C语言结构体、链表使用例(结构体数组、结构体指针、链表的插入、删除)
1.定义一个结构体变量(包含年月日)计算给定日期是该年的第几天
#include
#include
int main()
{
struct date
{
int y, m, d;
}da;
int flag, n, p, a[12] = { 31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };
printf("y,m,d=");
scanf("%d,%d,%d", &da.y, &da.m, &da.d);
flag = (da.y % 4 == 0 && da.y % 100 != 0 || da.y % 400 == 0); //判断是否闰年
if (da.m < 1 || da.m>12)
{
exit(0);
}
a[1] += flag;
if (da.d<1 || da.d>a[da.m - 1])
{
exit(0);
}
for (n = da.d, p = 1; p < da.m; p++)
{
n += a[p - 1];
}
printf("n=%d\n", n);
}
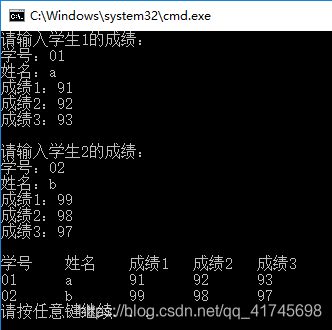
2.输入学生的成绩并显示
#include
struct student
{
char number[6];
char name[6];
int score[3];
}stu[2];
void output(struct student stu[2])
{
int i, j;
printf("学号 姓名 成绩1 成绩2 成绩3\n");
for(i=0;i<2;i++)
{
printf("%-8s%-8s", stu[i].number, stu[i].name);
for (j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
printf("%-8d", stu[i].score[j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
int main()
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
printf("请输入学生%d的成绩:\n", i + 1);
printf("学号:");
scanf("%s", stu[i].number);
printf("姓名:");
scanf("%s", stu[i].name);
for (j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
printf("成绩%d:", j + 1);
scanf("%d", &stu[i].score[j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
output(stu);
}
3.对3个人投票,投票数字必须是1,2,3,否则按废票处理,统计3个人的得票数,降序排序并输出
#include
#define N 3
#define M 20 //总票数
struct Candid
{
char name[10];
int num;
};
void count(int vote[],struct Candid cand[], int *va, int *nova)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
switch (vote[i])
{
case 1:cand[0].num++; (*va)++; break;
case 2:cand[1].num++; (*va)++; break;
case 3:cand[2].num++; (*va)++; break;
default:(*nova)++; break;
}
}
}
void sort(struct Candid cand[])
{
int i, j;
struct Candid temp;
for (i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < N -1- i; j++)
{
if (cand[j].num < cand[j + 1].num)
{
temp = cand[j]; cand[j] = cand[j + 1]; cand[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
void main()
{
int i, vote[M] = { 3,2,1,1,1,1,1,2,5,2,2,2,4,2,3,1,3,2,1,1 };
int valid, novalid;
struct Candid cand[N] = { {"AA",0} ,{"BB",0} ,{"CC",0} };
valid = novalid = 0;
count(vote, cand, &valid, &novalid);
printf("有效票数:%d\n", valid);
printf("无效票数:%d\n", novalid);
sort(cand);
for (i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
printf("%s:%d\n", cand[i].name, cand[i].num);
}
}
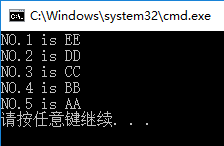
4.依据学生的总成绩进行排序(不改变结构体中元素顺序)
#include
struct Student
{
char Name[10];
int Score[3];
};
void sort(struct Student *pst[], int n) //不改变结构体中元素顺序进行降序排序
{
int i, j, sum1, sum2;
struct Student *temp;
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < n - 1 - i; j++)
{
sum1 = pst[j]->Score[0] + pst[j]->Score[1] + pst[j]->Score[2];
sum2 = pst[j + 1]->Score[0] + pst[j + 1]->Score[1] + pst[j + 1]->Score[2];
if (sum1 < sum2)
{
temp = pst[j]; pst[j] = pst[j + 1]; pst[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
void main()
{
struct Student stu[5]{ {"AA",90,80,70},{ "BB",93,83,73 },{ "CC",95,85,75 },{ "DD",97,87,77 },{ "EE",99,89,79 } };
struct Student *pst[5];
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
pst[i] = &stu[i];
}
sort(pst, 5);
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
printf("NO.%d is %s\n", i+1, pst[i]->Name);
}
}
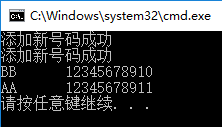
5.电话号码结构体Tel,电话号码簿结构体Tel_Book,函数 add 添加电话号码,函数 sort 进行升序排序
#include
#include
#define MAXNUM 300
struct Tel
{
char name[10];
char telno[12];
};
struct Tel_Book
{
struct Tel tels[MAXNUM];
int num_of_tels;
};
int add(struct Tel_Book *tb, struct Tel *tel)
{
if (tb->num_of_tels == MAXNUM)
{
return 0;
}
tb->tels[tb->num_of_tels++] = *tel;
return 1;
}
void sort(struct Tel_Book *tb)
{
int i, j;
struct Tel temp;
for (i = 0; i < tb->num_of_tels - 1; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < tb->num_of_tels - 1 - i; j++)
{
if (strcmp(tb->tels[j].telno, tb->tels[j + 1].telno) > 0)
{
temp = tb->tels[j];
tb->tels[j] = tb->tels[j + 1];
tb->tels[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
void main()
{
struct Tel_Book tb;
struct Tel tel;
int i;
tb.num_of_tels = 0;
strcpy(tel.name, "AA");
strcpy(tel.telno, "12345678911");
if (add(&tb, &tel))
{
printf("添加新号码成功\n");
}
else
{
printf("添加新号码没有成功\n");
}
strcpy(tel.name, "BB");
strcpy(tel.telno, "12345678910");
if (add(&tb, &tel))
{
printf("添加新号码成功\n");
}
else
{
printf("添加新号码没有成功\n");
}
sort(&tb);
for (i = 0; i < tb.num_of_tels; i++)
{
printf("%s\t%s\n", tb.tels[i].name, tb.tels[i].telno);
}
}
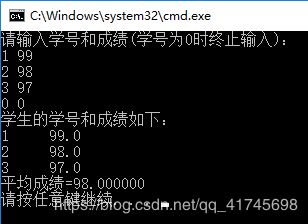
6.创建链表,函数aver的功能是求一个学生链表中的所有学生结点中成绩score的平均值
#include
#include
struct stud
{
int num;
float score;
struct stud *next;
};
float aver(struct stud *head)
{
struct stud *p;
int n = 0;
float sum = 0;
p = head;
while (p!=NULL)
{
sum = sum + p->score;
p = p->next;
n = n + 1;
}
return(sum / n);
}
struct stud *create()
{
struct stud *head, *p1, *p2;
int n = 0;
head = NULL;
p2 = p1 = (struct stud *)malloc(sizeof(struct stud));
printf("请输入学号和成绩(学号为0时终止输入):\n");
scanf("%d %f", &p1->num, &p1->score);
while (p1->num != 0)
{
n = n + 1;
if (n == 1)
{
head = p1;
}
else
{
p2->next = p1;
}
p2 = p1;
p1 = (struct stud *)malloc(sizeof(struct stud));
scanf("%d %f", &p1->num, &p1->score);
}
p2->next = NULL;
return head;
}
void print(struct stud *h)
{
struct stud *p;
p = h;
printf("学生的学号和成绩如下:\n");
while (p != NULL)
{
printf("%-5d%5.1f\n", p->num, p->score);
p = p->next;
}
}
void main()
{
struct stud *head;
head = create();
print(head);
printf("平均成绩=%f\n", aver(head));
}
7.假如链表为空,key生成的新节点就为头节点,假如key为偶数,生成的新节点插入到头节点,否则新节点作为尾节点
#include
#include
typedef struct node
{
int d;
struct node *next;
}NODE;
NODE *insert(NODE *head, int key)
{
NODE *s, *p;
s = (NODE *)malloc(sizeof(NODE));
s->d = key;
s->next = NULL;
if (head == NULL) //假如链表为空,key生成的新节点就为头节点
{
head = s;
return head;
}
if (s->d % 2 == 0) //key为偶数,生成的新节点插入头节点
{
s->next = head;
head = s;
return head;
}
else //key生成的新节点插入到链表尾
{
p = head;
while (p->next != NULL)
{
p = p->next;
}
p->next = s;
return head;
}
}
void print(NODE *head)
{
if (head == NULL)
{
return;
}
while (head->next != NULL)
{
printf("%d", head->d);
head = head->next;
}
printf("%d\n", head->d);
}
void main()
{
NODE *head = NULL;
head = insert(head, 1); print(head);
head = insert(head, 2); print(head);
head = insert(head, 3); print(head);
head = insert(head, 4); print(head);
}
8.删除链表数据中的非素数节点,生成一个素数节点链表
#include
#include
struct node
{
int d;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *create()
{
struct node *head = NULL, *p, *q = NULL;
int i;
for (i = 2; i <= 10; i++)
{
p = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
p->d = i;
p->next = NULL;
if (head == NULL)
{
head=p;
}
else
{
q->next = p;
}
q = p;
}
return head;
}
void print(struct node *head)
{
if (head == NULL)
{
return;
}
while (head->next != NULL)
{
printf("%d", head->d);
head = head->next;
}
printf("%d\n", head->d);
}
struct node *delst(struct node *head)
{
struct node *x, *y, *r;
x = r = head;
while (x != NULL)
{
y = x->next;
while (y != NULL)
{
if ((y->d) % (x->d) == 0)
{
r->next = y->next;
free(y);
y = r->next;
}
else
{
r = y;
y = y->next;
}
}
x = x->next;
}
return head;
}
int main()
{
struct node *head;
head = create();
print(head);
head = delst(head);
print(head);
}
9.createLink()函数根据输入节点数,生成链表;printfLink()输出链表,delstudent()根据输入年龄,如果在链表中找到该年龄的结点,则删除
#include
#include
#define LEN sizeof(struct student)
struct student
{
char num[6];
char name[8];
char sex[2];
int age;
struct student *next;
};
struct student *creatLink(int length)
{
int i;
struct student *head = NULL,*p,*pt;
for (i = 1; i <= length; i++)
{
p = (struct student *)malloc(LEN);
if (i == 1)
{
head = pt = p;
}
else
{
pt->next = p;
}
pt = p;
scanf("%s", p->num);
scanf("%s", p->name);
scanf("%s", p->sex);
scanf("%d", &p->age);
}
p->next = NULL;
return head;
}
int printfLink(struct student *head)
{
struct student *p = head;
printf("\nNO.\tName\tSex\tAge\n");
while (p != NULL)
{
printf("%s\t%s\t%s\t%d\n", p->num, p->name, p->sex, p->age);
p = p->next;
}
return 0;
}
struct student *delstudent(struct student *head, int iage)
{
struct student *p, *pt;
int find = 0;
p = pt = head;
if (pt->age == iage) //如果链头是待删元素
{
p = p->next;
head = pt = p;
find = 1;
}
else //链头不是待删元素
{
pt = p->next;
}
while (pt != NULL)
{
if (pt->age == iage)
{
p->next = pt->next;
find = 1;
}
else
{
p = pt;
}
pt = pt->next;
}
if (!find)
{
printf("not found %d", iage);
}
return head;
}
void main()
{
struct student *p, *pt, *head;
int length, iage;
printf("Input the number of students:");
scanf("%d", &length);
printf("Input %d nodes as flowing formate:", length);
printf("\nNO.\tName\tSex\tAge\n");
head = creatLink(length);
printf("Input the delet age:");
scanf("%d", &iage);
head = delstudent(head, iage);
printfLink(head);
}