深度学习基础要点和Pytorch常用命令汇总
文章目录
- 深度学习基础
- 卷积
- 池化
- 优化算法
- 梯度下降法
- 动量梯度下降 Momentum梯度下降
- RMSprop
- Adam(Adaptive Moment Estimation)
- pytorch框架
- 损失函数 Loss Functions
- L1Loss
- MSELoss
- NLLLoss & CrossEntropyLoss
- 非线性层(函数) Non-linear Activations
- F.softmax & nn.LogSoftmax() & F.log_softmax()
- F.max_pool2d
- F.relu
- torchvision
- tv.transforms.ToTensor()
- tv.transforms.Normalize()
- torch.nn
- nn.Conv2d
- nn.Linear
- nn.Normal2d
- nn.Module
- 保存和加载模型
- array numpy tensor Variable格式互转
- torch维度
- Variable的梯度grad属性
- 矩阵相乘
- 数学运算
- 平均值
- 直接相乘
- 正弦函数
- 随机数
- 均匀数列
- 激活函数
- matplotlib
- 画曲线图
- 散点图
深度学习基础
卷积
计算卷积后的图片size
s i z e = [ l + 2 ∗ p − k s + 1 size=[\frac{l+2*p-k}{s}+1 size=[sl+2∗p−k+1]
其中:
l = 图 片 原 尺 寸 l = 图片原尺寸 l=图片原尺寸
p = p a d d i n g 大 笑 p = padding大笑 p=padding大笑
k = 卷 积 核 大 小 k = 卷积核大小 k=卷积核大小
s = 步 长 s = 步长 s=步长
卷积参数个数
假设输入为388,输出为655,卷积核大小为333
那么因为输出有6个channel,所以需要6个333的卷积核
对于Pytorch可以用下面代码查看参数:
for name,parameters in net.named_parameters():
print(name,':',paramaters.size())
卷积层激活函数
激活函数一般是在每次卷积后就使用
池化
计算池化后的图片size
方法同卷积操作
优化算法
梯度下降法
batch梯度下降法(batch_size=样本大小)当样本数小于2000
mini_batch梯度下降法(batch_size介于之间)样本数大于2000,一般batch_size设为64~512(2的倍数)
随机梯度下降法(batch_size=1)
W : = W − α ∗ d W W:=W-\alpha*dW W:=W−α∗dW
动量梯度下降 Momentum梯度下降
首先理解加权指数平均
V 0 = 0 V_0=0 V0=0
V 1 = β ∗ V 0 + ( 1 − β ) ∗ θ 1 V_1=\beta*V_0+(1-\beta)*\theta_1 V1=β∗V0+(1−β)∗θ1
V 2 = β ∗ V 1 + ( 1 − β ) ∗ θ 2 V_2=\beta*V_1+(1-\beta)*\theta_2 V2=β∗V1+(1−β)∗θ2
. . . ... ...
V n = β ∗ V n − 1 + ( 1 − β ) ∗ θ n V_n=\beta*V_{n-1}+(1-\beta)*\theta_n Vn=β∗Vn−1+(1−β)∗θn
当β=0.9时,表示v_t平均了之前1/(1-β)即10时间的值,β值越大,v_t曲线越平滑
在前期,为了避免v_0=0这种异常值,用v_t/(1-β^t)代替v_t,这叫做偏差修正,但神经网络一般不使用
V d W : = β ∗ V d W + ( 1 − β ) ∗ d W V_{dW}:=\beta*V_{dW}+(1-\beta)*dW VdW:=β∗VdW+(1−β)∗dW
W : = W − α ∗ V d W W:=W-\alpha*V_{dW} W:=W−α∗VdW
RMSprop
S d W : = β ∗ S d W + ( 1 − β ) ∗ d W 2 S_{dW}:=\beta*S_{dW}+(1-\beta)*dW^{2} SdW:=β∗SdW+(1−β)∗dW2
W : = W − α ∗ d W S d W + ϵ W:=W-\alpha*\frac{dW}{\sqrt{S_{dW}}+\epsilon} W:=W−α∗SdW+ϵdW
ϵ 是 极 小 量 , 为 了 不 除 以 0 \epsilon是极小量,为了不除以0 ϵ是极小量,为了不除以0
Adam(Adaptive Moment Estimation)
V d W : = β 1 ∗ V d W + ( 1 − β 1 ) ∗ d W V_{dW}:=\beta1*V_{dW}+(1-\beta1)*dW VdW:=β1∗VdW+(1−β1)∗dW
S d W : = β 2 ∗ S d W + ( 1 − β 2 ) ∗ d W 2 S_{dW}:=\beta2*S_{dW}+(1-\beta2)*dW^2 SdW:=β2∗SdW+(1−β2)∗dW2
W : = W − α ∗ V d W S d W + ϵ W:=W-\alpha*\frac{V_{dW}}{\sqrt{S_{dW}}+\epsilon} W:=W−α∗SdW+ϵVdW
β 1 常 取 0.9 \beta1常取0.9 β1常取0.9
β 2 常 取 0.999 \beta2常取0.999 β2常取0.999
ϵ 常 取 1 0 − 8 \epsilon常取10^{-8} ϵ常取10−8
pytorch框架
损失函数 Loss Functions
L1Loss
class torch.nn.L1Loss(size_average=True, reduce=True)
创建一个衡量输入 x 与目标 y 之间差的绝对值的平均值的标准, 该 函数会逐元素地求出 x 和 y 之间差的绝对值, 最后返回绝对值的平均值.(在默认条件下,即size_average=True, reduce=True)
loss(x,y)=1/n∑|xi−yi|
当reduce=False时(此时size_average参数失效)
创建2*2*2矩阵,模拟batch_size=2,即每个mini_batch中有两个矩阵,每个矩阵大小2*2
v1=Variable(torch.FloatTensor([
[[1,2],[3,4]],
[[0,-1],[-2,0]]
]))
v2=Variable(torch.FloatTensor([
[[2,-1],[1,3]],
[[4,0],[-1,2]]
]))
print(v1)
#
Variable containing:
(0 ,.,.) =
1 2
3 4
(1 ,.,.) =
0 -1
-2 0
[torch.FloatTensor of size 2x2x2]
print(v2)
#
Variable containing:
(0 ,.,.) =
2 -1
1 3
(1 ,.,.) =
4 0
-1 2
[torch.FloatTensor of size 2x2x2]
然后求L1Loss
criterion=nn.L1Loss(reduce=False)
loss=criterion(v1,v2)
print(loss)
#
Variable containing:
(0 ,.,.) =
1 3
2 1
(1 ,.,.) =
4 1
1 2
[torch.FloatTensor of size 2x2x2]
返回同样是2*2*2矩阵,相当于每个位置求|xi-yi|
当reduce=True size_average=False时
测试样例同上
criterion=nn.L1Loss(size_average=False)
loss=criterion(v1,v2)
print(loss)
#
Variable containing:
15
[torch.FloatTensor of size 1]
是把每个位置差的绝对值求和(以mini_batch为单位)
当reduce=True size_average=False时
criterion=nn.L1Loss(size_average=True)
loss=criterion(v1,v2)
print(loss)
#
Variable containing:
1.8750
[torch.FloatTensor of size 1]
把上面所求的和再除以mini_batch所有矩阵内元素(如上,除以8)个数
MSELoss
class torch.nn.MSELoss(size_average=True, reduce=True)
同L1Loss,只不过这是求差的绝对值的平方和的平均loss(x,y)=1/n∑|xi−yi|^2
样例仍使用上面的v1 v2
criterion=nn.MSELoss(reduce=False)
loss=criterion(v1,v2)
print(loss)
#
Variable containing:
(0 ,.,.) =
1 9
4 1
(1 ,.,.) =
16 1
1 4
[torch.FloatTensor of size 2x2x2]
criterion=nn.MSELoss(size_average=False)
loss=criterion(v1,v2)
print(loss)
#
Variable containing:
37
[torch.FloatTensor of size 1]
criterion=nn.MSELoss()//默认参数设置
loss=criterion(v1,v2)
print(loss)
#
Variable containing:
4.6250
[torch.FloatTensor of size 1]
NLLLoss & CrossEntropyLoss
nn.CrossEntropyLoss = nn.LogSoftmax() + nn.NLLLoss()
m=nn.LogSoftmax()
loss=nn.NLLLoss(reduce=False)
loss2=nn.CrossEntropyLoss(reduce=False)
test=Variable(torch.randn(4,3))
target=Variable(torch.LongTensor([0,2,1,1]))
output=loss(m(test),target)
output2=loss2(test,target)
print(test)
print(F.log_softmax(test))
print(output)
print(output2)
# test 源数据
Variable containing:
0.4137 -0.4271 -0.7461
1.5289 -1.4904 2.1758
-1.8883 -0.0124 -1.6840
-0.2659 -0.7639 0.6339
[torch.FloatTensor of size 4x3]
# F.log_softmax()
Variable containing:
-0.5567 -1.3975 -1.7165
-1.0847 -4.1040 -0.4378
-2.1694 -0.2935 -1.9652
-1.4029 -1.9009 -0.5031
[torch.FloatTensor of size 4x3]
# nn.NLLLoss(input,target)
# input 为F.log_softmax()之后的值,target为一维数组,不是one-hot格式
Variable containing:
0.5567
0.4378
0.2935
1.9009
[torch.FloatTensor of size 4]
# nn.CrossEntropyLoss
# input 为源数据
Variable containing:
0.5567
0.4378
0.2935
1.9009
[torch.FloatTensor of size 4]
非线性层(函数) Non-linear Activations
F.softmax & nn.LogSoftmax() & F.log_softmax()
torch.nn.functional.softmax(input, dim=None, _stacklevel=3)
softmax(x)=exp(xi)/∑exp(xj)
data=Variable(torch.randn(4,3))
print(data)
print('F.softmax')
print(F.softmax(data))
print('log(F.softmax)')
print(np.log(F.softmax(data).data.numpy()))
print('F.log_softmax')
print(F.log_softmax(data))
m=nn.LogSoftmax()
print('nn.LogSoftmax')
print(m(data))
#
Variable containing:
0.8420 1.0236 1.4242
-0.7329 -0.7940 0.7947
-0.3812 -0.3296 -0.0830
0.6234 -1.7182 0.6242
[torch.FloatTensor of size 4x3]
#
F.softmax
Variable containing:
0.2507 0.3006 0.4487
0.1527 0.1437 0.7036
0.2941 0.3097 0.3963
0.4769 0.0459 0.4773
[torch.FloatTensor of size 4x3]
#
log(F.softmax)
[[-1.3836101 -1.2019439 -0.80135906]
[-1.8791015 -1.9402403 -0.35154063]
[-1.2239172 -1.1722705 -0.9256822 ]
[-0.7405206 -3.0821092 -0.7396687 ]]
#
F.log_softmax
Variable containing:
-1.3836 -1.2019 -0.8014
-1.8791 -1.9402 -0.3515
-1.2239 -1.1723 -0.9257
-0.7405 -3.0821 -0.7397
[torch.FloatTensor of size 4x3]
#
nn.LogSoftmax
Variable containing:
-1.3836 -1.2019 -0.8014
-1.8791 -1.9402 -0.3515
-1.2239 -1.1723 -0.9257
-0.7405 -3.0821 -0.7397
[torch.FloatTensor of size 4x3]
可见,F.softmax()求出的各元素在这一行占的比例(默认dim情况下),nn.LogSoftMax()求出的等同于在F.sofgmax()后再使用log函数
F.max_pool2d
document
F.relu
document
torchvision
tv.transforms.ToTensor()
将范围 [0, 255] 中的 PIL Image 或 numpy.ndarray (H x W x C) 转换形状为 (C x H x W) , 值范围为 [0.0, 1.0] 的 torch.FloatTensor.
tv.transforms.Normalize()
input[channel] = (input[channel] - mean[channel]) / std[channel]
transform=transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5,0.5,0.5),(0.5,0.5,0.5))
])
torch.nn
nn.Conv2d
torch.nn.Conv2d
nn.Linear
torch.nn.Linear
nn.Normal2d
torch.nn.Normal2d
批量归一化,和数据归一化不同,是在神经网络层中归一化
nn.Module
注意: 当神经网络有dropout和BatchNorm时,在训练前要加上net.train(),在测试时要加上net.eval()
保存和加载模型
# 保存和加载整个模型
torch.save(model_object, 'model.pkl')
model = torch.load('model.pkl')
# 仅保存和加载模型参数(推荐使用)
torch.save(model_object.state_dict(), 'params.pkl')
model_object.load_state_dict(torch.load('params.pkl'))
array numpy tensor Variable格式互转
array 转 numpy
arr_data=[1,2,3,4]
np_data=np.array(arr_data)
numpy 转 array
arr_data2=[np_data]
array 转 tensor
tensor=torch.FloatTensor(array)
numpy 转 tensor
tensor=torch.from_numpy(np_data)
tensor 转 numpy
data=tensor.numpy()
tensor 转 Variable
variable=Variable(tensor)
Variable 得 tensor
tensor_data=variable.data
Variable 得 numpy
numpy_data=variable.data.numpy()
torch维度
tensor.size()
Variable的梯度grad属性
v_out=torch.mean(variable*variable)
v_out.backward()
print(variable.grad)
//输出[[0.5,1],[1.5,2]]
矩阵相乘
mat_data=torch.FloatTensor([[1,2],[3,4]])
print(torch.mm(mat_data,mat_data))
//输出 [[7,10],[15,22]]
mat_data_flat=torch.FloatTensor([1,2,3,4])
print(mat_data_flat.dot(mat_data_flat.dot(mat_data_flat)))
// 输出 30.0
数学运算
平均值
mat_data=torch.FloatTensor([[1,2],[3,4]])
mat_mean=torch.mean(mat_data)
//输出2.5
直接相乘
mat_data=torch.FloatTensor([[1,2],[3,4]])
print(mat_data*mat_data)
// 输出 [[1,4],[9,16]]
正弦函数
torch.sin()
随机数
torch.rand(10)
# 10个0-1均匀分布
均匀数列
x=torch.linspace(-1,1,10)
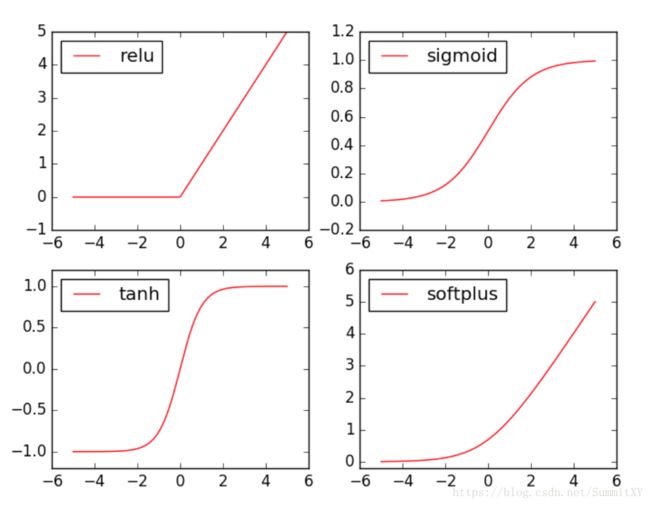
激活函数
matplotlib
pyplot只能处理numpy格式数据
画曲线图
plt.figure(1, figsize=(8, 6))
plt.subplot(221)
plt.plot(x_np, y_relu, c='red', label='relu')
plt.ylim((-1, 5))
plt.legend(loc='best')
...
plt.show()
散点图
plt.scatter(x_np, y_relu)