音视频学习(十三、音频数据处理)
其实对音频确实也没过多的研究,主要还是研究视频方面,不过有视频也有要音频,这样才是鲜活的视频,如果没音频看着视频也是假的,所以还是有必要学习一下音频。
13.1 音频编码
音频编码比较简单,直接使用FFmpeg的音频编码Demo就可以了,我这里也简单的列出调用的函数即可。
初始化函数:
1._code = avcodec_find_encoder(AV_CODEC_ID_AAC); //老规矩,找到编码器
2._ctx = avcodec_alloc_context3(_codec); //通过编码器找到context
3.avcodec_open2(_ctx, _codec, NULL); //初始化编码器
4._frame = av_frame_alloc();
5.av_frame_get_buffer(_frame, 0); //申请一个帧,并获取帧的buff
编码函数也比较简单:
1.av_init_packet(&pkt); //初始化一个packet
2.avcodec_encode_audio2(_ctx, &pkt, frame, &got_output); //进行音频编码
13.2 音频重采样
重采样初始化,这个也是有demo程序的,所以只是把函数的主干列出来就可以了:
1._src_channels = av_get_channel_layout_nb_channels(_resample_params.src_channel_layout) //通过布局情况,获取通道数
2._dst_channels = av_get_channel_layout_nb_channels(_resample_params.dst_channel_layout);
3._audio_fifo = av_audio_fifo_alloc(_resample_params.dst_sample_fmt, _dst_channels, 1); //以目标帧率为主,申请一个buff
4.swr_alloc(); //申请一个视频重采样的结构
5.swr_init(_swr_ctx); //填充数据,并且初始化swr
6.av_samples_alloc_array_and_samples(&_resampled_data, &linesize, _dst_channels, _resampled_data_size, _resample_params.dst_sample_fmt, 0); //申请接收数据
初始化完成了之后,就可以直接使用了,使用的步骤:
1.auto ret = _audio_resampler->SendResampleFrame(pcm, size); //采样到一帧数据之后,就会调用发送重采样函数
1.1 av_rescale_rnd //计算样本的目的数量
1.2 swr_convert //音频转化
1.3 av_audio_fifo_write //把转化后的数据写回audio_fifo
2._audio_resampler->ReceiveResampledFrame(resampled_frames,_audio_encoder->GetFrameSampleSize());
//接收音频重采样后的数据
2.1 av_audio_fifo_read(_audio_fifo, (void **)frame->data, desired_size);//通过读取一帧的数据,然后返回
然后把重采样到的数据送去音频编码
感觉写的很烂,但是不简单了解而无法进入下一步的学习,然后烂就烂把,反正以后再做修改就好了。
13.3 音频采集
音频采集我觉得就不用写了,这次音频采集跟视频采集是一样的,都是直接读取pcm文件,因为我们现在重点应该在rtmp上,所以这些采集可以先通过文件获取,反正以后需要其他方式采集的话,就重写一个类,替换现在的采集类就可以了。
13.4 rtmp推音频流
上面已经采集并编码好音频数据了,现在就可以做推流处理了,
case RTMP_BODY_AUD_SPEC:
{
AudioSpecMsg* audio_spec = (AudioSpecMsg*)data;
uint8_t aac_spec_[4];
aac_spec_[0] = 0xAF; //
aac_spec_[1] = 0x0; // 0 = aac sequence header
aacRtmpPackager::GetAudioSpecificConfig(&aac_spec_[2], audio_spec->_profile,
audio_spec->_sample_rate, audio_spec->_channels);
SendAudioSpecificConfig((char *)aac_spec_, 4);
break;
}
第一个字节0xAF,要回到FLV格式解析音频那一节看就明白了,那个位数对应什么我这里就不解析了,我只贴了一个flv格式的文件出来,看到音频的第一个字节就是0xAF
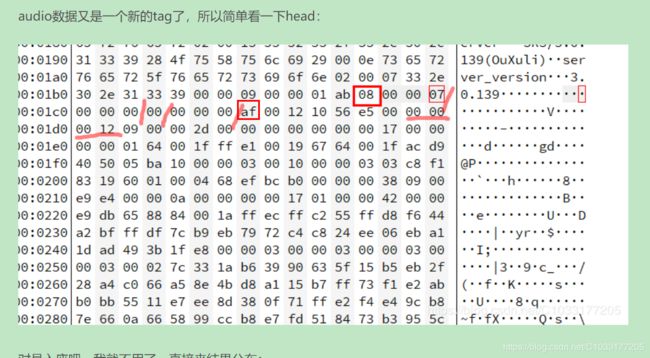
第二个字节就简单了:
如果是AAC配置信息,就是0,如果是裸数据就是1,
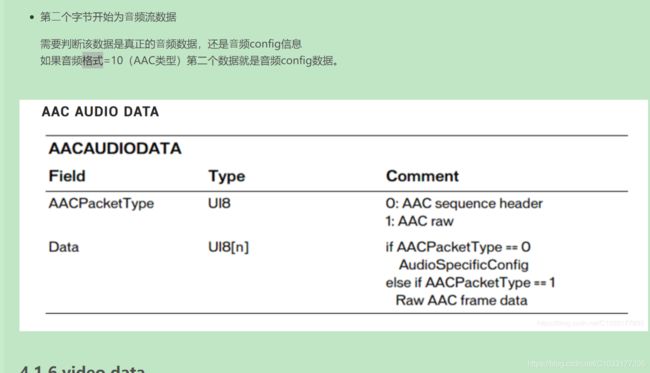
flv格式的数据准备好了之后,我们来看一下aac的编码格式,不过这个函数并没有按照AAC的编码格式来写的,详细分析AAC可以会到上一节,
int AACRTMPPackager::GetAudioSpecificConfig(uint8_t* data, const uint32_t profile,
const uint32_t samplerate,
const uint32_t channel_num)
{
//uint8_t type:5;//编码结构类型,AAC main编码为1,LOW低复杂度编码为2,SSR为3
//uint8_t sample_rate:4;//采样率
//uint8_t channel_num:4;//声道数
//uint8_t tail:3;//最后3位固定为0
uint16_t _profile = (uint16_t)profile+1; //哪个级别的AAC
_profile <<= 11;
uint32_t _samplerate = 0; //那个频率的采样
switch (samplerate)
{
case 96000:
_samplerate = 0;
break;
case 88200:
_samplerate = 1;
break;
case 64000:
_samplerate = 2;
break;
case 48000:
_samplerate = 3;
break;
case 44100:
_samplerate = 4;
break;
case 32000:
_samplerate = 5;
break;
case 24000:
_samplerate = 6;
break;
case 22050:
_samplerate = 7;
break;
case 16000:
_samplerate = 8;
break;
case 12000:
_samplerate = 9;
break;
case 11025:
_samplerate = 10;
break;
case 8000:
_samplerate = 11;
break;
case 7350:
_samplerate = 12;
break;
default:
_samplerate = 4;
return -1;
break;
}
_samplerate <<= 7;
uint16_t _channel_num = (uint16_t)channel_num; //通道
_channel_num <<= 3;
// 2 4 1 3
uint16_t audio_spec = _profile | _samplerate | _channel_num;
//这个就是自己数据的封装,到解码的时候,只有自己的解码程序才能解
data[0] = (uint8_t)(audio_spec >> 8);
data[1] = 0xff & audio_spec;
return 0;
}
发送裸数据就比较简单了,只要填充两个字节的数据就可以了,然后调用rtmp发送函数直接发送
aud_raw_msg->data[0] = 0xaf;
aud_raw_msg->data[1] = 0x01; // 1 = raw data数据
memcpy(&aud_raw_msg->data[2], _aac_buf, aac_size);
_rtmp_pusher->post(RTMP_BODY_AUD_RAW, aud_raw_msg);
13.5 rtmp接收音频流
我们来接收一下发送端发送过来的音频流,先接收音频的配置信息:
// AAC sequence
if (sequence)
{
format = (packet.m_body[0] & 0xf0) >> 4; //这个就是分析0xAF的 //音频格式
samplerate = (packet.m_body[0] & 0x0c) >> 2; //采样率
sampledepth = (packet.m_body[0] & 0x02) >> 1; //采样的长度
type = packet.m_body[0] & 0x01; //音频类型
// sequence = packet.m_body[1];
// AAC(AudioSpecificConfig)
if (format == 10) { // AAC格式
uint8_t ch0 = packet.m_body[2]; //这个字节的数据,就是我们自己封装的数据了
uint8_t ch1 = packet.m_body[3];
uint16_t config = ((ch0 << 8) | ch1);
_profile = (config & 0xF800) >> 11; //这个就是我们自己发过来的数据了,但是我们没有按adts格式发送
_sample_frequency_index = (config & 0x0780) >> 7;
_channels = (config & 0x78) >> 3;
frame_length_flag = (config & 0x04) >> 2;
depend_on_core_coder = (config & 0x02) >> 1;
extension_flag = config & 0x01;
}
// Speex(Fix data here, so no need to parse...)
else if (format == 11) { // MP3格式
// 16 KHz, mono, 16bit/sample
type = 0;
sampledepth = 1;
samplerate = 4;
}
audio_sample_rate = rtmpbase::GetSampleRateByFreqIdx(_sample_frequency_index);
AudioSpecMsg *aud_spec_msg = new AudioSpecMsg(_profile,
_channels,
audio_sample_rate);
audio_callable_object_(RTMP_BODY_AUD_SPEC, aud_spec_msg, false); //调用回调,把音频数据返回
}
接下来看看音频裸数据发送过来的结果:
// Audio frames
else
{
// 每帧都有一个adts
// ADTS(7 bytes) + AAC data
uint32_t data_len = packet.m_nBodySize - 2 + 7;
uint8_t adts[7];
//竟然是自己加adts
adts[0] = 0xff;
adts[1] = 0xf9;
adts[2] = ((_profile - 1) << 6) | (_sample_frequency_index << 2) | (_channels >> 2);
adts[3] = ((_channels & 3) << 6) + (data_len >> 11);
adts[4] = (data_len & 0x7FF) >> 3;
adts[5] = ((data_len & 7) << 5) + 0x1F;
adts[6] = 0xfc;
// Write audio frames
AudioRawMsg *aud_raw = new AudioRawMsg(data_len);
memcpy(aud_raw->data, adts, 7);
memcpy(aud_raw->data + 7, packet.m_body + 2, packet.m_nBodySize - 2); //保存数据-2是要把头去掉
if(_audio_pre_pts == -1){
_audio_pre_pts= packet.m_nTimeStamp;
if(!packet.m_hasAbsTimestamp) {
printf("no init video pts\n");
}
}
else {
if(packet.m_hasAbsTimestamp)
_audio_pre_pts= packet.m_nTimeStamp;
else
_audio_pre_pts += packet.m_nTimeStamp;
}
aud_raw->pts = _audio_pre_pts;
audio_callable_object_(RTMP_BODY_AUD_RAW, aud_raw, false);
}
还是按视频的老规矩,裸数据发送过来是不带adts头的,所以我们接受的时候需要补上adts头,这样才能符合AAC格式,AAC格式的详解请看以前的文章,这里我就不再过多分析了,就是对应各个位对应的是啥,保存数据的时候-2是要把FLV表示音频的数据减2,这样就是符合AAC的格式了,然后发送给回调函数。
13.6 接收数据回调函数
回调函数就比较简单了,只需要把数据压入队列,然后另外一个线程,音频解码线程,会自动判断队列中是否有数据,这个下节讲。
void PullWork::audioCallback(int what, MsgBaseObj *data, bool flush)
{
_audio_decode_loop->post(what, data, flush);
//int64_t diff = TimesUtil::GetTimeMillisecond() - cur_time;
// if(diff>5)
// LogInfo("audioCallback t:%ld", diff);
}
13.7 音频解码初始化
在上节已经提过了,这个是专门负责音频解码部分的,接下来我们看看这个初始化函数,这个类继承于Looper类,这个类之间有讲过,只要是负责创建一个新的线程,然后在线程中循环检测队列中是否有数据,如果有需要就提取出数据,然后传参给回调函数,回调函数就是我们当前音频解码类,这个等下讲述:
int AudioDecodeLopp::Init(const Properties &properties)
{
_aac_decoder = new aacDecoder(); //音频解码类创建
if(!_aac_decoder)
{
printf("new AACDecoder() failed\n");
return -1;
}
Properties properties2;
if(_aac_decoder->Init(properties2) != 0) //音频解初始化
{
printf("aac_decoder_ Init failed\n");
return -2;
}
_pcm_buf = new uint8_t[PCM_BUF_MAX_SIZE]; //申请一个buff
if(!_pcm_buf)
{
printf("pcm_buf_ new failed");
return -3;
}
return 0;
}
13.8 AAC解码部分
音频解码比较简单:
1.codec = avcodec_find_decoder(AV_CODEC_ID_AAC); //查找解码器
2.avcodec_alloc_context3(codec); //申请解码的数据结构
3.avcodec_open2(ctx, codec, NULL) //打开解码器
4.packet = av_packet_alloc(); //申请一个包
5.frame = av_frame_alloc(); //申请一帧内存
解码部分:
int aacDecoder::Decode(const uint8_t *in, int inLen, uint8_t *out, int &outLen)
{
//If we have input
if (inLen<=0)
return -1;
//Set data
packet->data = (uint8_t *)in;
packet->size = inLen;
//Decode it
if (avcodec_send_packet(ctx, packet)<0) //发送一帧数据
//nothing
{
printf("-AACDecoder::Decode() Error decoding AAC packet\n");
return -2;
}
//Release side data
av_packet_free_side_data(packet); //释放数据
//If we got a frame
if (avcodec_receive_frame(ctx, frame)<0) //接收到解码后的数据
//Nothing yet
{
outLen = 0;
return -3;
}
//Get data
//1024
float *buffer1 = (float *) frame->data[0]; // LLLLL float 32bit [-1~1]
float *buffer2 = (float *) frame->data[1]; // RRRRRR
auto len = frame->nb_samples;
int16_t *sample = (int16_t *)out;
//Convert to SWORD
for (size_t i=0; i<len; ++i) //转化陈lrlrlr格式
{
// lrlrlr
sample[i*2] = (int16_t)(buffer1[i] * 0x7fff);
sample[i*2 + 1] = (int16_t)(buffer2[i] * 0x7fff);
}
outLen = 4096;
static FILE *dump_pcm = NULL;
if(!dump_pcm)
{
dump_pcm = fopen("aac_dump.pcm", "wb");
if(!dump_pcm)
{
printf("fopen aac_dump.pcm failed\n");
}
}
if(dump_pcm)
{//ffplay -ar 48000 -ac 2 -f s16le -i aac_dump.pcm
fwrite(out, 1,outLen, dump_pcm);
fflush(dump_pcm);
}
//Return number of samples
return 0;
}
13.9 解码线程
上面已经介绍了AAC解码相关模块,虽然已经有了解码函数,但是需要一个驱动源,上面已经介绍过,我们的音频解码模块内部有一个线程,如果队列中有数据的话,就会取出数据,然后调用回调:
void AudioDecodeLopp::handle(int what, MsgBaseObj *data)
{
if(what == RTMP_BODY_AUD_SPEC) //这个是音频配置信息,我们接受到音频配置信息之后,会做音频相关的初始化
{
AudioSpecMsg *aud_spec = (AudioSpecMsg *)data;
// 目前没有做音视频同步,所以现在这里进行音频输出的初始化
if(!_audio_out_sdl)
{
//音频初始化
}
delete aud_spec;
}
else if(what == RTMP_BODY_AUD_RAW) //这个是音频的裸数据,接受到数据之后,会直接调用解码函数,解码函数返回了数据之后
//可以直接播放
{
AudioRawMsg *aud_raw = (AudioRawMsg *)data;
_pcm_buf_size = PCM_BUF_MAX_SIZE;
// 可以发送adts header, 如果不发送adts则要初始化 ctx的参数
if(_aac_decoder->Decode(aud_raw->data , aud_raw->size ,
_pcm_buf, _pcm_buf_size) == 0)
{
//直接播放
}
delete aud_raw; // 要手动释放资源
}
else
{
printf("can't handle what:%d", what);
delete data;
}
}
整个音频的推流拉流就介绍完成了,虽然我也尝试这个代码,感觉bug不少,不过没关系,先能跑起来再说,bug以后再修复,如果一直在修复的话,学习速度就慢,先往后走,这些细节以后再回来修复。