Trie树的基本原理及应用
- 前言
- 理论知识
- [什么是 Trie 树](#什么是 trie 树)
- [Trie 的优劣势](#trie 的优劣势)
- [Trie 的应用场景](#trie 的应用场景)
- 编码实现
- 参考文章
- 联系我
前言
在做用户 query 理解的过程中,有许多需要使用词典来"识别"的过程。在此期间,就避免不了使用 Trie 树这一数据结构。
因此今天我们来深入的学习一下 Trie 树相关的理论知识,并且动手编码实现。
理论知识
什么是 Trie 树
下面的定义引自维基百科。
在计算机科学中,trie,又称前缀树或字典树,是一种有序树,用于保存关联数组,其中的键通常是字符串。与二叉查找树不同,键不是直接保存在节点中,而是由节点在树中的位置决定。一个节点的所有子孙都有相同的前缀,也就是这个节点对应的字符串,而根节点对应空字符串。一般情况下,不是所有的节点都有对应的值,只有叶子节点和部分内部节点所对应的键才有相关的值。
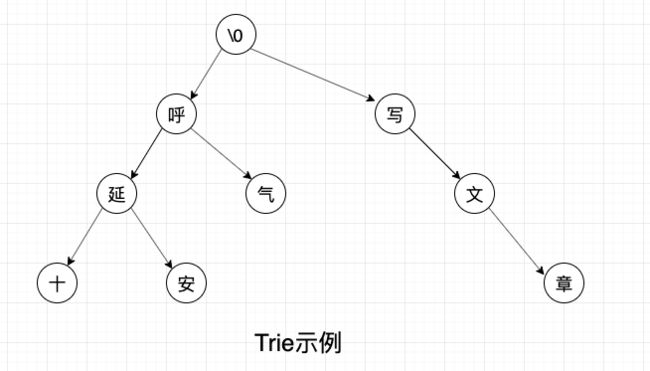
一个简单的 Trie 结构如下图所示:
从上面的图中,我们可以发现一些 Trie 的特性。
- 根节点不包含字符,除根节点外的每一个子节点都包含一个字符。
- 从根节点到某一节点,路径上经过的字符连接起来,就是该节点对应的字符串。
- 每个单词的公共前缀作为一个字符节点保存。
通常在实现的时候,会在节点结构中设置一个标志,用来标记该结点处是否构成一个单词(关键字), 或者存储一些其他相关的值。
可以看出,Trie 树的关键字一般都是字符串,而且 Trie 树把每个关键字保存在一条路径上,而不是一个结点中。另外,两个有公共前缀的关键字,在 Trie 树中前缀部分的路径相同,所以 Trie 树又叫做前缀树(Prefix Tree)。
Trie 树的每个节点的子节点,是一堆单字符的集合,我们可以很方便的进行对所有字符串进行字典序的排序工作。只需要将字典序先序输出,输出所有子节点时按照字典序遍历即可。所以 Trie 树又叫做字典树。
Trie 的优劣势
Trie 树的核心思想就是:用空间来换时间,利用字符串的公共前缀来降低查询时间的开销以达到提高效率的目的。
当然,在大数据量的情况下,Trie 树的空间也未必会大于哈希表。只要通过共享前缀节省的空间能够 Cover 对象的额外开销。
Trie 的强大之处就在于它的时间复杂度,插入和查询的效率很高,都为O(N),其中 N 是待插入/查询的字符串的长度,而与 Trie 中保存了多少个元素无关。
关于查询,会有人说 hash 表时间复杂度是O(1)不是更快?但是,哈希搜索的效率通常取决于 hash 函数的好坏,若一个坏的 hash 函数导致很多的冲突,效率并不一定比 Trie 树高。
而 Trie 树中不同的关键字就不会产生冲突。它只有在允许一个关键字关联多个值的情况下才有类似 hash 碰撞发生。
此外,Trie 树不用求 hash 值,对短字符串有更快的速度。因为通常,求 hash 值也是需要遍历字符串的。
也就是说,从理论上来讲,Trie 树的时间复杂度是稳定的,而 hash 表的时间复杂度是不稳定的,取决于 hash 函数的好坏,也和存储的字符串集有关系。
而从工业应用上来讲,个人推荐:如果你不需要用到 Trie 树前缀匹配的特性,直接用 hash 表即可。
原因有以下几点:
- hash 表实现极其简单,且大多数语言都有完善的内部库。使用方便。
- 大部分时间就 K-V 存储而言,hash 是由于 Trie 树的,尤其是 语言库中经过各方大佬优化的 hash 表。
- Trie 树要自己实现,且要经过各种逻辑上的测试,保证覆盖率,还要压测等等才能投入使用,成本太高。
Trie 的应用场景
作为一个工程师,我学习一个东西最重要的地方就是了解他的应用场景,所有只存在于书本上而没有成熟应用的技术,我都浅尝辄止。
在学习 Trie 树时,我也花了很多时间来查找,记录它的应用场景,列举在此处,如果各位同学有其他的应用场景,不妨留言大家讨论。
K-V 存储及检索
这是 Trie 树嘴原始朴素的使用方法,也就是需要和 hash 表进行竞争的地方。
词频统计
我们可以修改 Trie 树的实现,将每个节点的 是否在此构成单词标志位改成此处构成的单词数量. 这样我们可以用它进行搜索场景常见的词频统计。
当然这个需求 hash 表也是可以实现的。
字典序排序
将所有待排序集合逐个加入到 Trie 树中,然后按照先序遍历输出所有值。在遍历某个节点的所有子节点的时候,按照字典序进行输出即可。
前缀匹配
例如:找出一个字符串集合中所有以 ab 开头的字符串。我们只需要用所有字符串构造一个 trie 树,然后输出以 a − > b − > a->b-> a−>b−>开头的路径上的关键字即可。
trie 树前缀匹配常用于搜索提示。比如各种搜索引擎上的 自动联想后半段功能。
最长公共前缀
查找一组字符串的最长公共前缀,只需要将这组字符串构建成 Trie 树,然后从跟节点开始遍历,直到出现多个节点为止(即出现分叉)。
作为辅助结构
作为其他数据结构的辅助结构,如后缀树,AC 自动机等
编码实现
首先实现 Trie 树的节点:
package com.huyan.trie;
import java.util.*;
/**
* Created by pfliu on 2019/12/06.
*/
public class TNode {
/**
* 当前节点字符
*/
private char c;
/**
* 当前 节点对应数字
*/
int count = 0;
private TNode[] children;
private static int hash(char c) {
return c;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "TNode{" +
"c=" + c +
", count=" + count +
", children=" + Arrays.toString(children) +
'}';
}
TNode(char c) {
this.c = c;
}
/**
* 将 给定字符 添加到给定列表中。
* @param nodes 给定的 node 列表
* @param c 给定字符
* @return 插入后的节点
*/
private static TNode add(final TNode[] nodes, char c) {
int hash = hash(c);
int mask = nodes.length - 1;
for (int i = hash; i < hash + mask + 1; i++) {
int idx = i & mask;
if (nodes[idx] == null) {
TNode node = new TNode(c);
nodes[idx] = node;
return node;
} else if (nodes[idx].c == c) {
return nodes[idx];
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* 将 当前节点 放入到给定的 节点列表中。
* 用于 resize 的时候转移节点列表
* @param nodes 节点列表
* @param node 给定节点
*/
private static void add(final TNode[] nodes, TNode node) {
int hash = hash(node.c);
int len = nodes.length - 1;
for (int i = hash; i < hash + len + 1; i++) {
int idx = i & len;
if (nodes[idx] == null) {
nodes[idx] = node;
return;
} else if (nodes[idx].c == node.c) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Node not expected for " + node.c);
}
}
throw new IllegalStateException("Node not added");
}
/**
* 将 给定字符 插入到当前节点的子节点中。
* @param c 给定字符
* @return 插入后的节点
*/
TNode addChild(char c) {
// 初始化子节点列表
if (children == null) {
children = new TNode[2];
}
// 尝试插入
TNode node = add(children, c);
if (node != null)
return node;
// resize
// 转移节点列表到新的子节点列表中
TNode[] tmp = new TNode[children.length * 2];
for (TNode child : children) {
if (child != null) {
add(tmp, child);
}
}
children = tmp;
return add(children, c);
}
/**
* 查找当前节点的子节点列表中,char 等于给定字符的节点
* @param c 给定 char
* @return 对应的节点
*/
TNode findChild(char c) {
final TNode[] nodes = children;
if (nodes == null) return null;
int hash = hash(c);
int len = nodes.length - 1;
for (int i = hash; i < hash + len + 1; i++) {
int idx = i & len;
TNode node = nodes[idx];
if (node == null) {
return null;
} else if (node.c == c) {
return node;
}
}
return null;
}
}
然后实现 Trie 树。
package com.huyan.trie;
import java.util.*;
/**
* Created by pfliu on 2019/12/06.
*/
public class Trie {
/**
* 根节点
*/
final private TNode root = new TNode('\0');
/**
* 添加一个词到 Trie
*
* @param word 待添加词
* @param value 对应 value
*/
public void addWord(String word, int value) {
if (word == null || word.length() == 0) return;
TNode node = root;
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
char c = word.charAt(i);
// 当前 char 添加到 trie 中,并拿到当前 char 对应的那个节点
node = node.addChild(c);
}
node.count = value;
}
/**
* 查找 word 对应的 int 值。
*
* @param word 给定 word
* @return 最后一个节点上存储的 int.
*/
public int get(String word) {
TNode node = root;
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
node = node.findChild(word.charAt(i));
if (node == null) {
return 0;
}
}
return node.count;
}
private int get(char[] buffer, int offset, int length) {
TNode node = root;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
node = node.findChild(buffer[offset + i]);
if (node == null) {
return 0;
}
}
return node.count;
}
/**
* 从给定字符串的 offset 开始。
* 查找最大匹配的第一个 int 值。
*
* @param str 给定字符串
* @param offset 开始查找的偏移量
* @return 第一个匹配的字符串德最后一个节点的 int 值。
*/
public String maxMatch(String str, int offset) {
TNode node = root;
int lastMatchIdx = offset;
for (int i = offset; i < str.length(); i++) {
char c = str.charAt(i);
node = node.findChild(c);
if (node == null) {
break;
} else if (node.count != 0) {
lastMatchIdx = i;
}
}
return lastMatchIdx == offset ? null : str.substring(offset, lastMatchIdx + 1);
}
/**
* 从给定字符串的 offset 反向开始。
* 查找最大匹配的第一个 int 值。
*
* @param str 给定字符串
* @param offset 开始查找的偏移量
* @return 第一个匹配的字符串德最后一个节点的 int 值。
*/
public int maxMatchBack(String str, int offset) {
TNode node = root;
int lastMatchIdx = offset;
for (int i = offset; i >= 0; i--) {
char c = str.charAt(i);
node = node.findChild(c);
if (node == null) {
break;
} else if (node.count != 0) {
lastMatchIdx = i;
}
}
return offset - lastMatchIdx + 1;
}
/**
* 从给定字符串的 offset 开始。检查 length 长度。
* 查找最大匹配的第一个 int 值。
*
* @param buffer 给定字符串
* @param offset 开始查找的偏移量
* @return 第一个匹配的字符串德最后一个节点的 int 值。
*/
public int maxMatch(char[] buffer, int offset, int length) {
TNode node = root;
int lastMatchIdx = offset;
for (int i = offset; i < offset + length; i++) {
char c = buffer[i];
node = node.findChild(c);
if (node == null) {
break;
} else if (node.count != 0) {
lastMatchIdx = i;
}
}
return lastMatchIdx - offset + 1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Trie trie = new Trie();
for (String s : Arrays.asList("呼延", "呼延二十")) {
trie.addWord(s, 1);
}
String input = "延十在写文章";
System.out.println(trie.maxMatch(input, 0));
}
}
代码中基本上实现了 Trie 的基本功能,但是对 trie 的应用方法有很多,比如匹配前缀,比如求最长匹配前缀的长度等。这些就不一一实现了。
参考文章
https://www.cnblogs.com/huangxincheng/archive/2012/11/25/2788268.html
https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trie
完。
联系我
最后,欢迎关注我的个人公众号【 呼延十 】,会不定期更新很多后端工程师的学习笔记。
也欢迎直接公众号私信或者邮箱联系我,一定知无不言,言无不尽。
ChangeLog
2019-05-19 完成以上皆为个人所思所得,如有错误欢迎评论区指正。
欢迎转载,烦请署名并保留原文链接。
联系邮箱:[email protected]
更多学习笔记见个人博客或关注微信公众号 < 呼延十 >------>呼延十