matplotlib —— 注释及几何图形的绘制
可视化——matplotlib常用api(一)
可视化——matploblib常见api(二)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
t = np.arange(0, 5, .01)
y = np.cos(2*np.pi*t)
line, = ax.plot(t, y, lw=2)
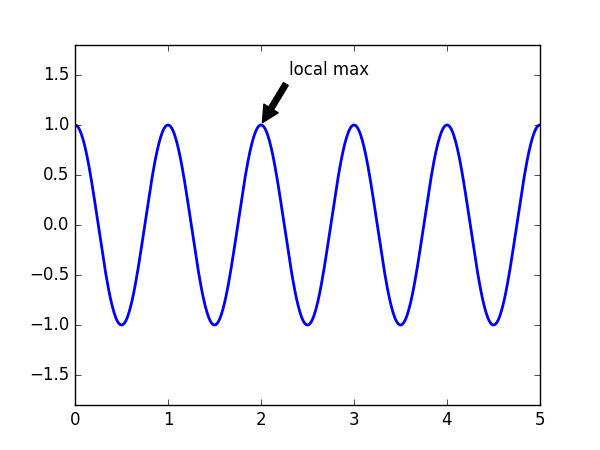
1. Annotating text
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
def main():
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
t = np.arange(0, 5, .01)
y = np.cos(2*np.pi*t)
line, = ax.plot(t, y, lw=2)
ax.set_ylim([-2+.2, 2-.2])
ax.annotate('local max', xy=(3, 0), xytext=(3.5, 1.5), arrowprops=dict(facecolor='k', shrink=.05))
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
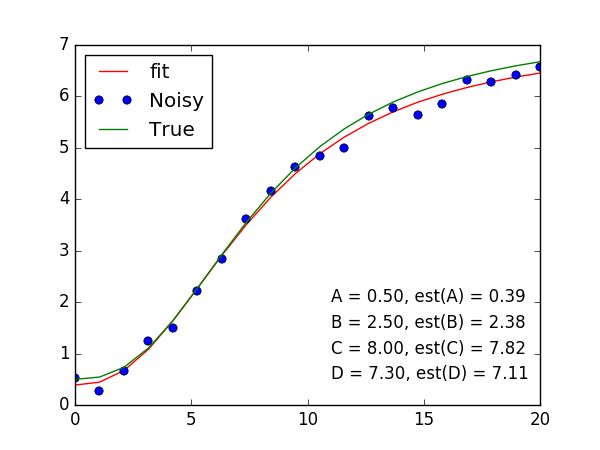
2. 有规律的在figure中写东西
规律自然用到循环;
for i, (param, true, est) in enumerate(zip('ABCD', [A, B, C, D], plesq[0])):
plt.text(10, 3-i*.5, '{} = {:.2f}, est({}) = {:.2f}'.format(param, true, param, est))
# text的前两个参数是需要根据图像的布局反复调整的
3. 画圆(矩形、椭圆)
from matploblib.patches import Cicle, Ellipse
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ell1 = Ellipse(xy=(.0, .0), width=4, height=8, angle=30, facecolor='y', alpha=.3)
cir1 = Circle(xy=(.0, .0), radius=2, alpha=.4)
# alpha的设置很重要,否则画出来的图会很丑
ax.add_patch(ell1)
ax.add_patch(cir1)
x, y = 0, 0
ax.plot(x, y, 'ro')
ax.axis('scaled')
plt.show()
4. 饼状图
- plt.pie():Python数据可视化:饼状图
5. 三角形
- 描点连线,起点和终点相同
triangle1 = ((0, sqrt(3)/2), (1, 3*sqrt(3)/2), (2, sqrt(3)/2), (0, sqrt(3)/2))
triangle2 = ((0, sqrt(3)), (1, 0), (2, sqrt(3)), (0, sqrt(3)))
plt.plot([e[0] for e in triangle1], [e[1] for e in triangle1],
[e[0]for e in triangle2], [e[1] for e in triangle2], 'b', lw=3)