自动驾驶路径规划算法学习(1)—Dijkstra算法
写这个系列的第一篇文章是自动驾驶路径规划算法学习(2)—A*算法
这篇文章的起源是看了古月居的文章运动规划入门 | 白话Dijkstra,从原理到Matlab实现,由于其中的编程风格与之前A*算法的风格不同,所以将其重写。
理论部分不再赘述,可查看古月居的文章。
一、问题
给定材料(CreateMAP.m)中包含的MATLAB代码,可以生成50X50的地图,x表示障碍物,起点和终点均已给定,用Dijkstra算法实现路径规划。
二、说明
古月居在文章中也给出了代码实现,可查看其文章。
之前采用了A *算法的Matlab实现来进行代码实现,个人认为其实现结构较完整,所以本文采用该结构进行Dijkstra算法的实现。
以下介绍各模块功能。
三、main.m
主程序文件,包括调用创建的地图,起止点,调用函数Dijkstra算法获取路径,绘制程序运行过程图像。
% 该文件为以map.mat为地图文件,point.mat为起止位置文件,
% 进行Dijkstra算法路径规划的主程序
clc
clear all
close all;
disp('Dijkstra Path Planing start!!')
load map.mat % 加载地图
load point.mat % 加载起止位置点
[map.XMAX,map.YMAX] = size(MAP); %%代表我们要画一个地图的长和宽
map.start = node(1:2); %起始点 注意必须在地图范围内
map.goal = node(3:4); %目标点 注意必须在地图范围内
obstacle = GetObstacle(map,MAP);% 获取边界数据和障碍物坐标
clear MAP node % 后续程序不再使用这两个变量
%obstacle = [obstacle;4,1; 4,2; 4,3; 4,4; 3,4 ;2,4;];%全封死的情况,是没有路的
% 画出地图和起止点
figure(1)
if length(obstacle)>=1
plot(obstacle(:,1)+.5,obstacle(:,2)+.5,'rx');hold on;
% plot(obstacle(:,1),obstacle(:,2),'om');hold on;
end
pause(1);
h=msgbox('Please confirm the map information and click the buttion "confirm".');
uiwait(h,20);% 5s后关闭消息框
if ishandle(h) == 1
delete(h);
end
close 1
figure(1)
axis([1 map.XMAX+1 1 map.YMAX+1])
set(gca,'YTick',0:1:map.YMAX);
set(gca,'XTick',0:1:map.XMAX);
grid on;hold on;
% 绘制边界和障碍点
plot(obstacle(:,1)+.5,obstacle(:,2)+.5,'rx');hold on;
% 绘制起始点
plot(map.start(1)+.5,map.start(2)+.5,'bo');hold on;
% 绘制终止点
plot(map.goal(1)+.5,map.goal(2)+.5,'gd');hold on;
text(map.goal(1)+1,map.goal(2)+.5,'Target');
% plot(map.start(1),map.start(2),'*r');hold on;
% plot(map.goal(1),map.goal(2),'*b');hold on;
% 采用Dijkstra算法进行路径规划
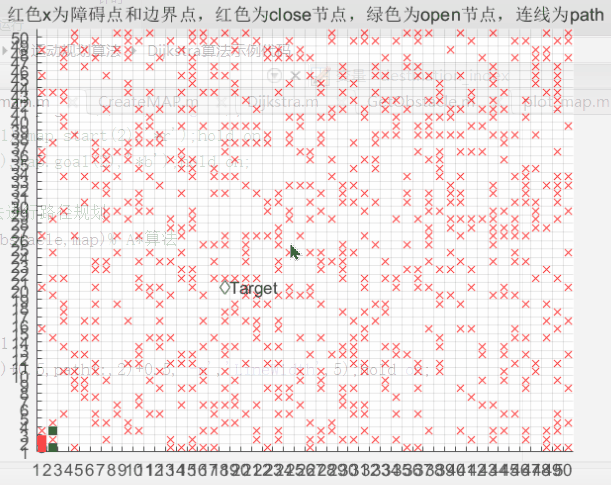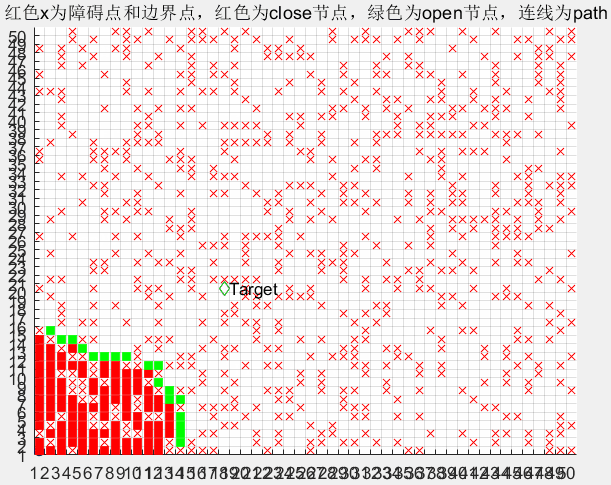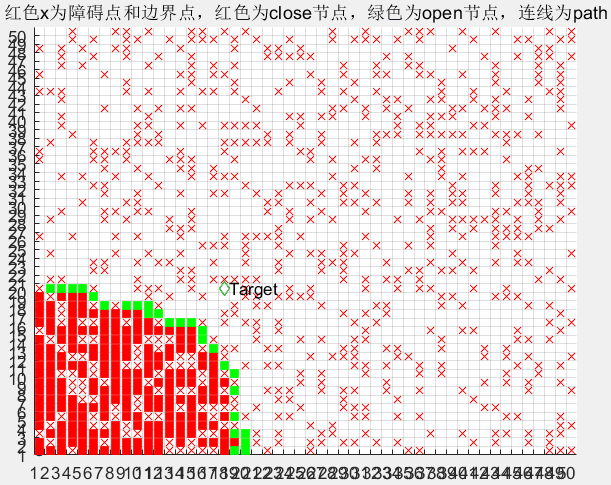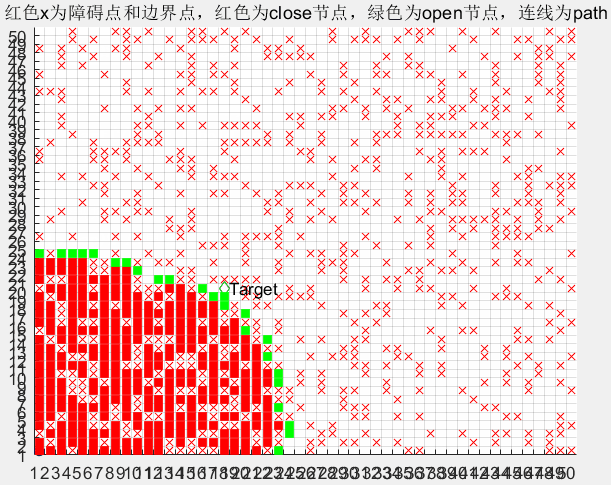
path = Dijkstra(obstacle,map)% A*算法
%画出路径
%
if length(path)>=1
plot(path(:,1)+0.5,path(:,2)+0.5,'-m','LineWidth',5);hold on;
end
%}
grid on;
四、GetObstacle.m
该文件用于生成地图的障碍点和边界点。
function obstacle=GetObstacle(map,MAP)
%获得地图的边界和障碍点的坐标
% 生成边界的坐标,此处XMAX表示MAP的行数,YMAX表示MAP的列数
boundary=[];
for i1=0:(map.YMAX+1)
boundary=[boundary;[0 i1]];
end
for i2=0:(map.XMAX+1)
boundary=[boundary;[i2 0]];
end
for i3=0:(map.YMAX+1)
boundary=[boundary;[map.XMAX+1 i3]];
end
for i4=0:(map.XMAX+1)
boundary=[boundary;[i4 map.YMAX+1]];
end
obstacle = boundary;
% 生成障碍点的坐标
for i=1:map.XMAX
for j=1:map.YMAX
if MAP(i,j) == -1
obstacle=[obstacle;[i j]];
end
end
end
end
五、CreateMAP.m
该文件包括参数初始化、设置障碍点、选择起止位置点;最后将地图数据存为map.mat,起止位置点存为point.mat。
clc;
clear all;
figure;
% 参数初始化
MAX_X=50;% 代表我们要画一个地图的长
MAX_Y=50;% 代表我们要画一个地图的宽
p_obstacle = 0.3;% 障碍率
% 设置障碍点
obstacle = ones(MAX_X,MAX_Y)*p_obstacle;
% 将MAP矩阵中障碍点置为-1,非障碍点置为9998
MAP = 9999*((rand(MAX_X,MAX_Y))>obstacle)-1; % -1值代表障碍物
j=0;
x_val = 1;
y_val = 1;
axis([1 MAX_X+1 1 MAX_Y+1])
set(gca,'YTick',0:1:MAX_Y);
set(gca,'XTick',0:1:MAX_X);
grid on;
hold on;
% 绘制出地图上的障碍物
for i=1:MAX_X
for j=1:MAX_Y
if MAP(i,j) == -1
plot(i+.5,j+.5,'rx');
end
end
end
%%地图上选择起始位置
pause(1);
h=msgbox('Please Select the Vehicle initial position using the Left Mouse button');
uiwait(h,5);% 5s后关闭消息框
if ishandle(h) == 1
delete(h);
end
xlabel('Please Select the Vehicle initial position ','Color','black');
but=0;
while (but ~= 1) %Repeat until the Left button is not clicked
[xval,yval,but]=ginput(1);
xval=floor(xval);
yval=floor(yval);
end
xStart=xval;%Starting Position
yStart=yval;%Starting Position
MAP(xval,yval) = 0;
plot(xval+.5,yval+.5,'bo');
%%地图上选择目标点
pause(1);
h=msgbox('Please Select the Target using the Left Mouse button in the space');
uiwait(h,5);
if ishandle(h) == 1
delete(h);
end
xlabel('Please Select the Target using the Left Mouse button','Color','black');
but = 0;
while (but ~= 1) %Repeat until the Left button is not clicked
[xval,yval,but]=ginput(1);
end
xval = floor(xval);
yval = floor(yval);
xTarget = xval;
yTarget = yval;
MAP(xval,yval) = 9998;
plot(xval+.5,yval+.5,'gd');
text(xval+1,yval+.5,'Target');
node = [xStart,yStart,xTarget,yTarget];
save map MAP;
save point node;
close(figure(1));
六、Dijkstra.m
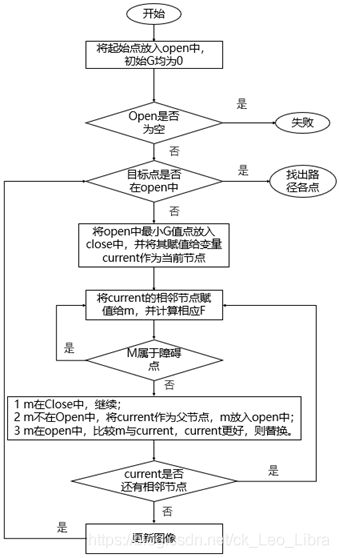
根据Dijkstra算法的理论:
在变量open中存放起始点以及所需考虑的路径点集合,其中每一行包括节点坐标、代价值G,父节点坐标;
在变量close中存放每个循环中最优路径点集合,其数据格式与open相同。
算法流程图如下图
function path=Dijkstra(obstacle,map)
% 该程序为A*算法
% 用于存储路径
path = [];
%OpenList
open = [];
%CloseList
close = [];
% findFlag用于判断While循环是否结束
findFlag=false;%目标标志
%===================1.将起始点放在Openlist中======================
%open变量每一行 [节点坐标,代价值G,父节点坐标]
open =[map.start(1), map.start(2) ,0 , map.start(1) , map.start(2)];
%更新状态--下一步的相邻点
next = MotionModel();
%=======================2.重复以下过程==============================
while ~findFlag
%--------------------首先判断是否达到目标点,或无路径-----
if isempty(open(:,1))
disp('No path to goal!!');
return;
end
%------------------判断目标点是否出现在open列表中
[isopenFlag,Id]=isopen(map.goal,open);
if isopenFlag
disp('Find Goal!!');
close = [open(Id,:);close]
findFlag=true;
break;
end
%------------------a.按照Openlist中的第三列(代价函数F)进行排序,
%--------------------查找F值最小的节点
[Y,I] = sort(open(:,3)); % 对OpenList中第三列排序
open=open(I,:);%open中第一行节点是F值最小的
%------------------b.将F值最小的节点(即open中第一行节点),放到close
%--------------------第一行(close是不断积压的),作为当前节点
close = [open(1,:);close];
current = open(1,:);
open(1,:)=[];% 因为已经从open中移除了,所以第一列需要为空
%--------------------c.对当前节点周围的相邻节点,算法的主体:------------------------
for in=1:length(next(:,1))
% 获得相邻节点的坐标,代价值F先等于0,代价值G先等于0 ,后面两个值是
% 其父节点的坐标值,暂定为零(因为暂时还无法判断其父节点坐标是多少)
m = [current(1,1)+next(in,1) , current(1,2)+next(in,2) , 0 , 0 ,0];
m(3) = current(1,3) + next(in,3); % m(4) 相邻节点G值
%>>如果它不可达,忽略它,处理下一个相邻节点 (注意,obstacle这个数
% 组中是包括边界的)
if isObstacle(m,obstacle)
continue;
end
%flag == 1:相邻节点 在Closelist中 targetInd = close中行号
%flag == 2:相邻节点不在Openlist中 targetInd = []
%flag == 3:相邻节点 在Openlist中 targetInd = open中行号
[flag,targetInd] = FindList(m,open,close);
%>>如果它在Closelist中,忽略此相邻节点
if flag==1
continue;
%>>如果它不在Openlist中,加入Openlist,并把当前节点设置为它的父节点
elseif flag==2
m(4:5)=[current(1,1),current(1,2)];%将当前节点作为其父节点
open = [open;m];%将此相邻节点加放openlist中
%>>剩下的情况就是它在Openlist中,检查由当前节点到相邻节点是否更好,
% 如果更好则将当前节点设置为其父节点,并更新G值;否则不操作
else
%由当前节点到达相邻节点更好(targetInd是此相邻节点在open中的行号 此行的第3列是代价函数G值)
if m(3) < open(targetInd,3)
%更好,则将此相邻节点的父节点设置为当前节点,否则不作处理
m(4:5)=[current(1,1),current(1,2)];%将当前节点作为其父节点
open(targetInd,:) = m;%将此相邻节点在Openlist中的数据更新
end
end
end
plot_map(map,obstacle,open,close);
end
%追溯路径
path=GetPath(close,map.start);
end
七、MotionModel.m
生成当前节点的相邻节点。
function next = MotionModel()
%当前节点 周围的八个相邻节点 与 当前节点的坐标差值(前两列)
%当前节点 周围的八个相邻节点 与 当前节点的距离值(最后一列)
next = [-1,1,14;...
0,1,10;...
1,1,14;...
-1,0,10;...
1,0,10;...
-1,-1,14;...
0,-1,10;...
1,-1,14];
end
八、Isopen.m、isObstacle.m
判断节点是否在open中,判断节点是否为障碍点。
function [isopenFlag,Id] = isopen( node,open )
%判断节点是否在open列表中,在open中,isopenFlag = 1,不在open中,isopenFlag = 0 .并反回索引号
isopenFlag = 0;
Id = 0;
%如果open列表为空,则不在open列表中
if isempty(open)
isopenFlag = 0;
else %open列表不为空时
for i = 1:length( open(:,1) )
if isequal( node(1:2) , open(i,1:2) ) %在Openlist中
isopenFlag = 1;
Id = i;
return;
end
end
end
end
function flag = isObstacle( m,obstacle )
%判断节点m是否为障碍点,如果是就返为1,不是就返回0
for io=1:length(obstacle(:,1))
if isequal(obstacle(io,:),m(1:2))
flag=true;
return;
end
end
flag=false;
end
九、FindList.m
函数功能:
如果相邻节点(m存储其信息)已经在Closelist中,则flag = 1,targetInd = 其所在close的行数,用来定位;
如果相邻节点(m存储其信息)不在Openlist 中,则flag = 2 targetInd = [];
如果相邻节点(m存储其信息) 已经在Openlist 中,则flag = 3 targetInd = 其所在open的行数,用来定位。
function [flag,targetInd]=FindList(m,open,close)
%{
函数功能:
如果相邻节点(m存储其信息) 已经在Closelist中,则flag = 1 targetInd = 其所在close的行数,用来定位
如果相邻节点(m存储其信息) 不在Openlist 中,则flag = 2 targetInd = []
如果相邻节点(m存储其信息) 已经在Openlist 中,则flag = 3 targetInd = 其所在open的行数,用来定位
%}
%如果openlist为空,则一定不在openlist中
if isempty(open)
flag = 2;
targetInd = [];
else %open不为空时,需要检查是否在openlist中
%遍历openlist,检查是否在openlist中
for io = 1:length(open(:,1))
if isequal( m(1:2) , open(io,1:2) ) %在Openlist中
flag = 3;
targetInd = io;
return;
else %不在Openlist中
flag = 2;
targetInd = [];
end
end
end
%如果能到这一步,说明: 一定不在Openlist中 那么需要判断是否在closelist中
%遍历Closelist(注意closelist不可能为空)
for ic = 1:length(close(:,1))
if isequal( m(1:2) , close(ic,1:2) ) %在Closelist中
flag = 1;
targetInd = ic;
return;%在Closelist中直接return
end
end
end
十、plot_map.m
绘制运行过程图像。
function plot_map( map,obstacle,open,close )
% %画出障碍点、起始点、终点
%绘制网格
% for i = 1:map.XMAX+3
% line([-0.5,map.XMAX+1.5],[i-1.5,i-1.5]);
% end
%
% for j = 1:map.YMAX+3
% line([j-1.5,j-1.5],[-0.5,map.YMAX+1.5]);
% end
pause(0.1);
title('黑色为障碍点和边界点,红色为close节点,绿色为open节点,连线为path');
%绘制节点
plot(close(:,1)+0.5,close(:,2)+0.5,'sr','MarkerFaceColor','r');
hold on;
%pause(0.1);
plot(open(:,1)+0.5,open(:,2)+0.5,'sg','MarkerFaceColor','g');
hold on;
%pause(0.1);
end
十一、GetPath.m
该函数功能为通过close中的数据反推出路径点。
function path=GetPath(close,start)
ind=1;
path=[];
while 1
path=[path; close(ind,1:2)];
if isequal(close(ind,1:2),start)
break;
end
for io=1:length(close(:,1))
if isequal(close(io,1:2),close(ind,4:5))
ind=io;
break;
end
end
end
end