数据结构-C++链表
插入到倒数第一个
随便插,自动按大小排序
基于数组的链表实习??? 这个会考么
NULL-C特性,考试可以用这个 nullptr -----C++11特性,上机如果单C++得用这个,混合另说
Lnode *creat() 表示返回值 是 一个指向struct node 类型的指针类型 ,等价于 linklist creat()
动态数组的空间申请和空间管理;动态数组的声明和实现;
链表的基本结构和创建方式;链表的遍历;链表的插入和删除;链表的归并和拆分;链表应用;
链表的基本结构
struct node
{
int data;
node *next;
};
链表的创建方式
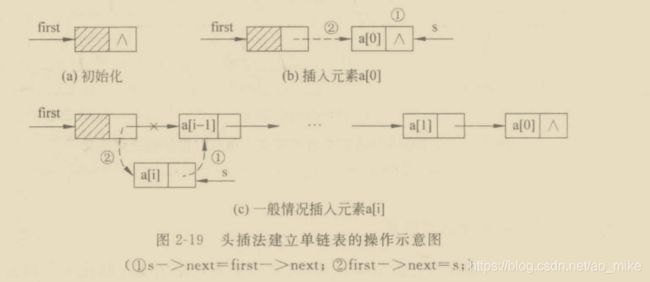
所谓头插法,就是按节点的逆序方法逐渐将结点插入到链表的头部。反之尾插法就是按节点的顺序逐渐将节点插入到链表的尾部。相对来说,头插法要比尾插法算法简单,但是最后产生的链表是逆序的,即第一个输入的节点实际是链表的最后一个节点。而为了习惯,通常用尾插法来创建链表。
程序补充:https://blog.csdn.net/abclixu123/article/details/8210109?utm_medium=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-BlogCommendFromMachineLearnPai2-1.channel_param&depth_1-utm_source=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-BlogCommendFromMachineLearnPai2-1.channel_param
头插法
node *CreateList_Front(Dataype a[],int n)
{
head = new node;
head->next = NULL; //初始化空链表
for(int i = 0;i < n; i++)
{
node *s = NULL;
s = new node;
s->data = a[i];
s-next = first->next;
first -> next = s; //将结点s插入头结点后
}
}
尾插法
node *CreateList_End(Dataype a[],int n)
{
head = new node; //生成头结点
node *r = head,*s = NULL; //尾指针初始化
for(int i = 0;i < n; i++)
{
s = new node;
s->data = a[i];
r-next = s;
r = s; //将结点s插入到终端结点之后
}
r->next = NULL; //建表完毕,将端结点指针域置空
}
链表的遍历
void printL(node *first)
{
node *p = first -> next;
while(p!=NULL)
{
cout <next;
}
cout <
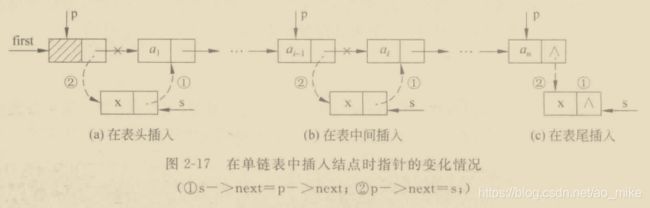
链表的插入
node *insert(node *head,int i,Dataype x)//这个x 一般是int Dataype是字符类型
{
node *p = head, *s = NULL;
int count = 0;
while(p!=NULL&&countnext;
count++;
}
if(p==NULL)
return false;
else
{
s = new node; //申请结点s,数据域为x;
s->data = x;
s->next = p->next; //将结点s插入到结点p之后
p->next=s;
}
}
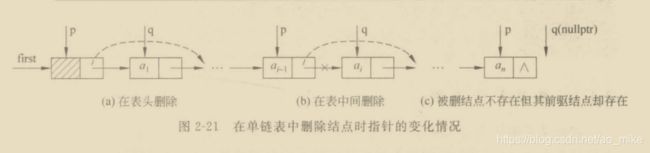
链表的删除
node *del(node *head,int i,Dataype x)
{
node *p = head; *q = NULL;
int count = 0;
while(p!=NULL&&countnext;
count++;
}
if(p==NULL||p->next==NULL)
return false;
else
{
q = p->next;
x = q->data; //暂存被删结点
p->next = q->next;
delete q;
}
}
链表的归并
按值的顺序从小到大, 合并两个链表
node * merge(node * h1, node * h2) //merge合并
{
if (h1 == NULL) return h2;
if (h2 == NULL) return h1;
node * head;
if (h1->data>h2->data) {
head = h2; h2=h2->next;
} else {
head = h1; h1=h1->next; //current 当前,现在 合并后的表
}
node * current = head;
while (h1 != NULL && h2 != NULL) {
if (h1 == NULL || (h2!=NULL && h1->data>h2->data)) {
current->next = h2; h2=h2->next; current = current->next;
} else {
current->next = h1; h1=h1->next; current = current->next;
}
}
current->next = NULL;
return head;
}链表的拆分?
链表应用;
考虑学习补充:逆置等等... 各种情况考虑
取交集,取并集,取重复等等
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_36963950/category_9427724.html