PyTorch入门实战教程笔记(二十四):卷积神经网络实现 2
PyTorch入门实战教程笔记(二十四):卷积神经网络实现 2:ResNet实现CIFAR10
CIFAR10数据集介绍
关于CIFAR-10数据集,可以访问它的官网进行下载:
http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar.html。
CIFAR包含常见的10类物体的照片,照片的size 为32×32,每一类照片有6000张,所以一共6万张照片,我们把6万张照片随机选出5万张照片作为training,剩余的1万张作为test.
![]()
CIFAR10代码实战准备
- 数据集的加载与使用,加载数据要用到的函数类:DataLoader、datasets、transforms,从对应的包中导入。过iter方法把DataLoader迭代器先得到,使用迭代器.next()方法得到一个batch,来验证数据的shape和label的shape,得到最终结果:x: torch.Size([32, 3, 32, 32]) label: torch.Size([32])。详细代码:
import torch
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torchvision import datasets
from torchvision import transforms
def main():
batchsz = 32
#当前目录下新建文件夹'cifar',train = True,transform对数据进行变换,download=True自动下载数据集
cifar_train = datasets.CIFAR10('cifar', True, transform=transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize((32, 32)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
]), download=True)
#DataLoader方便一次加载多个,第一个参数为数据集cifar_train,第二个参数batch_size为每次批处理数量,
#根据显卡设置batch_size,不要太小。第三个参数shuffle为打乱,设置成True。
cifar_train = DataLoader(cifar_train, batch_size=batchsz, shuffle=True)
cifar_test = datasets.CIFAR10('cifar', False, transform=transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize((32, 32)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
]), download=True)
cifar_test = DataLoader(cifar_test, batch_size=batchsz, shuffle=True)
#通过iter方法把DataLoader迭代器先得到,使用迭代器.next()方法得到一个batch。
x, label = iter(cifar_train).next()
print('x:', x.shape, 'label:', label.shape)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
- 新建一个类resnet,所有的pytorch的神经结构类都要继承自nn.Module这个类,使用from torch import nn,将其导入。新建类的初始化方法,调用super(ResBlk, self).init(),调用类的初始化方法类初始化父类。我们前面已经说了,最关键是resnet的基本单元,接下来参考下图来写这个基本单元。
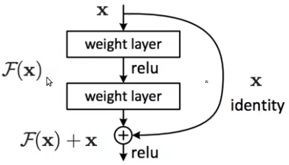
根据上图,我们应该这个单元块的输入,输出,所以定义函数传入参数:def init(self, ch_in, ch_out, stride=1),
然后通过super(ResBlk, self).init()初始化,使用nn.Conv2d()建立self.conv1层,通过nn.BatchNorm2d实现一个BN层bn1,把数据分布缩放到一定的范围,有利于训练。接着同样构造conv2, bn2。同样道理,新建一个forward()函数,通过F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))实现relu。接下来考虑shotcut,有一个问题,如果ch_in和ch_out一样的话,能够直接相加,如果不一样,就需要输入再加一个单元,将ch_in扩展成和ch_out一样。所以我们要有一个if的判断,判断如果不一样,通过self.extra = nn.Sequential()将其扩展为一样的。同时在forward中使用out = self.extra(x) + out。
此外,随着网络深度的加深,如果stride一直为1,由于padding的存在,会使图片的大小一直不变,所以我们在初始化时,应该设置一下stride参数,并使ResBlk的conv1的stride可以调节,同样,也要调节输入的图片的stride,即nn.Sequential()里面的stride。基本单元模块实现代码如下:
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
class ResBlk(nn.Module):
"""
resnet block
"""
def __init__(self, ch_in, ch_out, stride=1):
"""
:param ch_in:
:param ch_out:
"""
super(ResBlk, self).__init__()
# we add stride support for resbok, which is distinct from tutorials.
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(ch_in, ch_out, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(ch_out)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(ch_out, ch_out, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(ch_out)
self.extra = nn.Sequential()
if ch_out != ch_in:
# [b, ch_in, h, w] => [b, ch_out, h, w]
self.extra = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(ch_in, ch_out, kernel_size=1, stride=stride),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ch_out)
)
def forward(self, x):
"""
:param x: [b, ch, h, w]
:return:
"""
out = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))
out = self.bn2(self.conv2(out))
# short cut.
# extra module: [b, ch_in, h, w] => [b, ch_out, h, w]
# element-wise add:
out = self.extra(x) + out
out = F.relu(out)
return out
做完ResBlk类,我们开始构建一个ResNet18的类,参考下图:

通过super(ResNet18, self).init()初始化,然后建立第一层conv1,接着跟4个blocks,使用前面定义的ResBlk类,如:self.blk1 = ResBlk(64, 128, stride=2),最后一层输出层为线性层 。在forward中,先将构建的conv1(x)在上激活函数,然后连续四个x = self.blk n (x), 然后通过x = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(x, [1, 1])做一个全局平均池化,因为使用线性层要打平,所以使用x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)将其打平之后,在调用x = self.outlayer(x)。详细代码如下:
class ResNet18(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(ResNet18, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=3, padding=0),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
)
# followed 4 blocks
# [b, 64, h, w] => [b, 128, h ,w]
self.blk1 = ResBlk(64, 128, stride=2)
# [b, 128, h, w] => [b, 256, h, w]
self.blk2 = ResBlk(128, 256, stride=2)
# # [b, 256, h, w] => [b, 512, h, w]
self.blk3 = ResBlk(256, 512, stride=2)
# # [b, 512, h, w] => [b, 1024, h, w]
self.blk4 = ResBlk(512, 512, stride=2)
self.outlayer = nn.Linear(512*1*1, 10)
def forward(self, x):
"""
:param x:
:return:
"""
x = F.relu(self.conv1(x))
# [b, 64, h, w] => [b, 1024, h, w]
x = self.blk1(x)
x = self.blk2(x)
x = self.blk3(x)
x = self.blk4(x)
# print('after conv:', x.shape) #[b, 512, 2, 2]
# [b, 512, h, w] => [b, 512, 1, 1]
x = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(x, [1, 1])
# print('after pool:', x.shape)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.outlayer(x)
return x
综上,resnet18.py文件的整体代码如下:
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
class ResBlk(nn.Module):
"""
resnet block
"""
def __init__(self, ch_in, ch_out, stride=1):
"""
:param ch_in:
:param ch_out:
"""
super(ResBlk, self).__init__()
# we add stride support for resbok, which is distinct from tutorials.
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(ch_in, ch_out, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(ch_out)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(ch_out, ch_out, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(ch_out)
self.extra = nn.Sequential()
if ch_out != ch_in:
# [b, ch_in, h, w] => [b, ch_out, h, w]
self.extra = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(ch_in, ch_out, kernel_size=1, stride=stride),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ch_out)
)
def forward(self, x):
"""
:param x: [b, ch, h, w]
:return:
"""
out = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))
out = self.bn2(self.conv2(out))
# short cut.
# extra module: [b, ch_in, h, w] => [b, ch_out, h, w]
# element-wise add:
out = self.extra(x) + out
out = F.relu(out)
return out
class ResNet18(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(ResNet18, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=3, padding=0),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
)
# followed 4 blocks
# [b, 64, h, w] => [b, 128, h ,w]
self.blk1 = ResBlk(64, 128, stride=2)
# [b, 128, h, w] => [b, 256, h, w]
self.blk2 = ResBlk(128, 256, stride=2)
# # [b, 256, h, w] => [b, 512, h, w]
self.blk3 = ResBlk(256, 512, stride=2)
# # [b, 512, h, w] => [b, 1024, h, w]
self.blk4 = ResBlk(512, 512, stride=2)
self.outlayer = nn.Linear(512*1*1, 10)
def forward(self, x):
"""
:param x:
:return:
"""
x = F.relu(self.conv1(x))
# [b, 64, h, w] => [b, 1024, h, w]
x = self.blk1(x)
x = self.blk2(x)
x = self.blk3(x)
x = self.blk4(x)
# print('after conv:', x.shape) #[b, 512, 2, 2]
# [b, 512, h, w] => [b, 512, 1, 1]
x = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(x, [1, 1])
# print('after pool:', x.shape)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.outlayer(x)
return x
def main():
blk = ResBlk(64, 128, stride=4)
tmp = torch.randn(2, 64, 32, 32)
out = blk(tmp)
print('block:', out.shape)
x = torch.randn(2, 3, 32, 32)
model = ResNet18()
out = model(x)
print('resnet:', out.shape)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
resnet18 训练cifar10实战
- 前期准备:我们需要优化器optim,所以from torch import nn, optim,并且将上述的resnet5网络导入到主文件,from resnet import ResNet18。接下来配置:将需要运算的通过.to(device)装换到GPU上去,并且使用nn.CrossEntropyLoss().to(device)的loss,
和优化器:optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=1e-3),如下:
device = torch.device('cuda')
model = ResNet18().to(device)
criteon = nn.CrossEntropyLoss().to(device)
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=1e-3)
print(model)
- 训练代码:通过for batchidx, (x, label) in enumerate(cifar_train)来对一个batch迭代一次(一次batch 32张图片)。并且将(x,label)都加载到GPU上,执行logits = model(x),将数据送入模型,然后计算loss,在backward之前一定要将梯度清零,调用optimizer.step(),进行梯度更新。
for epoch in range(1): #1改为1000
model.train()
for batchidx, (x, label) in enumerate(cifar_train):
# 这里是对一个batch迭代一次,一次batch 32张图片
# [b, 3, 32, 32], [b]
x, label = x.to(device), label.to(device)
logits = model(x)
# logits: [b, 10], label: [b], loss: tensor scalar
loss = criteon(logits, label)
# backprop
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# 使用 .item()将最后一个标量loss转换成Numpy打印出来
print(epoch, 'loss:', loss.item())
- 测试代码:因为测试过程不需要梯度更新,为了保险起见,使用with torch.no_grad(),通过for x, label in cifar_test,来加载测试数据,将x传入模型:logits = model(x),然后将预测值最高的序列号作为预测结果,通过eq函数与真实label对比,将batch中正确的相加和,再最终累加,通过total_correct / total_num求得精度。
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
# test
total_correct = 0
total_num = 0
for x, label in cifar_test:
# [b, 3, 32, 32], [b]
x, label = x.to(device), label.to(device)
# [b, 10]
logits = model(x)
# [b]
pred = logits.argmax(dim=1)
# [b] vs [b] => scalar tensor
correct = torch.eq(pred, label).float().sum().item()
total_correct += correct
total_num += x.size(0)
# print(correct)
acc = total_correct / total_num
print(epoch, 'test acc:', acc)
- 将上述的完整的完整的 resnet.py和下面完整的 main.py放入一个工程下,运行main.py,即可实现数据加载、训练、测试全过程。完整的 main.py代码如下:
import torch
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torchvision import datasets
from torchvision import transforms
from torch import nn, optim
from resnet import ResNet18
def main():
batchsz = 32
#当前目录下新建文件夹'cifar',train = True,transform对数据进行变换,download=True自动下载数据集
cifar_train = datasets.CIFAR10('cifar', True, transform=transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize((32, 32)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
]), download=True)
#DataLoader方便一次加载多个,第一个参数为数据集cifar_train,第二个参数batch_size为每次批处理数量,
#根据显卡设置,不要太小。第三个参数shuffle为打乱,设置成True。
cifar_train = DataLoader(cifar_train, batch_size=batchsz, shuffle=True)
cifar_test = datasets.CIFAR10('cifar', False, transform=transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize((32, 32)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
]), download=True)
cifar_test = DataLoader(cifar_test, batch_size=batchsz, shuffle=True)
#通过iter方法把DataLoader迭代器先得到,使用迭代器.next()方法得到一个batch。
x, label = iter(cifar_train).next()
print('x:', x.shape, 'label:', label.shape)
device = torch.device('cuda')
model = ResNet18().to(device)
criteon = nn.CrossEntropyLoss().to(device)
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=1e-3)
print(model)
for epoch in range(1000):
model.train()
for batchidx, (x, label) in enumerate(cifar_train):
# 这里是对一个batch迭代一次,一次batch 32张图片
# [b, 3, 32, 32], [b]
x, label = x.to(device), label.to(device)
logits = model(x)
# logits: [b, 10], label: [b], loss: tensor scalar
loss = criteon(logits, label)
# backprop
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# 使用 .item()将最后一个标量loss转换成Numpy打印出来
print(epoch, 'loss:', loss.item())
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
# test
total_correct = 0
total_num = 0
for x, label in cifar_test:
# [b, 3, 32, 32], [b]
x, label = x.to(device), label.to(device)
# [b, 10]
logits = model(x)
# [b]
pred = logits.argmax(dim=1)
# [b] vs [b] => scalar tensor
correct = torch.eq(pred, label).float().sum().item()
total_correct += correct
total_num += x.size(0)
# print(correct)
acc = total_correct / total_num
print(epoch, 'test acc:', acc)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()