Java进阶笔记05
进阶20.5.24-20.6.30
- String字符串new与不new的区别
- 常量
- 包装类
- String,StringBuffer,StringBuilder
- 日期
- 数字格式化,数字类,random随机数
- IO流
- UML图
- InputStream OutputStream
- Reader Writer
- FileInputStream 文件字节输入流
- FileOutputStream 文件字节输出流
- FileReader 文件字符输入流
- FileWriter 文件字节输出流
- 多线程
- 面试题
String字符串new与不new的区别
String a =“abc” //abc会在方法区的常量池中创建
String a2=new String(“def”)//def会在常量池中创建 也会在(heap)堆中创建 需要创建两个 使用不推荐使用
面试题
判断底下创建几个对象 3个 堆中2个 常量池1个
String b1=new String(“def”)
String b2=new String(“def”)
常量
public class HelloWorld {
// 静态常量
public static final double PI = 3.14;
// 声明成员常量
final int y = 10;
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 声明局部常量
final double x = 3.3;
}
}
包装类
public class test {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int i=1;//基本数据类型
Integer j=new Integer(i);//引用数据类型
m1(j);
m1(i);//这样也可以
}
public static void m1(Object o){
System.out.println(o); //调用tostring方法 并且重新
}
}
String,StringBuffer,StringBuilder
public class test {
/**
* @param args
* stringbuffer stringbuilder 字符缓冲区
* 推荐字符串拼接使用
* 预先申请一块空间(16默认空间) 空间不够自动扩展
* 底层是char数组
* 优化 因为数组一旦创建无法改变长度 如果要改变需要频繁的从一个数组复制到另外一个数组 所以 需要预判数组大小 提高效率
*
* Stringbuffer 是线程安全的(可以在多线程下使用不会出现问题)
* stringbuilder 是线程不安全的(在多线程下使用可能出现问题)
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub 字符串拼接 用逗号隔开
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer();//默认16的长度
// StringBuffer sb1=new StringBuffer(30);//传入30的长度
String ins[]={"数学","英语","语文"};
for(int i=0;i<ins.length;i++){
if(i==ins.length-1){
sb.append(ins[i]);
}else{
sb.append(ins[i]);
sb.append(",");
}
}
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
日期
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
public class test {
/**
* @param args
* 日期SimpleDateFormat
* 日历calander
*
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub 字符串拼接 用逗号隔开
Date d=new Date(); //获取当前时间
System.out.println(d);
SimpleDateFormat sdf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-mm-dd");//数字格式转换格式 date—>String
System.out.println(sdf.format(d));
String strdate="2008-08-08";
try {
Date t=sdf.parse(strdate);//String—>date
System.out.println(t);
} catch (ParseException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
Date d2=new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()-1000*60*10);//系统当前时间的前10分钟
System.out.println(d2);
// 获取当前时间的星期几
// 先向系统获取日历
Calendar c=Calendar.getInstance();
// 查看星期几
int i=c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK);
System.out.println(i);
// 查看2008.8.8是星期几
String s="2008-08-08";
try {
Date d4=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-mm-dd").parse(s);//转换成日期型
c.setTime(d4);//转换成日历型
System.out.println(c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK));
} catch (ParseException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
数字格式化,数字类,random随机数
千分位
DecimalFormat df=newDecimalFormat("###,###")
System.out.println(df.format(1234567)) //1,234,567
千分位 保留两位小数
DecimalFormat df=newDecimalFormat("###,###.##")
千分位 保留4位小数 不够补0
DecimalFormat df=newDecimalFormat("###,###.0000")
java.math.BigDecimal 精确度极高 适合做财务软件
BigDecimal v1 =new BigDecimal(10)
BigDecimal v2 =new BigDecimal(10)
BigDecimal v3=v1.add(v2)
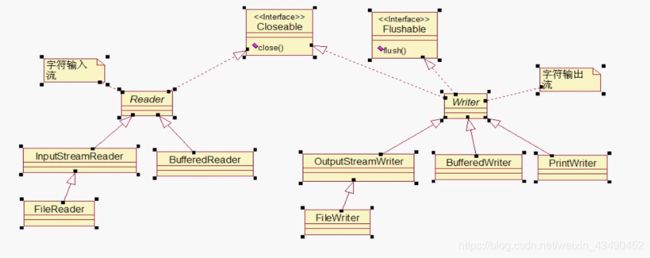
IO流
UML图
InputStream OutputStream
Reader Writer
FileInputStream 文件字节输入流
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
public class test1 {
/**
* @param args
* FileInputStream 文件字节输入流
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
FileInputStream fis=null;
try {
fis =new FileInputStream("test.txt"); //创建输入流
// int i=fis.read(); //读取文件中的第一个英文 字节形势 所以打印97
// while(i!= -1){
// System.out.println(i);
// i=fis.read();
// }
//
// 读的第二种方法
byte bytes[]=new byte[1024];
int i2=fis.read(bytes);
System.out.println(i2); //有3个元素
System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,i2)); //转换成字符串 从第0个开始 转到第 i2 元素
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
FileOutputStream 文件字节输出流
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class test2 {
/**
* @param args
* FileOutputStream 文件字节输出流
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
String i=sc.next();
FileOutputStream fos =null;
// fos=new FileOutputStream("test2.txt"); //覆盖的方式写
fos=new FileOutputStream("test2.txt",true); //添加的方式写
// String msg ="Hello";
byte bytes[] =i.getBytes();
fos.write(bytes); //写
fos.flush(); //强制写入 刷新
if(fos != null){
fos.close();
}
}
}
FileReader 文件字符输入流
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class test3 {
/**
* @param args
* FileReader 文件字符输入流 可以直接读取一个文字
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
FileReader fr=null;
try {
fr =new FileReader("test3.txt"); //创建输入流
char bytes[]=new char[1024];
int i2=fr.read(bytes);
System.out.println(i2); //有3个元素
System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,i2)); //转换成字符串 从第0个开始 转到第 i2 元素
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
FileWriter 文件字节输出流
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class test4 {
/**
* @param args
* FileWriter 文件字节输出流
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
FileWriter fw =null;
// fos=new FileOutputStream("test2.txt"); //覆盖的方式写
fw=new FileWriter("test2.txt",true); //添加的方式写
// String msg ="Hello";
fw.write("船袜"); //写
fw.flush(); //强制写入 刷新
if(fw != null){
fw.close();
}
}
}
多线程
public class test1 {
/**
* @param args
*
* 多线程
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Thread t=new Processor(); //创建线程
t.start();//线程启动
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { // main 方法结束 程序还在执行
System.out.println("2");
}
}
}
//定义一个线程
class Processor extends Thread{
// 重写run方法
public void run(){
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println("1");
}
}
}
public class test2 {
/**
* @param args
*
* 多线程
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Thread t=new Thread(new Processor2()); //创建线程
t.start();//线程启动
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { // main 方法结束 程序还在执行
System.out.println("2");
}
}
}
//定义一个线程
class Processor2 implements Runnable{
// 重写run方法
public void run(){
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println("1");
}
}
}
面试题
如果数据在(-128~127)之间,java 中引入了一个“整型常量池”,在方法区中
整型常量池中只存储集合中的数 ,没有超过集合的都在里面拿。
integer i5=127
integer i6=127 //内存地址一样 因为在集合区间
integer i5=-128
integer i6=-128 //内存地址一样 因为在集合区间
integer i5=128
integer i6=128 //内存地址不一样 因为不在集合区间