递归和分治 机考复习
递归策略
- 子问题必须与原始问题相同,且规模更小
- 不能无限制地调用本身,必须有一个递归出口
汉诺塔
原始问题:
三根杆,64个圆盘,不允许大圆盘放到小圆盘上,从最左边的杆子移动到最右边
规律:n个圆盘=》2^n-1
#include
count++;
hanoe(num - 1, mid, end, start);
}
}
int main()
{
hanoe(5, 1, 2, 3);
cout << count;
return 0;
}
升级:
增加一个条件:不允许直接从最左(右)边移动到最右(左)边
输入:圆盘数目(多组数据)
输出:移动的最小次数
#include杨辉三角形
题目描述
输入n值,使用递归函数,求杨辉三角形中各个位置上的值。
输入描述:
一个大于等于2的整型数n
输出描述:
题目可能有多组不同的测试数据,对于每组输入数据,
按题目的要求输出相应输入n的杨辉三角形。
自己在IDEA上写的代码是可以打印出正确结果的,但是实际上无法通过,整体逻辑比较混乱,不可取
#include还是没有把递归理解透彻,看了别人的代码,将子问题划分为一个一个值的求解。
#include全排列问题
题目描述
给定一个由不同的小写字母组成的字符串,输出这个字符串的所有全排列。 我们假设对于小写字母有’a’ < ‘b’ < … < ‘y’ < ‘z’,而且给定的字符串中的字母已经按照从小到大的顺序排列。
输入描述:
输入只有一行,是一个由不同的小写字母组成的字符串,已知字符串的长度在1到6之间。
输出描述:
输出这个字符串的所有排列方式,每行一个排列。要求字母序比较小的排列在前面。字母序如下定义:
已知S = s1s2…sk , T = t1t2…tk,则S < T 等价于,存在p (1 <= p <= k),使得
s1 = t1, s2 = t2, …, sp - 1 = tp - 1, sp < tp成立。
每组样例输出结束后要再输出一个回车。
这属于难度较小的全排列问题,但是在做的过程中受到思维定式的影响,想着字符串中index的问题,实际上每一次取得字符只要前面没有被取过就好了。
而对于字母序处理,只要保证原始字符串是按照从小到大处理的就好。
//全排列
#include分治
只要找到递推公式,都不困难。(自顶向下)
斐波那契数列
走楼梯(走一步,走两步)
二叉树
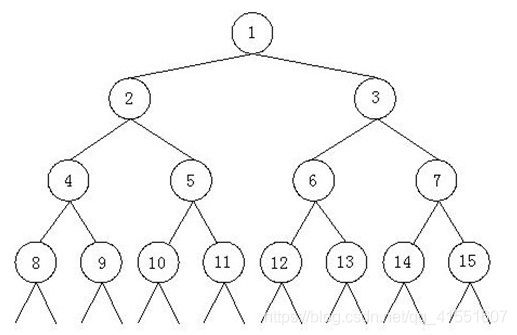
题目描述
如上所示,由正整数1,2,3……组成了一颗特殊二叉树。我们已知这个二叉树的最后一个结点是n。现在的问题是,结点m所在的子树中一共包括多少个结点。 比如,n = 12,m = 3那么上图中的结点13,14,15以及后面的结点都是不存在的,结点m所在子树中包括的结点有3,6,7,12,因此结点m的所在子树中共有4个结点。
输入描述:
输入数据包括多行,每行给出一组测试数据,包括两个整数m,n (1 <= m <= n <= 1000000000)。
输出描述:
对于每一组测试数据,输出一行,该行包含一个整数,给出结点m所在子树中包括的结点的数目。
要找到合适的底层子问题,在完成这道题时将底层子问题考虑成叶子节点,程序出现部分错误,因为并非平衡。
应该考虑成叶子节点下的空节点(m>n)的情况。
#include 二的幂次方
Every positive number can be presented by the exponential form.For example, 137 = 2^7 + 2^3 + 2^0。 Let’s present a^b by the form a(b).Then 137 is presented by 2(7)+2(3)+2(0). Since 7 = 2^2 + 2 + 2^0 and 3 = 2 + 2^0 , 137 is finally presented by 2(2(2)+2 +2(0))+2(2+2(0))+2(0). Given a positive number n,your task is to present n with the exponential form which only contains the digits 0 and 2.
For each case, the input file contains a positive integer n (n<=20000).
输出描述:
For each case, you should output the exponential form of n an a single line.Note that,there should not be any additional white spaces in the line.
示例1
输入
1315
输出
2(2(2+2(0))+2)+2(2(2+2(0)))+2(2(2)+2(0))+2+2(0)
该形式只包括数字2和数字0
这道题在理解起来难度并不大,但是在输出格式上调整了很长时间。
#include