带你了解响应式原理,以及Vue 响应式原理模拟实现
Study Notes
深入响应式原理
数据响应式、双向绑定、数据驱动
-
数据响应式
数据模型仅仅是普通的 JavaScript 对象,而当我们修改数据时,视图会进行更新,避免了繁琐的 DOM 操作,提高开发效率
-
双向绑定
- 数据改变,视图改变;视图改变,数据也随之改变
- 我们可以使用 v-model 在表单元素上创建双向数据绑定
-
数据驱动是 Vue 最独特的特性之一
开发过程中仅需要关注数据本身,不需要关心数据是如何渲染到视图
Vue2.x 响应式原理
当你把一个普通的 JavaScript 对象传入 Vue 实例作为 data 选项,Vue 将遍历此对象所有的 property,并使用 Object.defineProperty 把这些 property 全部转为 getter/setter。Object.defineProperty 是 ES5 中一个无法 shim 的特性,这也就是 Vue 不支持 IE8 以及更低版本浏览器的原因。
对象单属性数据劫持
-
configurable
当且仅当该属性的 configurable 键值为 true 时,该属性的描述符才能够被改变,同时该属性也能从对应的对象上被删除。
-
enumerable
当且仅当该属性的 enumerable 键值为 true 时,该属性才会出现在对象的枚举属性中。
默认为 false。
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta
name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0"
/>
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>Documenttitle>
head>
<body>
<script>
const el = document.createElement('p');
el.textContent = '在控制台输入vm.msg = 123';
document.body.append(el);
// 模拟Vue中的data选项
let data = { msg: 12 };
// 模拟vue实例
let vm = {};
// 数据劫持:当访问或者设置 vm 中的成员的时候,做一些干预操作
Object.defineProperty(vm, 'msg', {
configurable: true,
enumerable: true,
// 当获取值的时候执行
get: () => {
console.log('获取');
return data.msg;
},
// 当赋值的时候执行
set: (val) => {
console.log('赋值msg ==> ', val);
if (val === data.msg) {
return;
}
data.msg = val;
// 数据更改,更新 DOM 的值
document.getElementsByTagName('p')[0].textContent = val;
},
});
script>
body>
html>
对象多属性数据劫持
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<script>
const el = document.createElement('p');
el.textContent = '1231';
document.body.append(el);
let data = {
msg: '成功',
code: 1,
};
let vm = {};
Object.keys(data).forEach((key) => {
Object.defineProperty(vm, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: () => {
console.log(`获取 ${key}==>${data[key]}`);
return data[key];
},
set: (val) => {
if (val === data[key]) {
return;
}
console.log(`赋值 ${key}==>${val}`);
data[key] = val;
document.getElementsByTagName('p')[0].textContent = val;
},
});
});
script>
body>
html>
vue3.x 响应式原理
- Proxy
- 直接监听对象,而非属性。
ES6中新增,IE 不支持,性能由浏览器优化
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>body>
<script>
const el = document.createElement('p');
el.textContent = '在控制台输入vm.msg = 123';
document.body.append(el);
let data = {
msg: '成功',
code: 0,
};
const vm = new Proxy(data, {
get(target, key) {
console.log(`获取${key}===>${target[key]}`);
return target[key];
},
set(target, key, value) {
if (target[key] === value) return;
console.log(`设置${key}===>${value}`);
target[key] = value;
document.getElementsByTagName('p')[0].textContent = value;
},
});
script>
html>
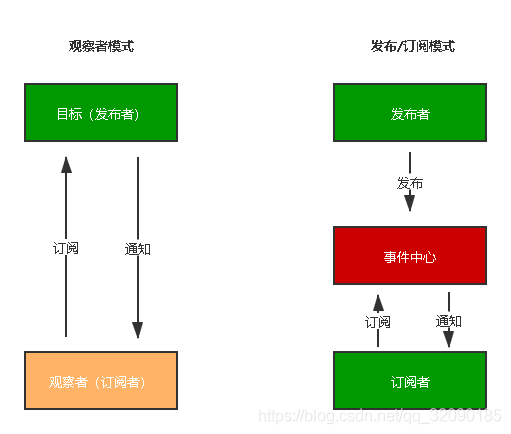
发布订阅模式和观察者模式
发布/订阅模式
- 订阅者
- 发布者
- 信号中心
我们假定,存在一个"信号中心",某个任务执行完成,就向信号中心"发布"(publish)一个信号,其他任务可以向信号中心"订阅"(subscribe)这个信号,从而知道什么时候自己可以开始执行。这就叫做"发布/订阅模式"(publish-subscribe pattern)
Vue 的自定义事件
let vm = new Vue();
vm.$on('dataChange', () => {
console.log('dataChange');
});
vm.$on('dataChange', () => {
console.log('dataChange1');
});
vm.$emit('dataChange');
兄弟组件通信过程
// eventBus.js
// 事件中心
export let eventHub = new Vue()
// ComponentA.vue
import {eventHub} from './eventBus'
// 发布者
addTodo: function () {
// 发布消息(事件)
eventHub.$emit('add-todo', { text: this.newTodoText })
this.newTodoText = ''
}
// ComponentB.vue
import {eventHub} from './eventBus'
// 订阅者
created: function () {
// 订阅消息(事件)
eventHub.$on('add-todo', this.addTodo)
}
模拟 Vue 自定义事件的实现
/**
* @author Wuner
* @date 2020/7/29 21:58
* @description
*/
class EventEmitter {
constructor() {
this.events = {};
}
// 订阅通知
$on(eventType, handle) {
this.events[eventType] = this.events[eventType] || [];
this.events[eventType].push(handle);
}
// 发布通知
$emit(eventType) {
if (this.events[eventType]) {
this.events[eventType].forEach((handle) => handle());
}
}
}
// 测试
let ev = new EventEmitter();
ev.$on('click', () => {
console.log('click1');
});
ev.$on('click', () => {
console.log('click2');
});
ev.$on('next', () => {
console.log('next');
});
ev.$emit('click');
ev.$emit('next');
观察者模式
- 观察者(订阅者) – Watcher
- update():当事件发生时,具体要做的事情
- 目标(发布者) – Dep
- subs 数组:存储所有的观察者
- addSub():添加观察者
- notify():当事件发生,调用所有观察者的 update() 方法
- 没有事件中心
/**
* @author Wuner
* @date 2020/7/29 22:45
* @description
*/
// 目标(发布者)
// Dependency
class Dep {
constructor() {
// 存储所有的观察者
this.subs = [];
}
// 添加观察者
addSub(sub) {
if (sub && sub.update) {
this.subs.push(sub);
}
}
// 通知所有观察者
notify() {
this.subs.forEach((sub) => sub.update());
}
}
// 观察者(订阅者)
class Watcher {
update() {
console.log('update');
}
}
// 测试
const watcher = new Watcher();
const dep = new Dep();
dep.addSub(watcher);
dep.notify();
总结
- 观察者模式是由具体目标调度,比如当事件触发,Dep 就会去调用观察者的方法,所以观察者模式的订阅者与发布者之间是存在依赖的。
- 发布/订阅模式由统一调度中心调用,因此发布者和订阅者不需要知道对方的存在。
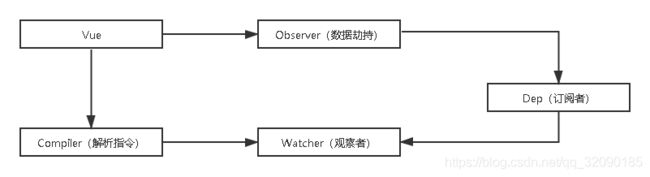
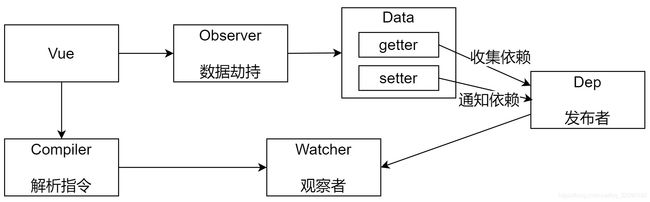
Vue 响应式原理模拟
整体分析
-
Vue
把 data 中的成员注入到 Vue 实例,并且把 data 中的成员转成 getter/setter
-
Observer(数据劫持)
能够对数据对象的所有属性进行监听,如有变动可拿到最新值并通知 Dep
-
Compiler(解析指令)
解析每个元素中的指令/插值表达式,并替换成相应的数据
-
Dep(订阅者)
添加观察者(watcher),当数据变化通知所有观察者
-
Watcher(观察者)
数据变化更新视图
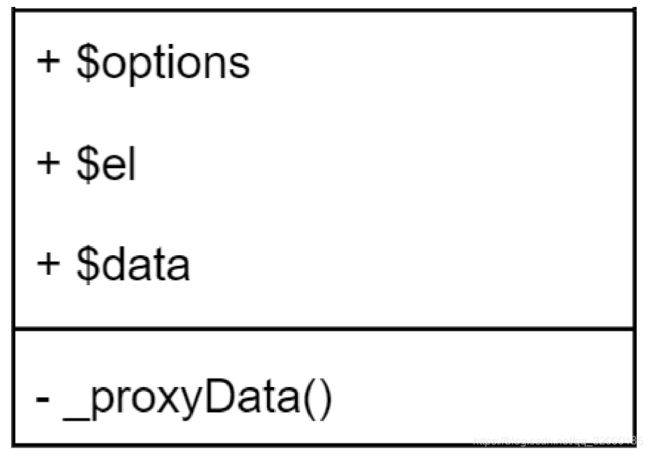
Vue
- 负责接收初始化的参数(选项)
- 负责把 data 中的属性注入到 Vue 实例,转换成 getter/setter
- 负责调用 observer 监听 data 中所有属性的变化
- 负责调用 compiler 解析指令/插值表达式
/**
* @author Wuner
* @date 2020/7/29 23:34
* @description
*/
class Vue {
constructor(options) {
// 初始化参数(选项)
this.$options = options || {};
this.$data = this.$options.data || {};
const el = this.$options.el;
// 判断el是否是字符串,如果是的话,则通过querySelector找到dom节点,否则直接赋值dom
this.$el = typeof el === 'string' ? document.querySelector(el) : el;
// 负责把data中的属性,注入到vue实例,并转换为getter和setter
this._proxyData(this.$data);
// 调用 observer 监听 data 中所有属性的变化
new Observer(this.$data);
// 编译
new Compiler(this);
}
_proxyData(data) {
// 遍历 data 的所有属性
Object.keys(data).forEach((key) => {
Object.defineProperty(this, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get() {
return data[key];
},
set(val) {
if (val === data[key]) {
return;
}
data[key] = val;
},
});
});
}
}
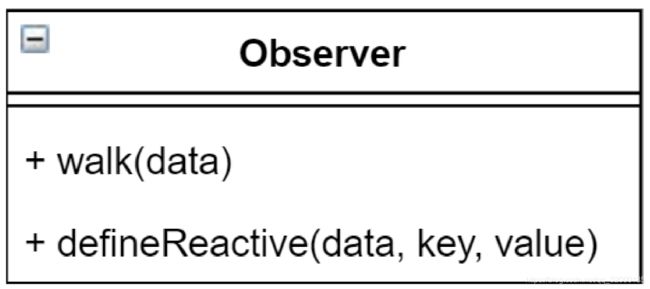
Observer
- 负责把 data 选项中的属性转换成响应式数据
- data 中的某个属性也是对象,把该属性转换成响应式数据
- 数据变化发送通知
/**
* @author Wuner
* @date 2020/7/30 0:12
* @description
*/
// 负责数据劫持
// 把 $data 中的成员转换成 getter/setter
class Observer {
constructor(data) {
this.walk(data);
}
walk(data) {
// 判断数据是否是对象,如果是对象,则遍历对象的所有属性,设置为 getter/setter
if (data && typeof data === 'object') {
// 遍历 data 的所有成员
Object.keys(data).forEach((key) =>
this.defineReactive(data, key, data[key]),
);
}
}
// 定义响应式成员
defineReactive(data, key, val) {
let dep = new Dep();
// 如果val是对象,,继续设置它下面的成员为响应式数据
this.walk(val);
Object.defineProperty(data, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: () => {
// 收集依赖
Dep.target && dep.addSub(Dep.target);
// 这里val不能通过data[key]获取,否则会陷入自调用死循环
return val;
},
set: (newVal) => {
// 这里val不能通过data[key]获取,否则会陷入自调用死循环
if (newVal === val) return;
val = newVal;
// 如果newVal被赋值为对象,则继续设置它下面的成员为响应式数据
this.walk(newVal);
// 发送通知
dep.notify();
},
});
}
}
Compiler
- 负责编译模板,解析指令/插值表达式
- 负责页面的首次渲染
- 当数据变化后重新渲染视图
nodeType
| 常量 | 值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| Node.ELEMENT_NODE | 1 | 一个 元素 节点,例如 和
。
|
| Node.TEXT_NODE | 3 | Element 或者 Attr 中实际的 文字 |
| Node.CDATA_SECTION_NODE | 4 | 一个 CDATASection,例如 。 |
| Node.PROCESSING_INSTRUCTION_NODE | 7 | 一个用于 XML 文档的 ProcessingInstruction ,例如 声明。 |
| Node.COMMENT_NODE | 8 | 一个 Comment 节点。 |
| Node.DOCUMENT_NODE | 9 | 一个 Document 节点。 |
| Node.DOCUMENT_TYPE_NODE | 10 | 描述文档类型的 DocumentType 节点。例如 就是用于 HTML5 的。 |
| Node.DOCUMENT_FRAGMENT_NODE | 11 | 一个 DocumentFragment 节点 |
已弃用的节点类型常量
| 常量 | 值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| Node.ATTRIBUTE_NODE | 2 | 元素 的耦合属性 。在 DOM4 规范里 Node 接口将不再实现这个元素属性。 |
| Node.ENTITY_REFERENCE_NODE | 5 | 一个 XML 实体引用节点。 在 DOM4 规范里被移除。 |
| Node.ENTITY_NODE | 6 | 一个 XML 节点。 在 DOM4 规范中被移除。 |
| Node.NOTATION_NODE | 12 | 一个 XML 节点。 在 DOM4 规范里被移除. |
/**
* @author Wuner
* @date 2020/7/30 2:52
* @description
*/
// 负责解析指令/插值表达式
class Compiler {
constructor(vm) {
this.el = vm.$el;
this.vm = vm;
this.compiler(this.el);
}
// 编译模板,处理文本节点和元素节点
compiler(el) {
// el.childNodes是一个伪数组
const childNodes = Array.from(el.childNodes);
childNodes.forEach((node) => {
// console.dir(node);
if (this.isTextNode(node)) {
// 处理文本节点
this.compilerText(node);
} else if (this.isElementNode(node)) {
// 处理元素节点
this.compilerElement(node);
}
// 判断当前节点是否存在子节点,并且子节点个数大于0,需递归调用compile
if (node.childNodes && node.childNodes.length) {
this.compiler(node);
}
});
}
// 编译元素节点,处理指令
compilerElement(node) {
// console.dir(node);
// attributes是一个伪数组
// 遍历元素节点中的所有属性,找到指令
Array.from(node.attributes).forEach((attr) => {
// 获取元素属性的名称
// 判断当前的属性名称是否是指令
if (this.isDirective(attr.name)) {
this.updater(node, attr);
}
});
}
// 负责更新 DOM
// 创建 Watcher
updater(node, attr) {
// attrName 的形式 v-text v-model
// 截取属性的名称,获取 text model
const attrName = attr.name.substr(2);
// 处理不同的指令
const fn = this[attrName + 'Updater'];
// 因为在 textUpdater等中要使用 this
fn && fn.call(this, node, attr.value);
}
// 处理 v-text 指令
textUpdater(node, key) {
node.textContent = this.vm[key];
// 每一个指令中创建一个 watcher,观察数据的变化
new Watcher(this.vm, key, (newValue) => {
node.textContent = newValue;
});
}
// 处理 v-model 指令
modelUpdater(node, key) {
node.value = this.vm[key];
// 监听视图的变化
node.addEventListener('input', () => (this.vm[key] = node.value));
// 每一个指令中创建一个 watcher,观察数据的变化
new Watcher(this.vm, key, (newValue) => {
node.value = newValue;
});
}
// 编译文本节点
compilerText(node) {
// console.dir(node);
let reg = /\{\{(.+?)\}\}/;
// 获取文本节点的内容
let textContent = node.textContent;
if (reg.test(textContent)) {
// 插值表达式中的值就是我们要的属性名称
let key = RegExp.$1.trim();
// 把插值表达式替换成具体的值
node.textContent = this.vm.$data[key];
new Watcher(this.vm, key, (newValue) => {
node.textContent = newValue;
});
}
}
// 判断是否属性是指令
isDirective(attrName) {
return attrName.startsWith('v-');
}
// 判断是否是文本节点
isTextNode(node) {
return node.nodeType === 3;
}
// 判断是否是元素节点
isElementNode(node) {
return node.nodeType === 1;
}
}
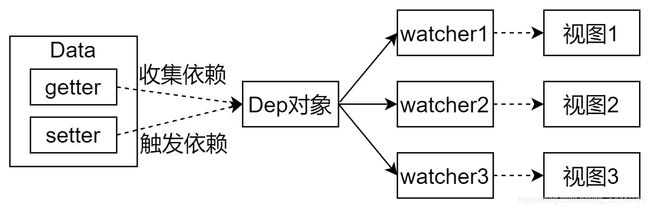
Dep(Dependency)
- 收集依赖,添加观察者(watcher)
- 通知所有观察者
/**
* @author Wuner
* @date 2020/7/30 22:00
* @description
*/
class Dep {
constructor() {
// 存储观察者的数组
this.subs = [];
}
// 添加观察者
addSub(sub) {
// 判断是否是观察者
sub && sub.update && this.subs.push(sub);
}
// 通知所有观察者
notify() {
this.subs.forEach((sub) => sub.update());
}
}
Watcher
- 当数据变化触发依赖, dep 通知所有的 Watcher 实例更新视图
- 自身实例化的时候往 dep 对象中添加自己
/**
* @author Wuner
* @date 2020/7/30 22:17
* @description
*/
class Watcher {
constructor(vm, key, callback) {
this.vm = vm;
this.key = key;
// 当数据变化的时候,调用 callback 更新视图
this.callback = callback;
// 在 Dep 的静态属性上记录当前 watcher 对象,当访问数据的时候把 watcher 添加到 dep 的 subs 中
Dep.target = this;
// 这里通过vm取值时,会调用到observer中的defineReactive中的get方法
this.oldValue = vm[key];
// 赋值后,将缓存清空,防止污染
Dep.target = null;
}
update() {
this.oldValue !== this.vm[this.key] && this.callback(this.vm[this.key]);
}
}
总结
问题
-
给属性重新赋值成对象,是否是响应式的?
是响应式
-
给 Vue 实例新增一个成员是否是响应式的?
不是响应式的。原因
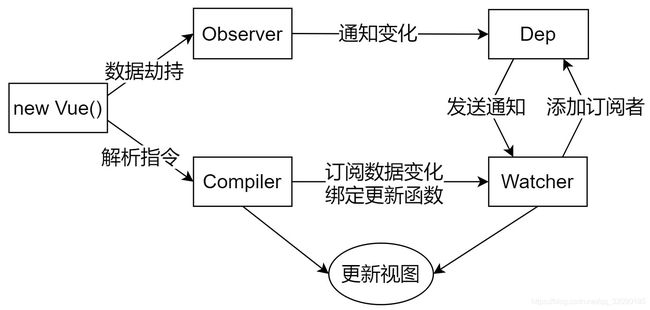
整体流程
- Vue
- 记录传入的选项,设置 d a t a / data/ data/el
- 把 data 的成员注入到 Vue 实例
- 负责调用 Observer 实现数据响应式处理(数据劫持)
- 负责调用 Compiler 编译指令/插值表达式等
- Observer
- 数据劫持
- 负责把 data 中的成员转换成 getter/setter
- 负责把多层属性转换成 getter/setter
- 如果给属性赋值为新对象,把新对象的成员设置为 getter/setter
- 添加 Dep 和 Watcher 的依赖关系
- 数据变化发送通知
- Compiler
- 负责编译模板,解析指令/插值表达式
- 负责页面的首次渲染过程
- 当数据变化后重新渲染
- Dep
- 收集依赖,添加订阅者(watcher)
- 通知所有订阅者
- Watcher
- 自身实例化的时候往 dep 对象中添加自己
- 当数据变化 dep 通知所有的 Watcher 实例更新视图