HDU 1392 入门水题凸包问题+叉乘讲解(Grahan Scan)
Surround the Trees
There are a lot of trees in an area. A peasant wants to buy a rope to surround all these trees. So at first he must know the minimal required length of the rope. However, he does not know how to calculate it. Can you help him?
The diameter and length of the trees are omitted, which means a tree can be seen as a point. The thickness of the rope is also omitted which means a rope can be seen as a line.
There are no more than 100 trees.
Input
The input contains one or more data sets. At first line of each input data set is number of trees in this data set, it is followed by series of coordinates of the trees. Each coordinate is a positive integer pair, and each integer is less than 32767. Each pair is separated by blank.
Zero at line for number of trees terminates the input for your program.
Output
The minimal length of the rope. The precision should be 10^-2.
Sample Input
9
12 7
24 9
30 5
41 9
80 7
50 87
22 9
45 1
50 7
0 Sample Output
243.06题目大意:有n个坐标,你需要将这些点全部圈起来,然后求最后的最小周长
明显的一个凸包问题,先说一说什么是凸包吧:转载:https://www.cnblogs.com/aiguona/p/7232243.html
一.概念:
凸包(Convex Hull)是一个计算几何(图形学)中的概念。
在一个实数向量空间V中,对于给定集合X,所有包含X的凸集的交集S被称为X的凸包。
X的凸包可以用X内所有点(X1,...Xn)的线性组合来构造.
在二维欧几里得空间中,凸包可想象为一条刚好包著所有点的橡皮圈。
用不严谨的话来讲,给定二维平面上的点集,凸包就是将最外层的点连接起来构成的凸多边型,它能包含点集中所有的点。
例子:假设平面上有p0~p12共13个点,过某些点作一个多边形,使这个多边形能把所有点都“包”起来。当这个多边形是凸多边形的时候,我们就叫它“凸包”。如下图: ![]()
二.解法:
Graham扫描法
时间复杂度:O(n㏒n)
思路:Graham扫描的思想是先找到凸包上的一个点,然后从那个点开始按逆时针方向逐个找凸包上的点,实际上就是进行极角排序,然后对其查询使用。 ![]()
步骤:
- 把所有点放在二维坐标系中,则纵坐标最小的点一定是凸包上的点,如图中的P0。
- 把所有点的坐标平移一下,使 P0 作为原点,如上图。
- 计算各个点相对于 P0 的幅角 α ,按从小到大的顺序对各个点排序。当 α 相同时,距离 P0 比较近的排在前面。例如上图得到的结果为 P1,P2,P3,P4,P5,P6,P7,P8。我们由几何知识可以知道,结果中第一个点 P1 和最后一个点 P8 一定是凸包上的点。
(以上是准备步骤,以下开始求凸包)
以上,我们已经知道了凸包上的第一个点 P0 和第二个点 P1,我们把它们放在栈里面。现在从步骤3求得的那个结果里,把 P1 后面的那个点拿出来做当前点,即 P2 。接下来开始找第三个点: - 连接P0和栈顶的那个点,得到直线 L 。看当前点是在直线 L 的右边还是左边。如果在直线的右边就执行步骤5;如果在直线上,或者在直线的左边就执行步骤6。
- 如果在右边,则栈顶的那个元素不是凸包上的点,把栈顶元素出栈。执行步骤4。
- 当前点是凸包上的点,把它压入栈,执行步骤7。
- 检查当前的点 P2 是不是步骤3那个结果的最后一个元素。是最后一个元素的话就结束。如果不是的话就把 P2 后面那个点做当前点,返回步骤4。
最后,栈中的元素就是凸包上的点了。
以下为用Graham扫描法动态求解的过程: ![]()
下面静态求解过程
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
这里还涉及到叉乘的概念:(三维)
向量的叉乘,即求同时垂直两个向量的向量,即c垂直于a,同时c垂直于b(a与c的夹角为90°,b与c的夹角为90°)
c = a×b = (a.y*b.z-b.y*a.z , b.x*a.z-a.x*b.z , a.x*b.y-b.x*a.y)
叉乘还需要注意的一点就是方向的问题,其中包含正旋转,还有负旋转,这个概念就是求凸包的关键:转载https://blog.csdn.net/keng_s/article/details/52131673
如果k>0时,那么a正旋转到b的角度为<180°,如果k<0,那么a正旋转到b的角度为>180°,如果k=0 那么a,b向量平行
一般的来讲大家喜欢称旋转为正时针旋转,或者逆时针旋转,例如我让一个点绕圆心旋转90°,大家都会理解为逆时针吧这个点旋转90°,实际上这个说法是存在漏洞和错误的,
当我们的坐标系不使用左手坐标系时这个说法是错误的,所以在此定义 一个正旋转。
即,2d中,坐标轴,x轴朝y轴方向旋转90°和y轴重合的方向视为正旋转。(通俗的来讲就是x轴旋转到y轴只需要旋转90°,那么这个旋转就是正旋转)
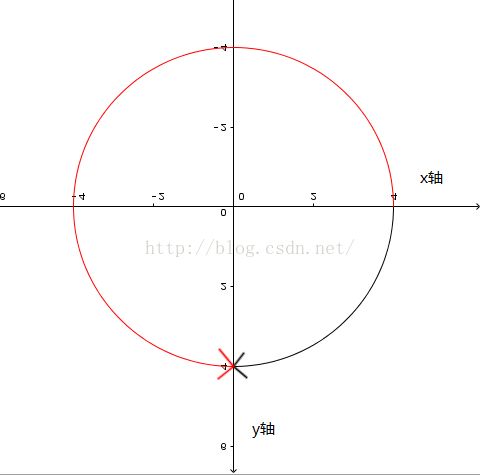
下图黑色旋转方向就是正旋转,红色就是负旋转。
如上定义之后就不会有歧义性的问题,例如计算机图形使用的坐标系一般都是y的正方向朝下,如下图
就如同这个图,如果还按照顺逆时针去说明旋转那么很明显是错误的,所以需要一个通用且没有歧义的正旋转定义。
然后就可以套模板了:
#include
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1005;
#define rep(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<=b;i++)
struct node
{
double x, y;
bool operator<(const node &a) const{
if(a.y==y)
return a.x>x;
return a.y>y;
}
}num[maxn];
node p0;
int n;
double dis(node a,node b)
{
double ans1=(a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)*1.0;
double ans2=(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y)*1.0;
return sqrt(ans1+ans2);
}
int coss(node p,node a,node b)
{
return (a.x-p.x)*(b.y-p.y)-(b.x-p.x)*(a.y-p.y);
}
bool cmp(node a,node b)
{
int t=coss(p0,a,b);
if(t>0) return 1;//叉乘大于0,就可以说a这个点在b的顺时针处,就是a的角度小于b的(从x轴正向)
if(t==0&&(dis(p0,a)-dis(p0,b))<=0) return 1;//平行的话,那将距离从小到大排序
else
return 0;
}
bool cmp1(node a,node b){
if(a.y==b.y) return a.x=0,等于0就是重合了,也需要换掉,因为
//一开始已经将num极角排序了,因此后面的点一定是最优的。
while(tot>=2&&coss(num[point[tot-1]],num[point[tot]],num[i])<=0) tot--;
point[++tot]=i;
}
}
int main()
{
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF,n)
{
memset(num,0,sizeof num);memset(point,0,sizeof point);
tot=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%lf %lf",&num[i].x,&num[i].y);
if(n==1) {printf("0.00\n");continue;}
if(n==2) {printf("%.2f\n",dis(num[1],num[2]));continue;}
sort(num+1,num+1+n);
p0=num[1];//找到一个最小值点
sort(num+2,num+1+n,cmp);//第一个点不需要排
graham(n);
double ans=0;
rep(i,2,tot)
ans+=dis(num[point[i]],num[point[i-1]]);
ans+=dis(num[point[1]],num[point[tot]]);
printf("%.2f\n",ans);
}
}
对于某些题目,凸包的排序最重要的就是极角排序,剩下的就是一些细节性的地方,起点不一定就是y最小的地方,比如可以看一下求上凸包和下凸包时的起点是根据x的坐标排序的