Transformer 结构分析
self-attetion
1. 输入
X = E m b e d d i n g L o o k u p ( X ) + P o s i t i o n a l E n c o d i n g X . s h a p e = = ( b a t c h _ s i z e , s e q _ l e n , e m b e d d i n g _ d i m ) X = EmbeddingLookup(X) + PositionalEncoding \\ X.shape == (batch\_size, seq\_len, embedding\_dim) X=EmbeddingLookup(X)+PositionalEncodingX.shape==(batch_size,seq_len,embedding_dim)
2. 计算Q,K,V
Q = L i n e a r ( X ) = X W Q K = L i n e a r ( X ) = X W K V = L i n e a r ( X ) = X W V W = = ( e m b e d d i n g _ d i m , e m b e d d i n g _ d i m ) Q , K , V = = ( b a t c h _ s i z e , s e q _ l e n , e m b e d d i n g _ d i m ) Q = Linear(X) = XW_{Q} \\ K = Linear(X) = XW_{K} \\ V = Linear(X) = XW_{V} \\ \\ W == (embedding\_dim, embedding\_dim) \\ Q, K, V == (batch\_size, seq\_len, embedding\_dim) Q=Linear(X)=XWQK=Linear(X)=XWKV=Linear(X)=XWVW==(embedding_dim,embedding_dim)Q,K,V==(batch_size,seq_len,embedding_dim)
3. 处理多头
将最后一维(embedding_dim) 拆成h份,需要保证embedding_dim能够被h整除。每个tensor的最后两个维度表示一个头,QKV各自都有h个头,接下来需要把这些头分别进行计算
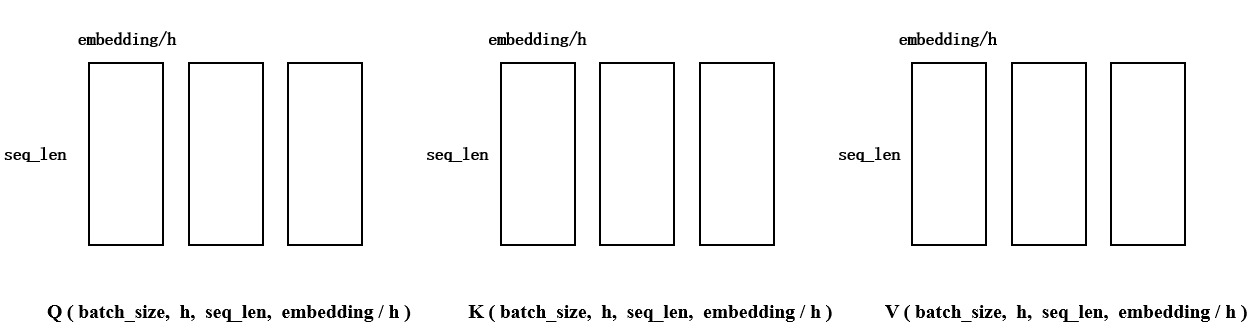
4. 计算
按顺序取出上图中的一组QKV,计算:
d = Q ⋅ K T (1) d = Q \cdot K^T \tag{1} d=Q⋅KT(1)
d = m a s k ( d ) (2) d = mask(d) \tag{2} d=mask(d)(2)
d = d / d k (3) d = d / d_k \tag{3} d=d/dk(3)
d = s o f t m a x ( d ) (4) d = softmax(d) \tag 4 d=softmax(d)(4)
-
(1)计算得到各个字之间的关系(相似度).这里的d的维度是
(batch_size, h, seq_len, embedding_dim) * (batch_size, h, embedding_dim, seq_len)==>(batch_size, h, seq_len, seq_len)。QKV分别有batch_size * h个矩阵,可以认为是在一个(batch_size, h)的棋盘中,每个位置放置了一个大小为(seq_len, embedding_dim)的矩阵。这里的前两个维度不变只是把棋盘中对应位置的矩阵拿出来做矩阵乘法,并把结果再放回到棋盘中。 -
(2)用mask矩阵遮盖掉超出句子长度的部分。将句子中用来pading的字符全部替换成 inf, 这样 计算softmax的时候它们的值会为0,就不会参与到接下来与V的计算当中
-
(3) d k d_k dk 是为了改变已经偏离的方差。我的理解是,由于矩阵转置后相乘会有很多内积运算,而内积运算将 d k d_k dk个数相加时会改变数据的分布。而这个分布的趋势是 m e a n = 0 , v a r i a n c e = d k mean=0, variance=d_k mean=0,variance=dk。为了使方差回归到1,把所有结果都除上一个 d k \sqrt{d_k} dk,这样求平方时会抵消已有的方差 d k d_k dk
# 均值为0,方差为1 a = np.random.randn(2,3000) b = np.random.randn(3000,2) c = a.dot(b) print(np.var(a)) print(np.mean(c)) print(np.var(c)) # 1.0262973662546435 # 25.625943965792157 # 1347.432397285718To illustrate why the dot products get large, assume that the components of q and k are independent random variables with > mean 0 and variance 1. Then their dot product, q ⋅ k = ∑ i = 1 d k q i k i q \cdot k=\sum_{i=1}^{d_{k}} q_{i} k_{i} q⋅k=∑i=1dkqiki, has mean 0 and variance dk.
-
(4)计算各个词义所占的比例 d ⋅ v d \cdot v d⋅v,按照权重融合了各个字的语义。最后将多个头的结果拼接成一个完成的embedding作为self-attendion的输出。
(batch_size, h, seq_len, seq_len)*batch_size, h, seq_len, embedding/h
部分代码如下:
# (batch, seq_len, h, embed/head) -> (batch, h, seq_len, embed/head)
q = self.qry(y).view(y.size(0), y.size(1), self.head, -1).transpose(1, 2)
k = self.key(x).view(x.size(0), x.size(1), self.head, -1).transpose(1, 2)
v = self.val(x).view(x.size(0), x.size(1), self.head, -1).transpose(1, 2)
d = torch.matmul(q, k.transpose(-2, -1)) / math.sqrt(k.size(-1)) # 相似度 (batch , h, seq, seq)
d = d.masked_fill(m, -float('inf')) # 把所有为true的地方替换成inf,这里是遮盖掉句子内部的pad
a = F.softmax(d, dim=-1) # (batch , h, seq, seq)
# (batch , h, seq_len, seq_len) * (batch, h, seq_len, embedding/h)
# => (batch, h, seq_len, embedding/h)
# => (batch, seq_len, h, embedding/h)
c = torch.matmul(a, v).transpose(1, 2)
# (batch, seq_len, embedding)
c = c.contiguous().view(c.size(0), c.size(1), -1)
结构图
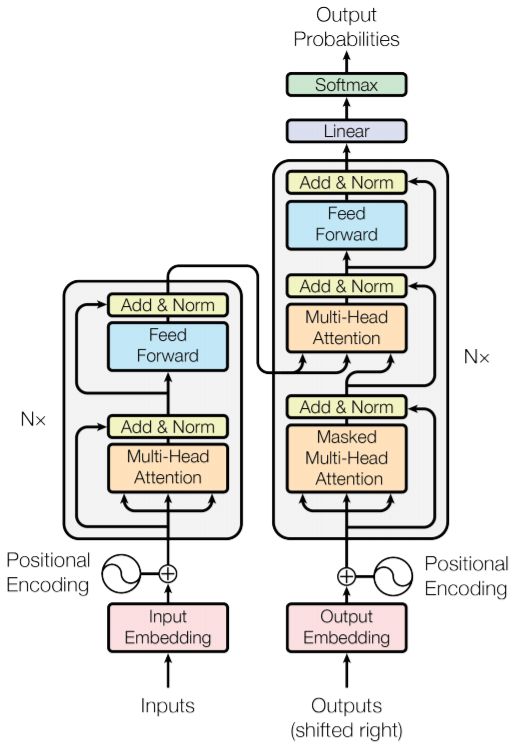
Encoder的完整过程:
1). 字向量与位置编码:
X = E m b e d d i n g L o o k u p ( X ) + P o s i t i o n a l E n c o d i n g (eq.2) X = EmbeddingLookup(X) + PositionalEncoding \tag{eq.2} X=EmbeddingLookup(X)+PositionalEncoding(eq.2)
X ∈ ( b a t c h _ s i z e ∗ s e q _ l e n ∗ e m b e d _ d i m ) X \in ({batch\_size * seq\_len * embed\_dim} ) X∈(batch_size∗seq_len∗embed_dim)
2). 自注意力机制:
Q = L i n e a r ( X ) = X W Q Q = Linear(X) = XW_{Q} Q=Linear(X)=XWQ
K = L i n e a r ( X ) = X W K (eq.3) K = Linear(X) = XW_{K} \tag{eq.3} K=Linear(X)=XWK(eq.3)
V = L i n e a r ( X ) = X W V V = Linear(X) = XW_{V} V=Linear(X)=XWV
X a t t e n t i o n = S e l f A t t e n t i o n ( Q , K , V ) (eq.4) X_{attention} = SelfAttention(Q, \ K, \ V) \tag{eq.4} Xattention=SelfAttention(Q, K, V)(eq.4)
3). 残差连接与 L a y e r N o r m a l i z a t i o n Layer \ Normalization Layer Normalization
X a t t e n t i o n = X + X a t t e n t i o n (eq. 5) X_{attention} = X + X_{attention} \tag{eq. 5} Xattention=X+Xattention(eq. 5)
X a t t e n t i o n = L a y e r N o r m ( X a t t e n t i o n ) (eq. 6) X_{attention} = LayerNorm(X_{attention}) \tag{eq. 6} Xattention=LayerNorm(Xattention)(eq. 6)
4). 两层线性映射并用激活函数激活, 比如说 R e L U ReLU ReLU:
X h i d d e n = L i n e a r ( A c t i v a t e ( L i n e a r ( X a t t e n t i o n ) ) ) (eq. 7) X_{hidden} = Linear(Activate(Linear(X_{attention}))) \tag{eq. 7} Xhidden=Linear(Activate(Linear(Xattention)))(eq. 7)
5). 重复3).:
X h i d d e n = X a t t e n t i o n + X h i d d e n X_{hidden} = X_{attention} + X_{hidden} Xhidden=Xattention+Xhidden
X h i d d e n = L a y e r N o r m ( X h i d d e n ) X_{hidden} = LayerNorm(X_{hidden}) Xhidden=LayerNorm(Xhidden)
X h i d d e n ∈ ( b a t c h _ s i z e ∗ s e q _ l e n . ∗ e m b e d _ d i m ) X_{hidden} \in ({batch\_size \ * \ seq\_len. \ * \ embed\_dim}) Xhidden∈(batch_size ∗ seq_len. ∗ embed_dim)
Decoder 的完整过程
1). 输入数据
-
输入y的embedding:
X = E m b e d d i n g L o o k u p ( X ) + P o s i t i o n a l E n c o d i n g X ∈ ( b a t c h _ s i z e ∗ s e q _ l e n ∗ e m b e d _ d i m ) X = EmbeddingLookup(X) + PositionalEncoding \\ X \in ({batch\_size * seq\_len * embed\_dim} ) X=EmbeddingLookup(X)+PositionalEncodingX∈(batch_size∗seq_len∗embed_dim) -
encoder层的输出
h = e n c o d e r ( x ) h ∈ ( b a t c h _ s i z e ∗ s e q _ l e n ∗ e m b e d _ d i m ) h = encoder(x) \\ h \in (batch\_size * seq\_len * embed\_dim) h=encoder(x)h∈(batch_size∗seq_len∗embed_dim) -
mx: x的mask;遮盖住pad的部分,替换为inf,这样计算softmax就会变成0,不会影响后面的计算
def get_pad(self, x): """ 根据句子的实际长度获取句子的句子的mask。用于计算attention的mask,它不是对角矩阵 维度是 (batch, head, seq_len, seq_len) :param x: :return: mask (batch, head, seq_len, seq_len) """ seq_len = x.size(1) pad = (x == 0) for _ in range(2): pad = torch.unsqueeze(pad, dim=1) return pad.repeat(1, self.head, seq_len, 1) -
my: y的mask;用于mask-self-attention,先经过和x的一样的mask过程,再用对角矩阵进行mask,这样在进行训练的时候,只能看到当前字和当前字之前的字。这里的mask是一个对角矩阵,它的形状类似下面这样:
torch.triu(torch.ones(seq_len, seq_len).byte(), diagonal=1) # [0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1], # [0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1], # [0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1], # [0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1], # [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1], # [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1], # [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1], # [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1], # [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1], # [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]def get_att(head: int, seq_len: int): """ 计算mask self attention的mask,对角矩阵 :param head: int :param seq_len: int :return: """ # 上三角矩阵, 不保留对角线 att = torch.triu(torch.ones(seq_len, seq_len).byte(), diagonal=1) for _ in range(2): # torch.squeeze() 删掉维度为1的维度:(1,3)==> (3) # torch.unsqueeze() 扩充维度,在指定位置加上维数为1的维度:(3)==> (1,3) att = torch.unsqueeze(att, dim=0) # 像瓦片一样平铺 return att.repeat(1, head, 1, 1)
2). 多层 decoder Layer结构
-
mask-self-attention + 残差 + LayerNorm; y经过mask之后含义已经改变,每一行表示当前词和之前的语义,表示的是某一时刻的可以获得的语义。比如0时刻只能获得第一个单词的语义,而第二个时刻可以获得前两个单词的语义。
mask_self_attention得到的结果,每一行就是一个时刻包含的语义关系,表示我当前已经翻译出的单词的语义。
y 0 = m a s k _ s e l f _ a t t e n t i o n ( y , y , m y ) y = L a y e r N o r m ( y + r ) y_0 = mask\_self\_attention(y, y, my) \\ y = LayerNorm(y + r) y0=mask_self_attention(y,y,my)y=LayerNorm(y+r) -
self-attention + 残差 + LayerNorm,这里每一层decoder layer的数据都来自encoder的输出x,x经过变换生成K,V,用当前的y计算得到Q。然后计算Q和K的相似度再应用到V上就是结果; 这里的 Q y , K x , V x Q_y, K_x, V_x Qy,Kx,Vx就类似于seq2seq中的attention,把每个时刻的y和所有的x进行内积运算,找到每个x的权重再从所有的x中抽取需要的信息。一个 Q y Q_y Qy已经包含了decoder中的所有时刻。最后得到的结果表示的是,每个时刻应该从encoder中抽取哪些信息。 y 0 y_0 y0的shape是
(batch_size, h, seq_len, embedding/h).
y 0 = s e l f _ a t t e n t i o n ( x , y , m x ) y = L a y e r N o r m ( y + r ) y_0 = self\_attention(x, y, mx) \\ y = LayerNorm(y + r) y0=self_attention(x,y,mx)y=LayerNorm(y+r) -
激活层:
y 0 = L i n e a r ( A c t i v a t e ( L i n e a r ( y ) ) ) y = L a y e r N o r m ( y 0 + y ) y_{0} = Linear(Activate(Linear(y))) \\ y = LayerNorm(y_0 + y) y0=Linear(Activate(Linear(y)))y=LayerNorm(y0+y)
class DecodeLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, embed_len, head):
super(DecodeLayer, self).__init__()
self.head = head
self.qrys = nn.ModuleList([nn.Linear(embed_len, embed_len / head) for _ in range(2)])
self.keys = nn.ModuleList([nn.Linear(embed_len, embed_len / head) for _ in range(2)])
self.vals = nn.ModuleList([nn.Linear(embed_len, embed_len / head) for _ in range(2)])
self.lal = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(embed_len, embed_len),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(embed_len, embed_len))
self.lns = nn.ModuleList([nn.LayerNorm(embed_len) for _ in range(3)])
def mul_att(self, x, y, m, i):
# q (batch, seq_len, head, embed/head) -> (batch, head, seq_len, embed/head)
q = self.qrys[i](y).view(y.size(0), y.size(1), self.head, -1).transpose(1, 2)
k = self.keys[i](x).view(x.size(0), x.size(1), self.head, -1).transpose(1, 2)
v = self.vals[i](x).view(x.size(0), x.size(1), self.head, -1).transpose(1, 2)
# (batch, head, seq_len, embed/head)
d = torch.matmul(q, k.transpose(-2, -1)) / math.sqrt(k.size(-1))
d = d.masked_fill(m, -float('inf'))
a = F.softmax(d, dim=-1)
# (batch , h, seq_len, seq_len) * (batch, h, seq_len, embedding/h)
# => (batch, h, seq_len, embedding/h)
# => (batch, seq_len, h, embedding/h)
c = torch.matmul(a, v).transpose(1, 2)
c = c.contiguous().view(c.size(0), c.size(1), -1)
return c
def forward(self, y, x, my, mx):
"""
:param y: 带上positional encoder的embedding。 (batch, seq_len, embedding)
:param x: encoder的输出 (batch, seq_len, embedding)
:param my: y 的mask (batch, head, seq_len, seq_len)
:param mx: x 的mask (batch, head, seq_len, seq_len)
:return:
"""
r = y # 暂时保存用于计算残差网络
y = self.mul_att(y, y, my, 0)
y = self.lns[0](y + r)
r = y
y = self.mul_att(x, y, mx, 1)
y = self.lns[1](y + r)
r = y
y = self.lal(y)
return self.lns[2](y + r)
3)输出:
y = L i n e a r ( y ) l o g i t s = s o f t m a x ( y ) y = Linear(y) \\ logits = softmax(y) y=Linear(y)logits=softmax(y)