C++中armadillo矩阵库使用说明
在http://blog.csdn.net/piaoxuezhong/article/details/58055709博文中介绍了eigen矩阵库的使用,这里介绍另一种矩阵库:armadillo~
Armadillo:C++下的Matlab替代品
armadillo是目前使用比较广的C++矩阵运算库之一,许多Matlab的矩阵操作函数都可以找到对应,这 对习惯了Matlab的人来说实在是非常方便,另外如果要将Matlab下做研究的代码改写成C++,使用Armadillo也会很方便。下面列了一些Armadillo的特性:- 支持整数,浮点数,和复数矩阵。
- 支持矩阵逐元素操作,包括abs · conj · conv_to · eps · imag/real · misc functions (exp, log, pow, sqrt, round, sign, ...) · trigonometric functions (cos, sin, ...)等等。
- 支持矩阵分块操作。
- 支持对整体矩阵的操作diagvec · min/max · prod · sum · statistics (mean, stddev, ...) · accu · as_scalar · det · dot/cdot/norm_dot · log_det · norm · rank · trace等等。
- Matlab用户,你甚至可以找到你熟悉的hist · histc · unique · cumsum · sort_index · find · repmat · linspace等函数。
- 除了自带的矩阵基本运算之外,可自动检测是否安装有BLAS,或更快的 OpenBLAS, Intel MKL, AMD ACML,并使用他们替代自带基本运算实现。
- 提供接口使用LAPACK进行矩阵分解运算,svd · qr · lu · fft等等。
- 提供了稀疏矩阵类,支持常用操作,但暂时没有矩阵分解的实现。
vs下安装Armadillo
1、下载Armadillo,解压后把其中的include文件夹完整拷贝出来,放到某处,如D:\Armadillo;
2、修改D:\Armadillo\include\armadillo_bits\config.hpp,将
#define ARMA_USE_LAPACK
#define ARMA_USE_BLAS
这两句取消注释。表示使用这两个库。
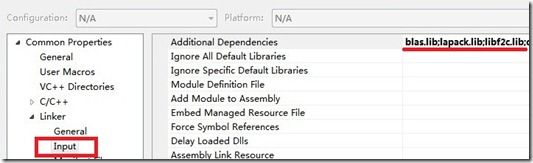
3、安装lapack和blas。实际上第一步中下载的压缩包里自带了这两个库,但是在vs2010中用这两个库会出现卡死现象,其他编译环境没有测试。可以去http://icl.cs.utk.edu/lapack-for-windows/clapack/index.html下载blas.lib,libf2c.lib,lapack.lib三个库,并在编译环境的额外依赖库中添加这三个库。(linker-> input-> additional dependencies)
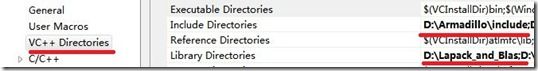
4、在编译器的include目录中添加include文件夹的路径以及第三步中三个库文件所在位置。如图:
矩阵类Mat简介:
Mat
mat = Mat //mat为double类型
fmat = Mat //fmat为float类型
cx_mat = Mat //cx_表示复数类型
cx_fmat = Mat
umat = Mat //相当于unsign int类型
imat = Mat //相当于int类型 创建方式:
mat()
mat(n_rows, n_cols)
mat(n_rows, n_cols, fill_type)
mat(size(X))
mat(size(X), fill_type)
mat(mat)
mat(sp_mat)
mat(vec)
mat(rowvec)
mat(initializer_list)
mat(string)
mat(std::vector)
cx_mat(mat,mat)
实例:
mat A(5, 5, fill::randu);
double x = A(1,2);
mat B = A + A;
mat C = A * B;
mat D = A % B;
cx_mat X(A,B);
B.zeros();
B.set_size(10,10);
B.ones(5,6);
B.print("B:")Armadillo中常见的功能说明:
| Function/Variable | Description |
| :n rows :n cols :n elem |
number of rows (read only) number of columns (read only) total number of elements (read only) |
| (i) (r, c) [i] .at(r, c) :memptr() |
access the i-th element, assuming a column-by-column layout access the element at row r and column c as per (i), but no bounds check; use only after debugging as per (r, c), but no bounds check; use only after debugging obtain the raw memory pointer to element data |
| :in range(i) :in range(r, c) |
test whether the i-th element can be accessed test whether the element at row r and column c can be accessed |
| :reset() :copy size(A) :set size(rows, cols) .reshape(rows, cols) .resize(rows, cols) |
set the number of elements to zero set the size to be the same as matrix A change size to specified dimensions, without preserving data (fast) change size to specified dimensions, with elements copied column-wise (slow) change size to specified dimensions, while preserving elements & their layout (slow) |
| :ones(rows, cols) :zeros(rows, cols) :randu(rows, cols) :randn(rows, cols) :fill(k) :for each( [ ] (double& val) f...g) |
set all elements to one, optionally first resizing to specified dimensions as above, but set all elements to zero as above, but set elements to uniformly distributed random values in [0,1] interval as above, but use a Gaussian/normal distribution with µ = 0 and σ = 1 set all elements to be equal to k for each element, pass its reference to a lambda function (C++11 only) |
| :is empty() :is finite() :is square() :is vec() :is sorted() |
test whether there are no elements test whether all elements are finite test whether the matrix is square test whether the matrix is a vector test whether the matrix is sorted |
| :has inf() :has nan() |
test whether any element is ±1 test whether any element is not-a-number |
| :begin() :end() :begin row(i) :end row(j) :begin col(i) :end col(j) |
iterator pointing at the first element iterator pointing at the past-the-end element iterator pointing at first element of row i iterator pointing at one element past row j iterator pointing at first element of column i iterator pointing at one element past column j |
| :print(header) :raw print(header) |
print elements to the cout stream, with an optional text header as per .print(), but do not change stream settings |
| :save(name, format) :load(name, format) |
store matrix in the specified file, optionally specifying storage format retrieve matrix from the specified file, optionally specifying format |
| :diag(k) :row(i) :col(i) :rows(a, b) :cols(c, d) :submat( span(a,b), span(c,d) ) :submat( p, q, size(A) ) :rows( vector of row indices ) :cols( vector of col indices ) :elem( vector of indices ) |
read/write access to k-th diagonal read/write access to row i read/write access to column i read/write access to submatrix, spanning from row a to row b read/write access to submatrix, spanning from column c to column d read/write access to submatrix spanning rows a to b and columns c to d read/write access to submatrix starting at row p and col q with size same as matrix A read/write access to rows corresponding to the specified indices read/write access to columns corresponding to the specified indices read/write access to matrix elements corresponding to the specified indices |
| :each row() :each col() :swap rows(p, q) :swap cols(p, q) :insert rows(row, X) :insert cols(col, X) :shed rows(first row, last row) :shed cols(first col, last col) |
repeat a vector operation on each row (eg. A.each row() += row vector) repeat a vector operation on each column (eg. A.each col() += col vector) swap the contents of specified rows swap the contents of specified columns insert a copy of X at the specified row insert a copy of X at the specified column remove the specified range of rows remove the specified range of columns |
| :min() :max() :index min() :index max() |
return minimum value return maximum value return index of minimum value return index of maximum value |
实例:
mat A = randu(10,10);
A(9,9) = 123.0;
double x = A.at(9,9);
double y = A[99];
vec p = randu(10,1);
p(9) = 123.0;
double z = p[9]; Armadillo与Matlab的对比:
| Matlab & Octave | Armadillo | Notes |
| A(1, 1) A(k, k) |
A(0, 0) A(k-1, k-1) |
indexing in Armadillo starts at 0, following C++ convention |
| size(A,1) size(A,2) size(Q,3) numel(A) |
A.n rows A.n cols Q.n slices A.n elem |
member variables are read only Q is a cube (3D array) .n elem indicates the total number of elements |
| A(:, k) A(k, :) A(:, p:q) A(p:q, :) A(p:q, r:s) |
A.col(k) A.row(k) A.cols(p, q) A.rows(p, q) A( span(p, q), span(r, s) ) |
read/write access to a specific column read/write access to a specific row read/write access to a submatrix spanning the specified cols read/write access to a submatrix spanning the specified rows A( span(first row, last row), span(first col, last col) ) |
| Q(:, :, k) Q(:, :, t:u) |
Q.slice(k) Q.slices(t, u) |
Q is a cube (3D array) |
| A0 A:0 |
A.t() or trans(A) A.st() or strans(A) |
transpose (for complex matrices the conjugate is taken) simple transpose (for complex matrices the conjugate is not taken) |
| A = zeros(size(A)) A = ones(size(A)) A = zeros(k) A = ones(k) |
A.zeros() A.ones() A = zeros(k,k) A = ones(k,k) |
set all elements to zero set all elements to one create a matrix with elements set to zero create a matrix with elements set to one |
| C = complex(A,B) | cx mat C = cx mat(A,B) | construct a complex matrix out of two real matrices |
| A ∗ B A :∗ B A := B A n B A = A + 1 A = A - 1 |
A ∗ B A % B A = B solve(A,B) A++ A-- |
% indicates element-wise multiplication = indicates element-wise division solve a system of linear equations |
| A = [ 1 2; 3 4; ] |
A = f f 1, 2 g, f 3, 4 g g |
requires C++11 compiler |
| X = [ A B ] X = [ A; B ] |
X = join rows(A,B) X = join cols(A,B) |
|
| A | A.print(“A:”) or cout << A << endl |
print the contents of a matrix to the standard output |
| save -ascii ‘A.dat’ A load -ascii ‘A.dat’ |
A.save(“A.dat”, raw ascii) A.load(“A.dat”, raw ascii) |
Matlab/Octave matrices saved as ascii text are readable by Armadillo (and vice-versa) |
| A = rand(2,3); B = randn(4,5); F = f A; B g; |
mat A = randu(2,3); mat B = randn(4,5); field<mat> F(2,1); F(0,0) = A; F(1,2) = B; |
randu generates uniformly distributed random numbers the field class can store multiple varying size matrices |
综合测试程序:
#include
#include
using namespace std;
using namespace arma;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
cout<<"Armadillo version: "<(A.memptr())<=BB);
ZZ.print("ZZ:");
// 2D field of matrices; 3D fields are also supported
field F(4, 3);
for (uword col = 0; col(2, 3); // each element in field is a matrix
}
F.print("F:");
return 0;
} 参考:
http://blog.csdn.net/jnulzl/article/details/46808515
http://www.cnblogs.com/einyboy/p/3852319.html