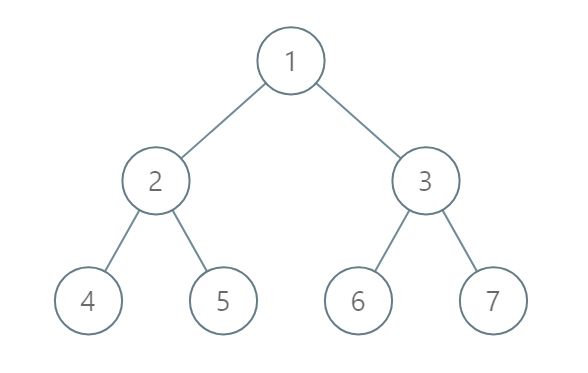
Input: [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
Output: [[4],[2],[1,5,6],[3],[7]]
Explanation:
The node with value 5 and the node with value 6 have the same position according to the given scheme.
However, in the report "[1,5,6]", the node value of 5 comes first since 5 is smaller than 6.
Note:
- The tree will have between
1and1000nodes. - Each node’s value will be between
0and1000.
题目大意
一个二叉树从左到右竖着看,每列的结果放到一起,那么结果是什么样的。
规定:一个节点水平方向的位置是X,竖直方向的高度是Y,其坐标是(X, Y)。那么其左右孩子的坐标分别是(X-1, Y-1) and (X+1, Y-1).
即要求把相同X的节点位置放在一起,并且要求结果中节点的存放是从上到下的。如果两个节点的坐标相同,那么value小的节点排列在前面。
解题方法
DFS
最直白的方法就是把每个节点的位置给求出来,然后构建出题目要求的排列方式。为了方便,我们在求的过程中就把相同X值的放到一起,同时保存Y坐标和值。
所以定义了一个Map,这个Map的结构是map
在求出相同X的所有(-y, value)对之后,我们进行了排序使得Y值是严格递增的,当Y值相同时按照value值进行排序。然后把排序好了的节点的value值都取出来放到结果里即可。
一个不引起注意的点是,nodeMap一定要使用map数据结构,而不是unordered_map。因为map会保证有序的,也就是说对nodeMap遍历的时候,X是已经排序好了。而unordered_map是无序结构,遍历不会保证X是有序,增加了麻烦。
另外一个C++的知识点是当使用 for (auto nm : nodeMap)的时候,nm不是一个指针,而是一个复制了的对象,所以不要使用nm->second,而应该使用nm.second.
时间复杂度是O(N + N*(N*log(N) + N))。第一个N是DFS要把每个节点进行遍历一次;for循环有层N,循环里面有层排序是NlogN,遍历是N)。
空间复杂度是O(N)。
C++代码如下:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> verticalTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
nodeMap.clear();
dfs(root, 0, 0);
vector<vector<int>> res;
for (auto nm : nodeMap) {
sort(nm.second.begin(), nm.second.end());
vector<int> cols;
for (auto p : nm.second)
cols.push_back(p.second);
res.push_back(cols);
}
return res;
}
private:
map<int, vector<pair<int, int>>> nodeMap; // x ==> (-y, value)
void dfs(TreeNode* root, int x, int y) {
if (!root) return;
nodeMap[x].emplace_back(-y, root->val);
dfs(root->left, x - 1, y - 1);
dfs(root->right, x + 1, y - 1);
}
};
下面的python代码没有使用字典,而是使用了list保存了(x, -y, value)三元组的方式,可以直接使用sort进行排序。这样带来的麻烦是需要使用比较前后两个相邻的三元组对应的x值是否相等来判断是否放到同一个列的list中,代码如下:
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def verticalTraversal(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
self.m_ = list()
self.dfs(root, 0, 0)
self.m_.sort()
res = [[self.m_[0][2]]]
for i in range(1, len(self.m_)):
if self.m_[i][0] == self.m_[i - 1][0]:
res[-1].append(self.m_[i][2])
else:
res.append([self.m_[i][2]])
return res
def dfs(self, root, x, y):
if not root: return
self.m_.append((x, -y, root.val))
self.dfs(root.left, x - 1, y - 1)
self.dfs(root.right, x + 1, y - 1)
BFS
这个题同样也可以使用BFS来解决,通过维护一个队列,我们从上到下依次遍历每个节点,给每个节点设置好了坐标。这个队列存储的是个三元组(TreeNode*,int x,int y)做法和DFS的方法极其类似,就不再详细讲了。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> verticalTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
queue<pair<TreeNode*, pair<int, int>>> q; // node, x, y
q.push(make_pair(root, make_pair(0, 0)));
map<int, vector<pair<int, int>>> nodeMap;
while (!q.empty()) {
auto d = q.front(); q.pop();
TreeNode* curNode = d.first;
int x = d.second.first;
int y = d.second.second;
nodeMap[x].emplace_back(-y, curNode->val);
if (curNode->left)
q.push(make_pair(curNode->left, make_pair(x - 1, y - 1)));
if (curNode->right)
q.push(make_pair(curNode->right, make_pair(x + 1, y - 1)));
}
vector<vector<int>> res;
for (auto nm : nodeMap) {
sort(nm.second.begin(), nm.second.end());
vector<int> cols;
for (auto p : nm.second)
cols.push_back(p.second);
res.push_back(cols);
}
return res;
}
};
python版本的BFS如下,同样是先把所有的节点遍历一遍并保存每个节点的位置,然后根据位置再排序遍历求解的方式做到的。
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def verticalTraversal(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
q = collections.deque()
q.append((root, 0, 0))
m_ = list()
while q:
node, x, y = q.popleft()
m_.append((x, -y, node.val))
if node.left:
q.append((node.left, x - 1, y - 1))
if node.right:
q.append((node.right, x + 1, y - 1))
m_.sort()
res = [[m_[0][2]]]
for i in range(1, len(m_)):
if m_[i][0] == m_[i - 1][0]:
res[-1].append(m_[i][2])
else:
res.append([m_[i][2]])
return res
日期
2019 年 2 月 20 日 —— 少刷知乎多做题