Android getWidth和getMeasuredWidth的理解
前段时间了解了getWidth和getMeasuredWidth区别,有一段时间不看发现具体还又有些遗忘,所以在此还是要记下来,俗话说,好记性不如烂笔头,俗话诚不欺我。
首先,先来个图吧,下图为我从http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_6e519585010152s5.html博客拷贝过来的一个图片,又是拿来主义了,在此非常感谢博主分享。
一定要注意:此处的getheight是在布局中的view,即view的父布局必须是个layout。下面继续引用:
Google文档的英文说明:
getWidth():
Return the width of the your view.
Returns: the width of your view, in pixels
getMeasuredWidth():
The width of this view as measured in the most recent call to measure(). This should be used during measurement and layout calculations only. Use getWidth() to see how wide a view is after layout.
Returns: the measured width of this view
前提知识点:
1. 在一个类初始化时,即在构造函数当中是得不到View的实际大小的(这个我测试过,的确)。大家可以试试,getWidth()和getMeasuredWidth()得到的结果都是0,但是可以从onDraw()方法或者dispatchDraw()方法里面获得。可以通过调用invalidate()来执行onDraw()和dispatchDraw()方法。
2. 这两个方法所得到的结果的单位是像素即pixel
正确的理解:
getWidth(): View在设定好布局后,整个View的宽度
getMeasuredWidth():对View上的内容进行测量后得到的View内容占据的宽度。前提是你必须在父布局的onLayout()方法或者此View的onDraw()方法里调用measure(0,0);(measure参数的值可以知己定义),否则得到的结果和getWidth()得到的结果是一样的。
这两个方法最主要的区别在于,是否使用了measure()方法,同时measure()使用的位置也很重要。
getHeight() 和 get MeasuredHeight() 区别同理。
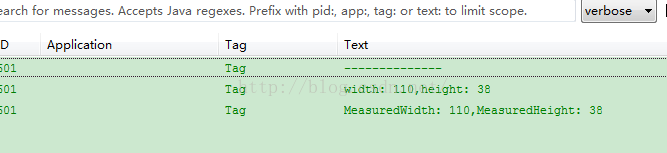
好了,图片直观展示有了,文字描述也有了,下面该上代码了。public class MainActivity extends ActionBarActivity {
private LinearLayout mBackgroundLayout;
private TextViewTest mTextViewTest;
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
mBackgroundLayout = new MyLayout(this);
mBackgroundLayout.setLayoutParams(new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(
500,
500));
mTextViewTest = new TextViewTest(this);
mBackgroundLayout.addView(mTextViewTest);
setContentView(mBackgroundLayout);
}
public class MyLayout extends LinearLayout{
public MyLayout(Context context) {
super(context);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);
Log.i("Tag", "--------------");
View mView=getChildAt(0);
mView.measure(0, 0);
}
}
public class TextViewTest extends TextView {
public TextViewTest(Context context) {
super(context);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
setText("test test ");
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onDraw(canvas);
// measure(0, 0);
Log.i("Tag", "width: " + getWidth() + ",height: " + getHeight());
Log.i("Tag", "MeasuredWidth: " + getMeasuredWidth()
+ ",MeasuredHeight: " + getMeasuredHeight());
}
}
}下面在稍微改动一下,代码如下:
public class MainActivity extends ActionBarActivity {
private LinearLayout mBackgroundLayout;
private TextViewTest mTextViewTest;
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
mBackgroundLayout = new MyLayout(this);
mBackgroundLayout.setLayoutParams(new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(
LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT,
LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT));
mTextViewTest = new TextViewTest(this);
mBackgroundLayout.addView(mTextViewTest);
setContentView(mBackgroundLayout);
}
public class MyLayout extends LinearLayout{
public MyLayout(Context context) {
super(context);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);
Log.i("Tag", "--------------");
View mView=getChildAt(0);
mView.measure(0, 0);
}
}
public class TextViewTest extends TextView {
public TextViewTest(Context context) {
super(context);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
setText("test test ");
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onDraw(canvas);
// measure(0, 0);
Log.i("Tag", "width: " + getWidth() + ",height: " + getHeight());
Log.i("Tag", "MeasuredWidth: " + getMeasuredWidth()
+ ",MeasuredHeight: " + getMeasuredHeight());
}
}
}运行结果:
在改动一下:
public class MainActivity extends ActionBarActivity {
private TextViewTest mTextViewTest;
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
mTextViewTest = new TextViewTest(this);
setContentView(mTextViewTest);
}
public class TextViewTest extends TextView {
public TextViewTest(Context context) {
super(context);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
setText("test test ");
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onDraw(canvas);
measure(0, 0);
Log.i("Tag", "width: " + getWidth() + ",height: " + getHeight());
Log.i("Tag", "MeasuredWidth: " + getMeasuredWidth()
+ ",MeasuredHeight: " + getMeasuredHeight());
}
}
}好了,相信通过这几个实验,可以看出来文字的验证描述了