Python第九,十章练习题 (第五周作业)
9-3 用户 :创建一个名为User 的类,其中包含属性first_name 和last_name ,还有用户简介通常会存储的其他几个属性。在类User 中定义一个名
为describe_user() 的方法,它打印用户信息摘要;再定义一个名为greet_user() 的方法,它向用户发出个性化的问候。
创建多个表示不同用户的实例,并对每个实例都调用上述两个方法
9.3
class User:
def __init__(self,first_name,last_name,age):
self.first_name=first_name
self.last_name=last_name
self.age=age
def describe_user(self):
print("User first_name: "+self.first_name)
print("User last_name: "+self.last_name)
print("User age: "+str(self.age))
def greet_user(self):
print("Hello,I'm "+self.first_name+" "+self.last_name)
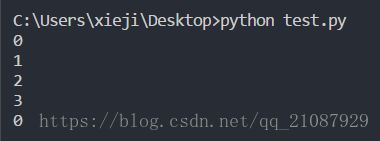
a=User("One","Two",20)
b=User("Third","Fourth",21)
a.describe_user()
a.greet_user()
b.describe_user()
b.greet_user()9-5 尝试登录次数 :在为完成练习9-3而编写的User 类中,添加一个名为login_attempts 的属性。编写一个名为increment_login_attempts() 的方法,
它将属性login_attempts 的值加1。再编写一个名为reset_login_attempts() 的方法,它将属性login_attempts 的值重置为0。
根据User 类创建一个实例,再调用方法increment_login_attempts() 多次。打印属性login_attempts 的值,确认它被正确地递增;然后,调用方
法reset_login_attempts() ,并再次打印属性login_attempts 的值,确认它被重置为0。
9.5
class User:
def __init__(self,first_name,last_name,age):
self.first_name=first_name
self.last_name=last_name
self.age=age
self.login_attempts=0
def describe_user(self):
print("User first_name: "+self.first_name)
print("User last_name: "+self.last_name)
print("User age: "+str(self.age))
def greet_user(self):
print("Hello,I'm "+self.first_name+" "+self.last_name)
def increment_login_attempts(self):
self.login_attempts+=1
def reset_login_attempts(self):
self.login_attempts=0
a=User("One","Two",20)
print(a.login_attempts)
for i in range(3):
a.increment_login_attempts()
print(a.login_attempts)
a.reset_login_attempts()
print(a.login_attempts)9-7 管理员 :管理员是一种特殊的用户。编写一个名为Admin 的类,让它继承你为完成练习9-3或练习9-5而编写的User 类。添加一个名为privileges 的属性,用
于存储一个由字符串(如”can add post” 、”can delete post” 、”can ban user” 等)组成的列表。编写一个名为show_privileges() 的方法,它
显示管理员的权限。创建一个Admin 实例,并调用这个方法。
class User:
def __init__(self,first_name,last_name,age):
self.first_name=first_name
self.last_name=last_name
self.age=age
self.login_attempts=0
def describe_user(self):
print("User first_name: "+self.first_name)
print("User last_name: "+self.last_name)
print("User age: "+str(self.age))
def greet_user(self):
print("Hello,I'm "+self.first_name+" "+self.last_name)
def increment_login_attempts(self):
self.login_attempts+=1
def reset_login_attempts(self):
self.login_attempts=0
class Admin(User):
__cando=["can add post","can delete post","can ban user"]
def __init__(self,first_name,last_name,age):
super().__init__(first_name,last_name,age)
def show_privileges(self):
for i in self.__cando:
print(self.first_name+" "+self.last_name+" "+i)
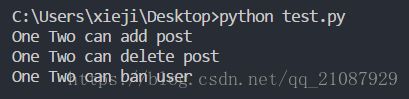
a=Admin("One","Two",20)
a.show_privileges()10-1 Python学习笔记 :在文本编辑器中新建一个文件,写几句话来总结一下你至此学到的Python知识,其中每一行都以“In Python you can”打头。将这个文件命名为
learning_python.txt,并将其存储到为完成本章练习而编写的程序所在的目录中。编写一个程序,它读取这个文件,并将你所写的内容打印三次:第一次打印时读取整个
文件;第二次打印时遍历文件对象;第三次打印时将各行存储在一个列表中,再在with 代码块外打印它们。
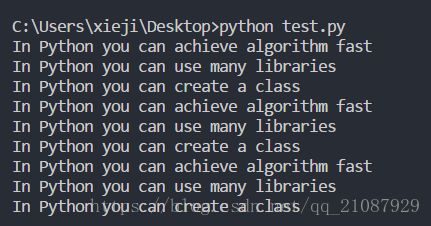
with open('learning_python.txt') as file_obj:
contents=file_obj.read()
print(contents)
with open('learning_python.txt') as file_obj:
for line in file_obj:
print(line.rstrip())
with open('learning_python.txt') as file_obj:
lines=file_obj.readlines()
for line in lines:
print(line.rstrip())10-4 访客名单 :编写一个while 循环,提示用户输入其名字。用户输入其名字后,在屏幕上打印一句问候语,并将一条访问记录添加到文件guest_book.txt中。确保这
个文件中的每条记录都独占一行。
10.4
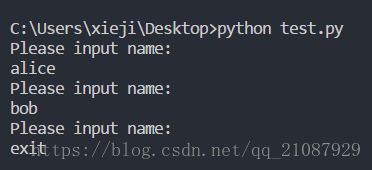
with open('guest_book.txt','w') as file_obj:
while True:
user_input=input("Please input name: \n")
if user_input=='exit':break
else:
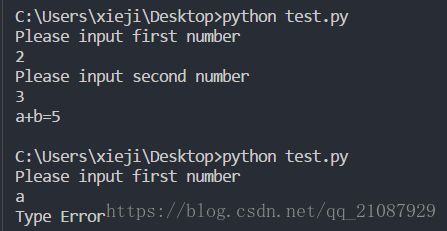
file_obj.write(user_input+'\n')10-6 加法运算 :提示用户提供数值输入时,常出现的一个问题是,用户提供的是文本而不是数字。在这种情况下,当你尝试将输入转换为整数时,将引
发TypeError 异常。编写一个程序,提示用户输入两个数字,再将它们相加并打印结果。在用户输入的任何一个值不是数字时都捕获TypeError 异常,并打印一
条友好的错误消息。对你编写的程序进行测试:先输入两个数字,再输入一些文本而不是数字。
10.6
try:
a=int(input("Please input first number\n"))
b=int(input("Please input second number\n"))
print("a+b="+str(a+b))
except ValueError:
print("Type Error")