tensorflow的多线程处理方式:tf.train.coordinator()和tf.train.start_queue_runners()
原网页:https://blog.csdn.net/dcrmg/article/details/79780331
tensorflow在一个会话(session)中,利用协调器和队列管理器(start_queue_runners)来控制多线程的运行。
Coordinator类用来管理在Session中的多个线程,可以用来同时停止多个工作线程并且向那个在等待所有工作线程终止的程序报告异常,该线程捕获到这个异常之后就会终止所有线程。使用 tf.train.Coordinator()来创建一个线程管理器(协调器)对象。
QueueRunner类用来启动tensor的入队线程,可以用来启动多个工作线程同时将多个tensor(训练数据)推送入文件名称队列中,具体执行函数是 tf.train.start_queue_runners , 只有调用 tf.train.start_queue_runners 之后,才会真正把tensor推入内存序列中,供计算单元调用,否则会由于内存序列为空,数据流图会处于一直等待状态。
tf的数据读取机制:
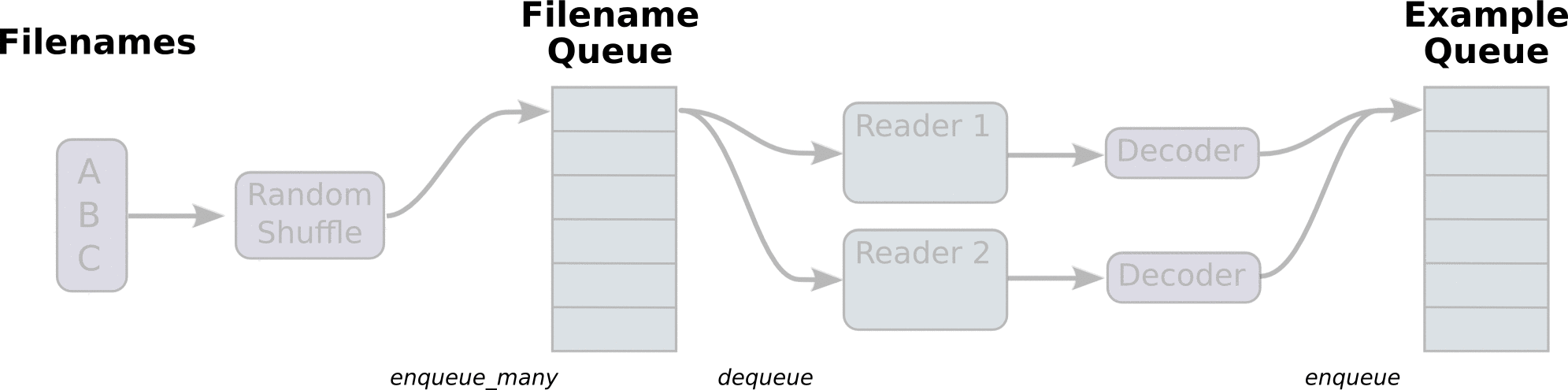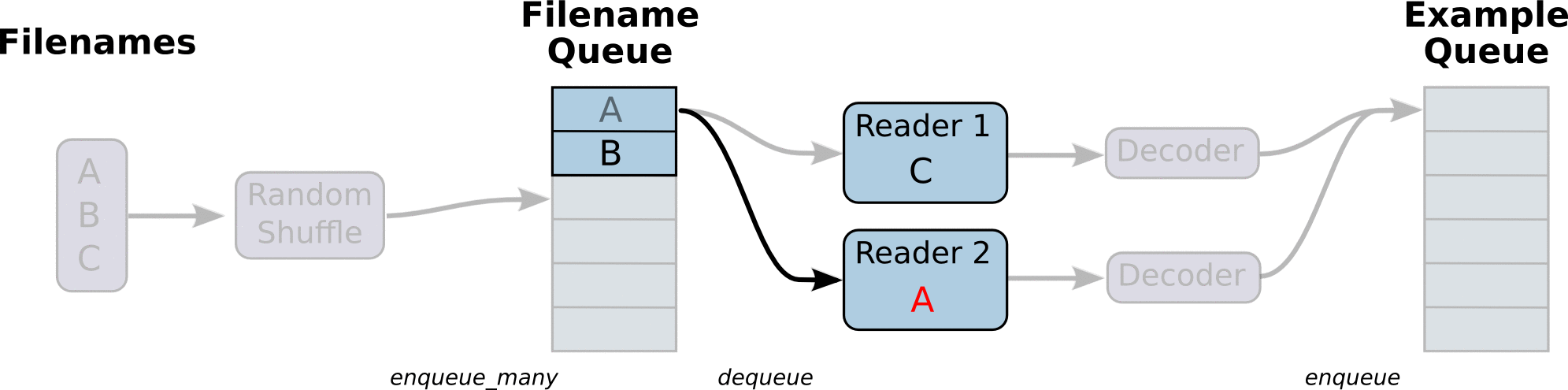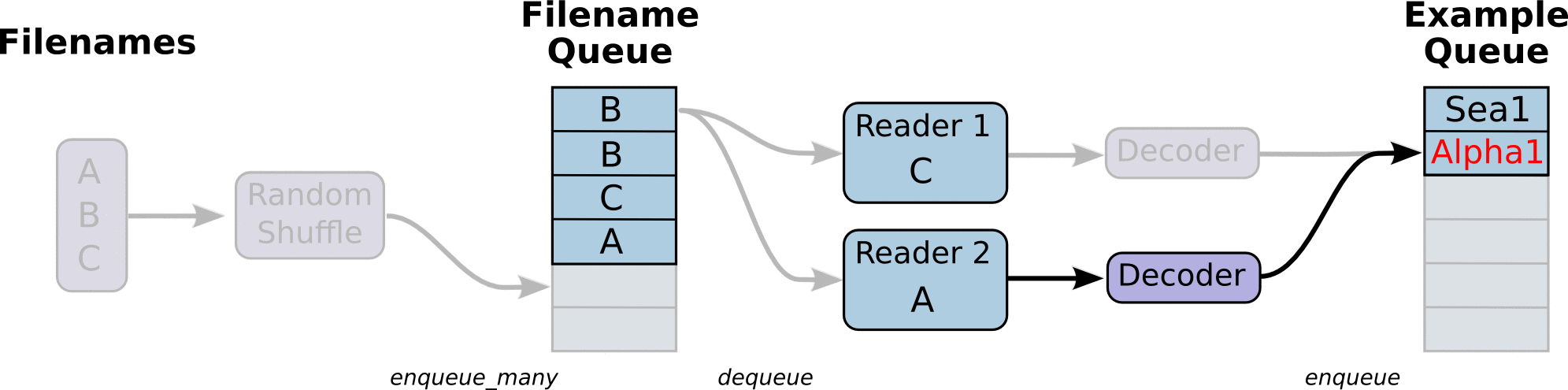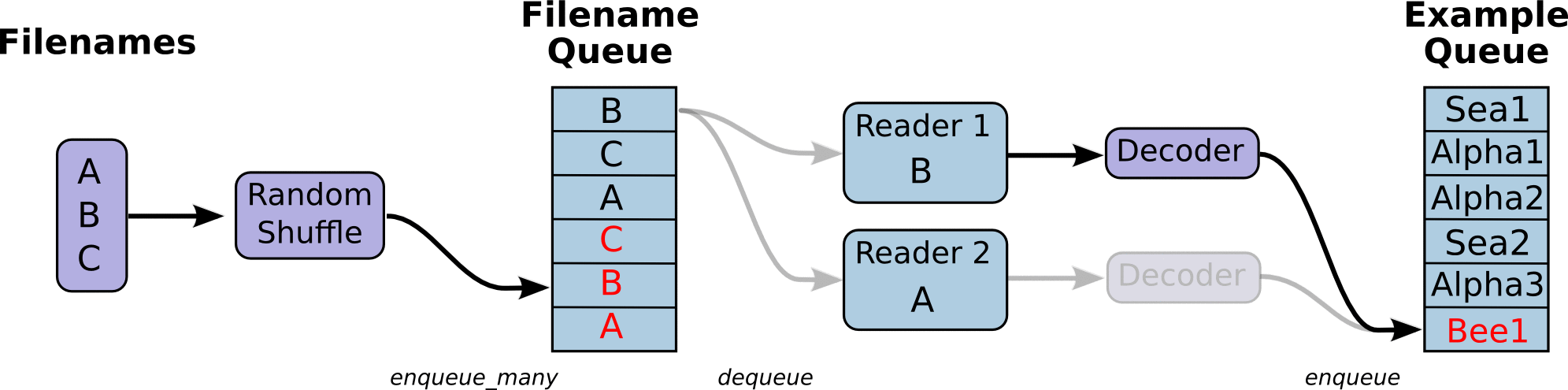
- 调用 tf.train.slice_input_producer,从 本地文件里抽取tensor,准备放入Filename Queue(文件名队列)中;
- 调用 tf.train.batch,从文件名队列中提取tensor,使用单个或多个线程,准备放入文件队列;
- 调用 tf.train.Coordinator() 来创建一个线程协调器,用来管理之后在Session中启动的所有线程;
- 调用tf.train.start_queue_runners, 启动入队线程,由多个或单个线程,按照设定规则,把文件读入Filename Queue中。函数返回线程ID的列表,一般情况下,系统有多少个核,就会启动多少个入队线程(入队具体使用多少个线程在tf.train.batch中定义);
- 文件从 Filename Queue中读入内存队列的操作不用手动执行,由tf自动完成;
- 调用sess.run 来启动数据出列和执行计算;
- 使用 coord.should_stop()来查询是否应该终止所有线程,当文件队列(queue)中的所有文件都已经读取出列的时候,会抛出一个 OutofRangeError 的异常,这时候就应该停止Sesson中的所有线程了;
- 使用coord.request_stop()来发出终止所有线程的命令,使用coord.join(threads)把线程加入主线程,等待threads结束。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
# 样本个数
sample_num=5
# 设置迭代次数
epoch_num = 2
# 设置一个批次中包含样本个数
batch_size = 3
# 计算每一轮epoch中含有的batch个数
batch_total = int(sample_num/batch_size)+1
# 生成4个数据和标签
def generate_data(sample_num=sample_num):
labels = np.asarray(range(0, sample_num))
images = np.random.random([sample_num, 224, 224, 3])
print('image size {},label size :{}'.format(images.shape, labels.shape))
return images,labels
def get_batch_data(batch_size=batch_size):
images, label = generate_data()
# 数据类型转换为tf.float32
images = tf.cast(images, tf.float32)
label = tf.cast(label, tf.int32)
#从tensor列表中按顺序或随机抽取一个tensor准备放入文件名称队列
input_queue = tf.train.slice_input_producer([images, label], num_epochs=epoch_num, shuffle=False)
#从文件名称队列中读取文件准备放入文件队列
image_batch, label_batch = tf.train.batch(input_queue, batch_size=batch_size, num_threads=2, capacity=64, allow_smaller_final_batch=False)
return image_batch, label_batch
image_batch, label_batch = get_batch_data(batch_size=batch_size)
with tf.Session() as sess:
# 先执行初始化工作
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
sess.run(tf.local_variables_initializer())
# 开启一个协调器
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
# 使用start_queue_runners 启动队列填充
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess, coord)
try:
while not coord.should_stop():
print '************'
# 获取每一个batch中batch_size个样本和标签
image_batch_v, label_batch_v = sess.run([image_batch, label_batch])
print(image_batch_v.shape, label_batch_v)
except tf.errors.OutOfRangeError: #如果读取到文件队列末尾会抛出此异常
print("done! now lets kill all the threads……")
finally:
# 协调器coord发出所有线程终止信号
coord.request_stop()
print('all threads are asked to stop!')
coord.join(threads) #把开启的线程加入主线程,等待threads结束
print('all threads are stopped!')
输出:
******************************
(2, 256, 256, 3) [0. 1.]
******************************
(2, 256, 256, 3) [2. 3.]
******************************
(2, 256, 256, 3) [0. 2.]
******************************
(2, 256, 256, 3) [1. 3.]
******************************
done
all threads are asked to stop!
all threads are stopped
Process finished with exit code 0