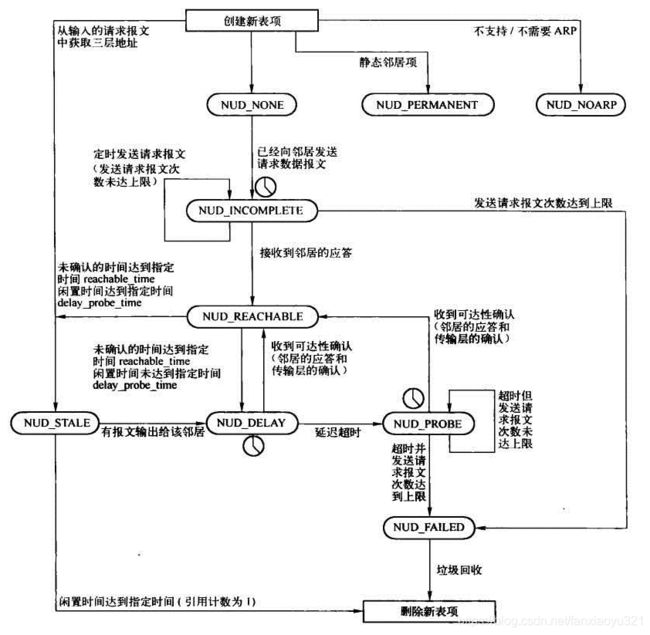
邻居子系统之邻居项状态更新
邻居项一旦创建,邻居子系统就按照状态机来管理它的生命周期,状态机的实现核心是定时器。
| 名称 | 值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| NUD_NONE | 0x00 | 邻居项新建后的状态,此时还没有有效的映射信息,如果需要可以启动可达性确认过程 |
| NUD_INCOMPLETE | 0x01 | solicitations请求已经发送,正在解析该邻居地址 |
| NUD_REACHABLE | 0x02 | |
| NUD_STALE | 0x04 | 邻居项有映射地址,但是该地址已经有一段时间没有使用了,如果要使用需要启动可达性确认,但不是立即确认,而是延时一段时间再确认,在这段延时期内该邻居项保存的映射关系依然有效 |
| NUD_DELAY | 0x08 | NUD_STALE启动可达性延时确认后迁移到该状态 |
| NUD_PROBE | 0x10 | NUD_DELAY超时后,开始发送solicitations请求后迁移到该状态 |
| NUD_FAILED | 0x20 | 地址解析失败或者可达性验证失败后设置为该状态,该状态下邻居项将会被删除 |
| NUD_NOARP | 0x40 | 无需做地址映射,直接发送数据包即可,也是一种有效状态 |
| NUD_PERMANENT | 0x80 | 邻居项永久有效,在用户空间通过命令创建的邻居项属于该状态 |
其中NUD_PERMANENT和NUD_NOARP状态一旦设定后就不能再更改。
此外,还定义了一些上述状态的组合,使得程序更加的简洁:
// 这些状态下都会启动状态更新定时器
#define NUD_IN_TIMER (NUD_INCOMPLETE | NUD_REACHABLE | NUD_DELAY | NUD_PROBE)
#define NUD_VALID (NUD_PERMANENT | NUD_NOARP | NUD_REACHABLE | NUD_PROBE | NUD_STALE | NUD_DELAY)
// 连接态,这些状态下邻居项的映射关系可用(包括根本无需映射)
#define NUD_CONNECTED (NUD_PERMANENT | NUD_NOARP | NUD_REACHABLE)
下面分析上图中典型的状态转移。
NUD_NONE–>NUD_INCOMPLETE
当L3协议查询路由后,确定了出口网络设备和下一跳L3地址时,如果需要会先新建一个邻居项,然后将数据包交给邻居子系统,由邻居子系统继续数据包的发送流程。
邻居子系统根据自己当前的输出函数继续发送数据包,往往会调用neigh_event_send()来处理邻居协议相关的逻辑。
neigh_envent_send()
neigh_envent_send()根据当前邻居项所处状态决定是否要发送solicitations请求报文
// 返回0表示邻居项有效,直接发送skb即可;返回非0表示邻居项的可达性正在验证或者邻居地址正在解析,skb
// 已经被放入队列,调用者无需继续处理该skb
static inline int neigh_event_send(struct neighbour *neigh, struct sk_buff *skb)
{
neigh->used = jiffies;
// 下面三种状态邻居项是有效的,不需要发送solicitations请求报文
if (!(neigh->nud_state & (NUD_CONNECTED | NUD_DELAY | NUD_PROBE)))
return __neigh_event_send(neigh, skb);
return 0;
}
int __neigh_event_send(struct neighbour *neigh, struct sk_buff *skb)
{
int rc;
unsigned long now;
write_lock_bh(&neigh->lock);
rc = 0;
// 这三种状态要么不需要发送、要么延迟发送、要么已经发送Solicitations请求报文
if (neigh->nud_state & (NUD_CONNECTED | NUD_DELAY | NUD_PROBE))
goto out_unlock_bh;
now = jiffies;
if (!(neigh->nud_state & (NUD_STALE | NUD_INCOMPLETE))) { // 需要解析邻居地址
// mcast_probes指定了为了解析一个邻居地址,可以发出的多播(或者广播)solicitations请求的数量,
// 当可达性由用户态程序(如ARPD)控制时,该参数指定了用户态可以发送的solicitations请求的数量,
// 这里是内核态,不知为何会判断app_probes
if (neigh->parms->mcast_probes + neigh->parms->app_probes) {
// 初始化neigh->probes,指定solicitations请求发送次数
atomic_set(&neigh->probes, neigh->parms->ucast_probes);
// 迁移状态为NUD_INCOMPLETE
neigh->nud_state = NUD_INCOMPLETE;
neigh->updated = jiffies;
// 启动定时器,solicitations请求是再定时器函数中发送的,定时器函数是立即执行的(now+1)
neigh_add_timer(neigh, now + 1);
} else {
// 配置的solicitations请求次数为0,直接设置为NUD_FAILED状态,并且丢弃skb,返回非0,
// 这种请求skb将无法被发送。这种个人理解应该是配置有误
neigh->nud_state = NUD_FAILED;
neigh->updated = jiffies;
write_unlock_bh(&neigh->lock);
if (skb)
kfree_skb(skb);
return 1;
}
} else if (neigh->nud_state & NUD_STALE) { // 需要验证邻居的可达性
NEIGH_PRINTK2("neigh %p is delayed.\n", neigh);
// 更新状态为NUD_DELAY,启动定时器验证地址的可达性
neigh->nud_state = NUD_DELAY;
neigh->updated = jiffies;
neigh_add_timer(neigh, jiffies + neigh->parms->delay_probe_time);
}
// NUD_INCOMPLETE状态下,正在解析邻居地址,skb需要先缓存
if (neigh->nud_state == NUD_INCOMPLETE) {
if (skb) {
// 可见,当队列达到上限时,会丢弃最老的skb,然后将新的skb加入队列
if (skb_queue_len(&neigh->arp_queue) >= neigh->parms->queue_len) {
struct sk_buff *buff;
buff = neigh->arp_queue.next;
__skb_unlink(buff, &neigh->arp_queue);
kfree_skb(buff);
}
__skb_queue_tail(&neigh->arp_queue, skb);
}
// 修改返回值为非0,表示数据包没有被真的发送
rc = 1;
}
out_unlock_bh:
write_unlock_bh(&neigh->lock);
return rc;
}
状态更新定时器: neigh_timer_handler()
在邻居项创建时,见neigh_alloc(),为邻居项初始化了状态更新定时器neigh_timer_handler()。该定时器是邻居项状态维护的核心。
/* Called when a timer expires for a neighbour entry. */
static void neigh_timer_handler(unsigned long arg)
{
unsigned long now, next;
struct neighbour *neigh = (struct neighbour *)arg;
unsigned state;
int notify = 0;
write_lock(&neigh->lock);
state = neigh->nud_state;
now = jiffies;
next = now + HZ;
// 状态合法性检查
if (!(state & NUD_IN_TIMER)) {
#ifndef CONFIG_SMP
printk(KERN_WARNING "neigh: timer & !nud_in_timer\n");
#endif
goto out;
}
if (state & NUD_REACHABLE) {
if (time_before_eq(now, neigh->confirmed + neigh->parms->reachable_time)) {
NEIGH_PRINTK2("neigh %p is still alive.\n", neigh);
next = neigh->confirmed + neigh->parms->reachable_time;
} else if (time_before_eq(now, neigh->used + neigh->parms->delay_probe_time)) {
NEIGH_PRINTK2("neigh %p is delayed.\n", neigh);
neigh->nud_state = NUD_DELAY;
neigh->updated = jiffies;
neigh_suspect(neigh);
next = now + neigh->parms->delay_probe_time;
} else {
NEIGH_PRINTK2("neigh %p is suspected.\n", neigh);
neigh->nud_state = NUD_STALE;
neigh->updated = jiffies;
neigh_suspect(neigh);
notify = 1;
}
} else if (state & NUD_DELAY) {
if (time_before_eq(now, neigh->confirmed + neigh->parms->delay_probe_time)) {
NEIGH_PRINTK2("neigh %p is now reachable.\n", neigh);
neigh->nud_state = NUD_REACHABLE;
neigh->updated = jiffies;
neigh_connect(neigh);
notify = 1;
next = neigh->confirmed + neigh->parms->reachable_time;
} else {
NEIGH_PRINTK2("neigh %p is probed.\n", neigh);
neigh->nud_state = NUD_PROBE;
neigh->updated = jiffies;
atomic_set(&neigh->probes, 0);
next = now + neigh->parms->retrans_time;
}
} else {
/* NUD_PROBE | NUD_INCOMPLETE */
// 下一次solicitations请求报文的重试超时时间
next = now + neigh->parms->retrans_time;
}
// cond1: INCOMPLETE和PROBE两个状态下需要对路由项的有效性进行验证
// cond2: solicitations请求发送次数已经超过了上限
if ((neigh->nud_state & (NUD_INCOMPLETE | NUD_PROBE)) &&
atomic_read(&neigh->probes) >= neigh_max_probes(neigh))
{
// solicitations请求报文的发送次数已经超过了最大限制,地址解析失败(可达性验证失败)
struct sk_buff *skb;
// 更新为NUD_FAILED状态
neigh->nud_state = NUD_FAILED;
neigh->updated = jiffies;
notify = 1; // 设置通知标记位
NEIGH_CACHE_STAT_INC(neigh->tbl, res_failed);
NEIGH_PRINTK2("neigh %p is failed.\n", neigh);
/* It is very thin place. report_unreachable is very complicated
routine. Particularly, it can hit the same neighbour entry!
So that, we try to be accurate and avoid dead loop. --ANK
*/
// 清空该邻居项的skb缓存队列,并向外发送error_report()
while (neigh->nud_state == NUD_FAILED && (skb = __skb_dequeue(&neigh->arp_queue)) != NULL) {
write_unlock(&neigh->lock);
neigh->ops->error_report(neigh, skb);
write_lock(&neigh->lock);
}
// 删除队列中的skb
skb_queue_purge(&neigh->arp_queue);
}
// 根据需要重新启动定时器,间隔不短于0.5s
if (neigh->nud_state & NUD_IN_TIMER) {
if (time_before(next, jiffies + HZ/2))
next = jiffies + HZ/2;
if (!mod_timer(&neigh->timer, next))
neigh_hold(neigh);
}
// 发送solicitations请求报文
if (neigh->nud_state & (NUD_INCOMPLETE | NUD_PROBE)) {
struct sk_buff *skb = skb_peek(&neigh->arp_queue);
/* keep skb alive even if arp_queue overflows */
if (skb)
skb = skb_copy(skb, GFP_ATOMIC);
write_unlock(&neigh->lock);
neigh->ops->solicit(neigh, skb); // 对于ARP是arp_solicit()
atomic_inc(&neigh->probes);
if (skb)
kfree_skb(skb);
} else {
out:
write_unlock(&neigh->lock);
}
// 如上,如果邻居项状态被设置为NUD_FAILED,那么需要对外通知这一事件(用户态和内核通知链)
if (notify)
neigh_update_notify(neigh);
neigh_release(neigh);
}
邻居项状态更新: neigh_update()
/* Generic update routine.
-- lladdr is new lladdr or NULL, if it is not supplied.
-- new is new state.
-- flags
NEIGH_UPDATE_F_OVERRIDE allows to override existing lladdr,
if it is different.
NEIGH_UPDATE_F_WEAK_OVERRIDE will suspect existing "connected"
lladdr instead of overriding it
if it is different.
It also allows to retain current state
if lladdr is unchanged.
NEIGH_UPDATE_F_ADMIN means that the change is administrative.
NEIGH_UPDATE_F_OVERRIDE_ISROUTER allows to override existing
NTF_ROUTER flag.
NEIGH_UPDATE_F_ISROUTER indicates if the neighbour is known as
a router.
Caller MUST hold reference count on the entry.
*/
int neigh_update(struct neighbour *neigh, const u8 *lladdr, u8 new, u32 flags)
{
u8 old;
int err;
int notify = 0;
struct net_device *dev;
int update_isrouter = 0;
write_lock_bh(&neigh->lock);
dev = neigh->dev;
old = neigh->nud_state;
err = -EPERM;
// 只有管理员能够更新状态为NOARP、和PERMANENT的邻居项
if (!(flags & NEIGH_UPDATE_F_ADMIN) && (old & (NUD_NOARP | NUD_PERMANENT)))
goto out;
// 新的状态为非法状态,清理该邻居项的状态
if (!(new & NUD_VALID)) {
neigh_del_timer(neigh);
if (old & NUD_CONNECTED)
neigh_suspect(neigh);
neigh->nud_state = new;
err = 0;
notify = old & NUD_VALID;
goto out;
}
/* Compare new lladdr with cached one */
if (!dev->addr_len) {
/* First case: 通过该网络设备通信不需要L2地址,用邻居项中的保存的L2地址,一般也是空. */
lladdr = neigh->ha;
} else if (lladdr) {
/* The second case: if something is already cached
and a new address is proposed:
- compare new & old
- if they are different, check override flag
*/
if ((old & NUD_VALID) && !memcmp(lladdr, neigh->ha, dev->addr_len))
lladdr = neigh->ha;
} else {
/* No address is supplied; if we know something,
use it, otherwise discard the request.
*/
err = -EINVAL;
if (!(old & NUD_VALID))
goto out;
lladdr = neigh->ha;
}
// 邻居项有效,记录确认时间戳
if (new & NUD_CONNECTED)
neigh->confirmed = jiffies;
neigh->updated = jiffies;
/* If entry was valid and address is not changed,
do not change entry state, if new one is STALE.
*/
err = 0;
update_isrouter = flags & NEIGH_UPDATE_F_OVERRIDE_ISROUTER;
// 原来邻居项状态有效,需要根据标记来确定是否更新L2地址
if (old & NUD_VALID) {
if (lladdr != neigh->ha && !(flags & NEIGH_UPDATE_F_OVERRIDE)) {
update_isrouter = 0;
if ((flags & NEIGH_UPDATE_F_WEAK_OVERRIDE) && (old & NUD_CONNECTED)) {
lladdr = neigh->ha;
new = NUD_STALE;
} else
goto out;
} else {
if (lladdr == neigh->ha && new == NUD_STALE &&
((flags & NEIGH_UPDATE_F_WEAK_OVERRIDE) || (old & NUD_CONNECTED)))
new = old;
}
}
// 新旧状态不同,更新状态,并且根据需要重新启动状态更新定时器
if (new != old) {
neigh_del_timer(neigh);
if (new & NUD_IN_TIMER)
neigh_add_timer(neigh, (jiffies + ((new & NUD_REACHABLE) ? neigh->parms->reachable_time : 0)));
neigh->nud_state = new;
}
// 更新L2地址
if (lladdr != neigh->ha) {
memcpy(&neigh->ha, lladdr, dev->addr_len);
neigh_update_hhs(neigh);
if (!(new & NUD_CONNECTED))
neigh->confirmed = jiffies - (neigh->parms->base_reachable_time << 1);
notify = 1;
}
if (new == old)
goto out;
// 更新ops操作函数集
if (new & NUD_CONNECTED)
neigh_connect(neigh);
else
neigh_suspect(neigh);
// 如果邻居项原来时非法状态,那么尝试发送队列中的skb
if (!(old & NUD_VALID)) {
struct sk_buff *skb;
/* Again: avoid dead loop if something went wrong */
while (neigh->nud_state & NUD_VALID && (skb = __skb_dequeue(&neigh->arp_queue)) != NULL) {
struct neighbour *n1 = neigh;
write_unlock_bh(&neigh->lock);
/* On shaper/eql skb->dst->neighbour != neigh :( */
if (skb->dst && skb->dst->neighbour)
n1 = skb->dst->neighbour;
n1->output(skb);
write_lock_bh(&neigh->lock);
}
skb_queue_purge(&neigh->arp_queue);
}
out:
if (update_isrouter) {
neigh->flags = (flags & NEIGH_UPDATE_F_ISROUTER) ?
(neigh->flags | NTF_ROUTER) :
(neigh->flags & ~NTF_ROUTER);
}
write_unlock_bh(&neigh->lock);
if (notify)
neigh_update_notify(neigh);
return err;
}