hadoop生态系统学习之路(五)hbase的简单使用
最近,参与了公司的一个大数据接口平台的开发,具体的处理过程是这样的。我们公司负责数据的入库,也就是一个etl过程,使用MR将数据入到hive里面,然后同步到impala,然后此接口平台提供查询接口,前台会将sql语句以参数传过来,然后接口平台通过调用impala提供的java api接口,将数据查询出来返回给用户。另外,如果查询的数据量很大,那么前台就会传一个taskId过来,第一次只需将数据查询出来,入到impala临时表,下次再查便将数据返回。那么,如何记录此任务的状态变化呢,这里我们就使用到了hbase,以taskId为row key,然后创建一个列簇记录状态信息。
下面,分以下几步对hbase进行介绍。
一、hbase的基本原理
HBase是一个构建在HDFS上的分布式列存储系统,主要用于海量结构化数据存储。
hbase的特点:
1. 大,一个表可以有数十亿行,上百万列;
2. 无模式,每行都有一个可排序的主键和任意多的列,列可以根据需要动态的增加,同一张表中不同的行可以有截然不同的列;
3. 面向列,面向列(族)的存储和权限控制,列(族)独立检索;
4. 稀疏,空(null)列并不占用存储空间,表可以设计的非常稀疏;
5. 数据多版本,每个单元中的数据可以有多个版本,默认情况下版本号自动分配,是单元格插入时的时间戳;
6. 数据类型单一,Hbase中的数据都是字符串,没有类型。
下面,再来看看hbase相关的组件:
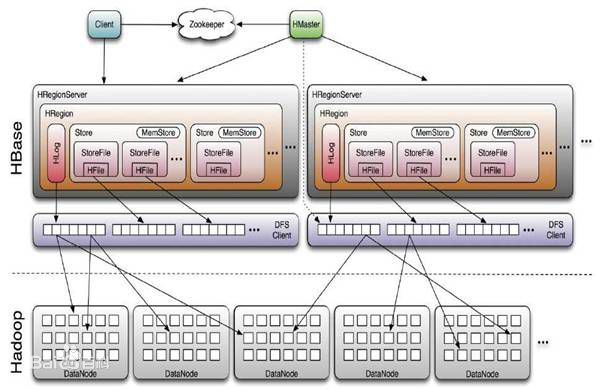
Master:为Region server分配region,负责Region server的负载均衡,发现失效的Region server并重新分配其上的region,管理用户对table的增删改查操作。
RegionServer:Regionserver维护region,处理对这些region的IO请求,Regionserver负责切分在运行过程中变得过大的region。
Zookeeper:通过选举,保证任何时候,集群中只有一个master,Master与RegionServers 启动时会向ZooKeeper注册,存贮所有Region的寻址入口,实时监控Region server的上线和下线信息,并实时通知给Master,存储HBase的schema和table元数据,默认情况下,HBase 管理ZooKeeper 实例,比如, 启动或者停止ZooKeeper。Zookeeper的引入使得Master不再是单点故障。
大概的介绍下,关于hbase表结构,笔者下面再进行介绍。
二、hbase的常用命令
首先,我们可以执行hbase shell进入hbase命令行,如下:
然后,执行list,可以看到所有的表,如下:
 ,接下来,我们可以describe ‘表名’来查看表结构,如下:
,接下来,我们可以describe ‘表名’来查看表结构,如下:
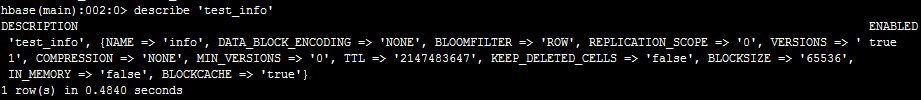
可以看到,这个表有一个列族info。
然后,我们可以使用scan ‘表名’来查看,整张表的数据。
下面,我们使用get ‘result_info’,’test02’获取表中某个row key的所有列值,如下:
![]()
好了,就说这几个命令,还有很多,大家可以查阅下,多练练就熟了。
三、hbase 的java api基本操作
hbase包依赖,如下:
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8project.build.sourceEncoding>
<hadoop.version>2.3.0-cdh5.0.0hadoop.version>
<hbase.version>0.96.1.1-cdh5.0.0hbase.version>
<hive.version>0.12.0-cdh5.0.0hive.version>
properties>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hbasegroupId>
<artifactId>hbase-clientartifactId>
<version>${hbase.version}version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<artifactId>jdk.toolsartifactId>
<groupId>jdk.toolsgroupId>
exclusion>
exclusions>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hbasegroupId>
<artifactId>hbase-commonartifactId>
<version>${hbase.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hbasegroupId>
<artifactId>hbase-serverartifactId>
<version>${hbase.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hbasegroupId>
<artifactId>hbase-thriftartifactId>
<version>${hbase.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hbasegroupId>
<artifactId>hbase-testing-utilartifactId>
<version>${hbase.version}version>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>首先,我直接贴出代码,如下:
package org.hbase.demo;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.HBaseConfiguration;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Get;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.HTable;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Put;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Result;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.util.Bytes;
/**
* 关键点1_:将自动提交关闭,如果不关闭,每写一条数据都会进行提交,是导入数据较慢的做主要因素。
* 关键点2:设置缓存大小,当缓存大于设置值时,hbase会自动提交。此处可自己尝试大小,一般对大数据量,设置为5M即可,本文设置为3M。
* 关键点3:每一个分片结束后都进行flushCommits(),如果不执行,当hbase最后缓存小于上面设定值时,不会进行提交,导致数据丢失。
*
* @author qiyongkang
*
*/
public class Example {
/**
*
* insertBatch: 批量插入.
*
* @author qiyongkang
* @throws IOException
* @since JDK 1.6
*/
public static void insertBatch() throws IOException {
Configuration config = HBaseConfiguration.create();
config.set("hbase.zookeeper.quorum", "172.31.25.8,172.31.25.2,172.31.25.3");
HTable htable = new HTable(config, "qyk_info");
htable.setAutoFlush(false, false); // 关键点1
htable.setWriteBufferSize(3 * 1024 * 1024); // 关键点2
int num = 1;
while (num <= 10) {
Put put = new Put(Bytes.toBytes(num + ""));
put.add(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("age"), Bytes.toBytes("18"));
put.add(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("name"), Bytes.toBytes("qyk" + num));
put.add(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("id"), Bytes.toBytes(num + ""));
htable.put(put);
num++;
if (num % 100 == 0) {
System.out.println("..." + num);
}
}
htable.flushCommits();// 关键点3
htable.close();
}
/**
*
* insertSingle:单个插入.
*
* @author qiyongkang
* @throws IOException
* @since JDK 1.6
*/
public static void insertSingle() throws IOException {
Configuration config = HBaseConfiguration.create();
config.set("hbase.zookeeper.quorum", "172.31.25.8,172.31.25.2,172.31.25.3");
HTable htable = new HTable(config, "qyk_info");
Put put = new Put(Bytes.toBytes("0"));
put.add(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("age"), Bytes.toBytes("18"));
put.add(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("name"), Bytes.toBytes("qyk" + 0));
put.add(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("id"), Bytes.toBytes("0"));
htable.put(put);
htable.close();
}
/**
*
* getData:根据row key获取列信息.
*
* @author qiyongkang
* @throws IOException
* @since JDK 1.6
*/
public static void getData() throws IOException {
Configuration config = HBaseConfiguration.create();
config.set("hbase.zookeeper.quorum", "172.31.25.8,172.31.25.2,172.31.25.3");
HTable htable = new HTable(config, "qyk_info");
Get get = new Get(Bytes.toBytes("1"));
Result result = htable.get(get);
String age = Bytes.toString(result.getValue(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("age")));
String name = Bytes.toString(result.getValue(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("name")));
String id = Bytes.toString(result.getValue(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("id")));
System.out.println("age:" + age + ",name:" + name + ",id:" + id);
htable.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//单个插入
insertSingle();
//批量插入
insertBatch();
//根据row key获取数据
getData();
}
}
分别对应三个操作,首先我们在hbase命令行执行create ‘qyk_info’, ‘info’创建表和列族,然后,再执行程序,可以看到控制台如下:
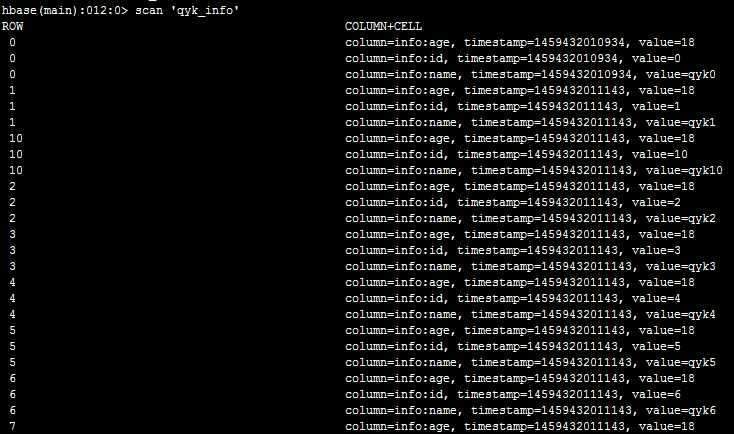
然后,我们执行scan ‘qyk_info’可以看到,如下:
然后,我们使用单个插入,rowkey还是0,将id改为11,age改为19,执行单个插入。
然后,在命令行执行get ‘qyk_info’, ‘0’可以看到:
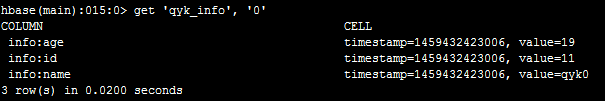
其实,这个就是更新操作,cell中的值会有一个时间戳,每次显示此列的最新值。
好了,关于hbase的基本使用就讲到这儿了,比较粗浅,希望给大家带来帮助!