SpringBoot-2.2.5入门-环境配置-程序启动-配置文件加载
目录
- SpringBoot简介
- 环境准备
- Maven设置
- IDEA设置maven环境配置
- 创建helloWord程序
- pom文件
- 主程序入口
- 程序入口类:HelloWordApplication类
- @SpringBootApplication: springboot标注在一个类上说明这是一个主配置类,运行这个类的main方法来启动springboot应用。
- @SpringBootConfiguration注解
- @EnableAutoConfiguration开启自动配置功能
- @AutoConfigurationPackage:自动配置包
- @Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class);
- 配置文件
- YMAL语法
- 值得写法
- 字面量--数字、字符串、布尔值
- 对象(属性: 值)map(key: value)
- 数组(list、set)
- 配置文件数据绑定
- 配置文件代码提示
- 中文乱码
- @Vaule注解
- @Value与@ConfigurationProperties功能对比
- 4、@PropertySource&@ImportResource&@Bean
- Profile
- 1、多Profile文件
- 2、yml支持多文档块方式
- 激活指定profile
- 配置文件加载位置
- 外部配置加载顺序
SpringBoot简介
简化Spring应用开发的一个框架;
整个Spring技术栈的一个大整合;
J2EE开发的一站式解决方案;
环境准备
本文章的环境为:
–jdk1.8:java version “1.8.0_191”
–maven3.x:maven 3.3以上版本;Apache Maven 3.6.1
–IntelliJIDEA2017:IntelliJ IDEA 2017.2.2 x64、STS
–SpringBoot 2.2.5.RELEASE;
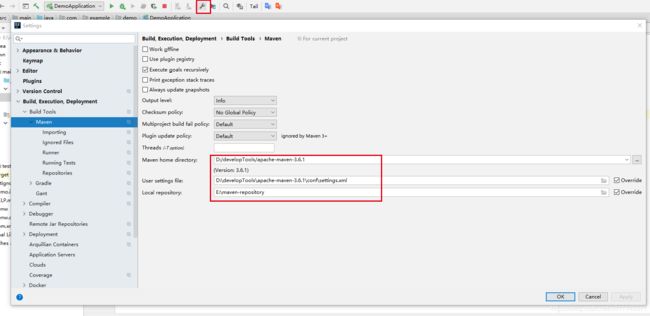
Maven设置
给maven的setting文件的Profiles标签添加profile标签
<profile>
<id>jdk-1.8id>
<activation>
<activeByDefault>trueactiveByDefault>
<jdk>1.8jdk>
activation>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8maven.compiler.target>
<maven.compiler.compilerVersion>1.8maven.compiler.compilerVersion>
properties>
profile>
IDEA设置maven环境配置
创建helloWord程序
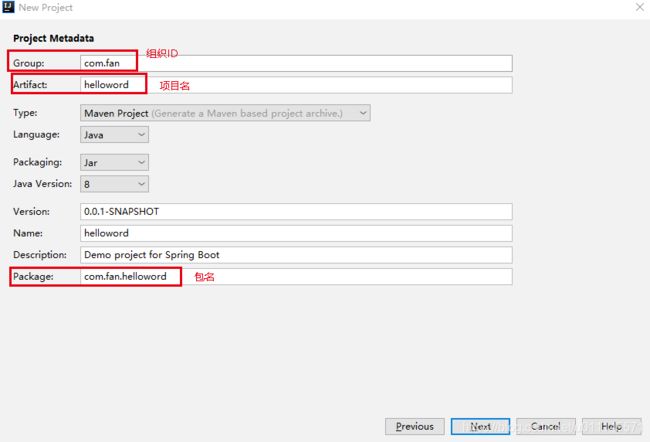
选择需要的启动器
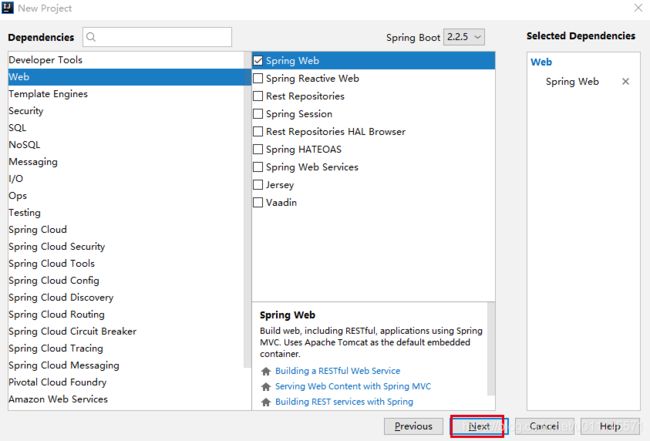
创建helloController类
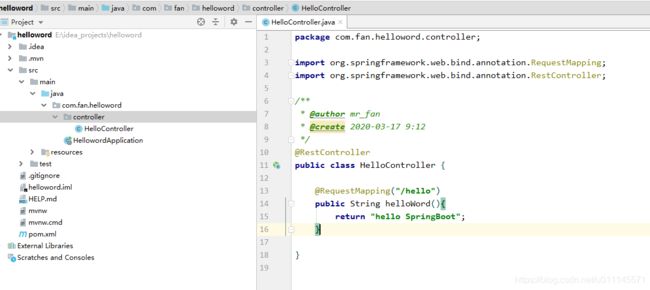
启动程序测试,运行main方法启动。
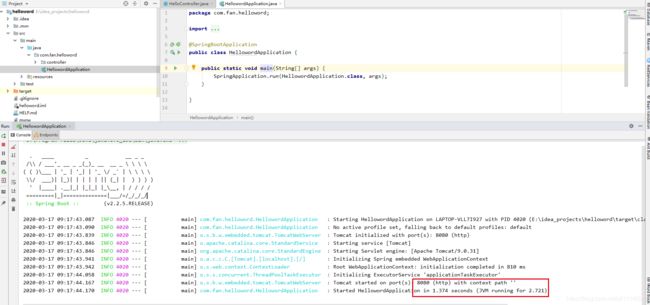
浏览器访问
pom文件
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId>
<version>2.2.5.RELEASEversion>
<relativePath/>
parent>
<groupId>com.fangroupId>
<artifactId>hellowordartifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOTversion>
<name>hellowordname>
<description>Demo project for Spring Bootdescription>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8java.version>
properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId>
<scope>testscope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.junit.vintagegroupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engineartifactId>
exclusion>
exclusions>
dependency>
dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-pluginartifactId>
plugin>
plugins>
build>
project>
主程序入口
程序入口类:HelloWordApplication类
@SpringBootApplication //来标注一个主程序,这是一个springboot应用
public class HellowordApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(HellowordApplication.class, args);
}
}
@SpringBootApplication: springboot标注在一个类上说明这是一个主配置类,运行这个类的main方法来启动springboot应用。
@SpringBootConfiguration注解
点击@SpringBootApplication注解,进入到SpringBootApplication类
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
/**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration classes such that they will never be applied.
* @return the classes to exclude
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class)
Class<?>[] exclude() default {};
这个类上标注了@SpringBootConfiguration注解,说明这是一个springboot的配置类。
@EnableAutoConfiguration开启自动配置功能
在该类上也有两个注解,
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
我们需要配置的东西,Spring Boot帮我们自动配置;@EnableAutoConfiguration告诉SpringBoot开启自动配置功能;这样自动配置才能生效;
@AutoConfigurationPackage:自动配置包
将主配置类(@SpringBootApplication标注的类)的所在包及下面所有子包里面的所有组件扫描到Spring容器
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class);
Spring的底层注解@Import,给容器中导入一个组件;导入的组件由AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class;给容器中导入组件?
AutoConfigurationImportSelector:导入哪些组件的选择器;
将所有需要导入的组件以全类名的方式返回;这些组件就会被添加到容器中;
会给容器中导入非常多的自动配置类(xxxAutoConfiguration);就是给容器中导入这个场景需要的所有组件,并配置好这些组件;
可以在该类的selectImports方法上断点方式启动,查看返回值
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return NO_IMPORTS;
}
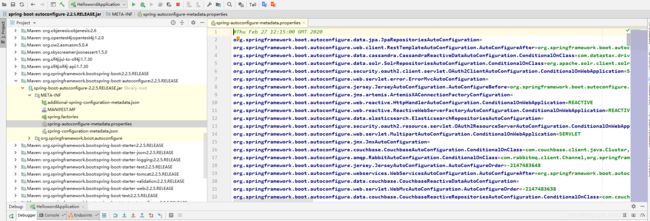
//通过类加载器获取类路径下的META-INF/spring-autoconfigure-metadata.properties文件并解析文件中的属性值
AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata = AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader
.loadMetadata(this.beanClassLoader);
//经properties中的默认的组件以全类名进行封装
AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = getAutoConfigurationEntry(autoConfigurationMetadata,
annotationMetadata);
//返回默认配置组件的全类名数组,通过impot加入到容器中
return StringUtils.toStringArray(autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations());
}
这样就省去了我们手动编写配置文件的方式去注入相关组件的工作。
Spring Boot在启动的时候从类路径下的META-INF/spring-autoconfigure-metadata.properties指定的值,将这些值作为自动配置类导入到容器中,自动配置类就生效,帮我们进行自动配置工作;==以前我们需要自己配置的东西,自动配置类都帮我们
配置文件
springboot使用一个默认的全局配置文件,文件名是application.properties、application.yml。
作用:修改springboot自动配置的默认值
YMAL文件:是springboot的配置文件,该配置文件的特点是以数据为中心,省去了之前xml配置文件中的各种标签的繁琐。该文件的格式语法简单。
以配置端口号为例:
YMAL配置:
server:
port: 8081
xml配置:
<server>
<port>8081port>
server>
YMAL语法
1、基本语法:
k:(空格)v 以键值对的方式进行标识,中间必须要有空格
2、空格缩进标识层级关系,只要缩进对其的一列都是同一层级的
例如:
server:
port: 8081
servlet:
context-path: /test
值得写法
字面量–数字、字符串、布尔值
语法k: v
字符串默认不用写单引号或者双引号
“”:双引号标识,不会对特殊字符进行转义
‘’:单引号会对特殊字符进行转义
对象(属性: 值)map(key: value)
friends:
lastName: zhangsan
age: 20
行内写法:
friends: {lastName: zhangsan,age: 18}
数组(list、set)
pets:
- cat
- dog
- pig
行内写法
pets: [cat,dog,pig]
配置文件数据绑定
配置文件
person:
age: ${random.int} #占位符
last-name: 张三 #松散绑定
isDel: false
friends:
-小明
-小红
animals:
dag: 小黑
pig: 小猪
绑定的java.class
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
public class Person {
private String lastName;
private Integer age;
private boolean isDel;
private List<String> friends;
private Map<String,String> animals;
@Comment将bean注入到容器中
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “person”)与配置文件数据绑定,通过配置文件注入属性值,prefix属性值,指定配置文件的哪个属性。
运行测试:
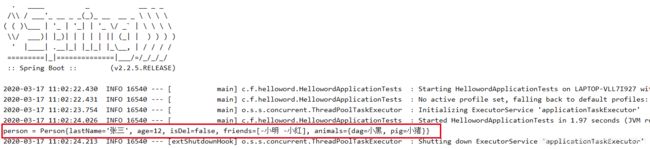
配置文件代码提示
在pom文件中引入配置文件处理器依赖包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processorartifactId>
<optional>trueoptional>
dependency>
中文乱码
运行时可能会出现中文乱码,因为properties在idea中的默认编码是utf8编码,设置如下:
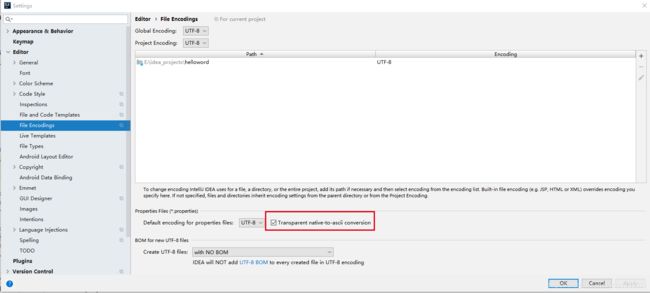
@Vaule注解
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
@Validated
public class Person {
@Value("${person.last-name}")
//@Email //数据校验
private String lastName;
@Value("#{11*2}")//spEL表达式
private Integer age;
@Value("true")
private boolean isDel;
private List<String> friends;
private Map<String,String> animals;
@Value与@ConfigurationProperties功能对比
| 功能 | @Value | ConfigurationProperties |
|---|---|---|
| 描述 | 单个值注入 | 批量值注入 |
| 松散绑定 | 不支持 | 支持 |
| spEL | 支持 | 不支持 |
| GRS303数据验证 | 不支持 | 支持 |
| 复杂类型封装 | 不支持 | 支持 |
4、@PropertySource&@ImportResource&@Bean
@PropertySource:加载指定的配置文件;
/**
* 将配置文件中配置的每一个属性的值,映射到这个组件中
* @ConfigurationProperties:告诉SpringBoot将本类中的所有属性和配置文件中相关的配置进行绑定;
* prefix = "person":配置文件中哪个下面的所有属性进行一一映射
*
* 只有这个组件是容器中的组件,才能容器提供的@ConfigurationProperties功能;
* @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")默认从全局配置文件中获取值;
*
*/
@PropertySource(value = {"classpath:person.properties"})
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
//@Validated
public class Person {
//@Value("${person.last-name}")
//@Email //数据校验
private String lastName;
// @Value("#{11*2}")//spEL表达式
private Integer age;
// @Value("true")
private boolean isDel;
private List<String> friends;
private Map<String,String> animals;
@ImportResource:导入Spring的配置文件,让配置文件里面的内容生效;
Spring Boot里面没有Spring的配置文件,我们自己编写的配置文件,也不能自动识别;
想让Spring的配置文件生效,加载进来;@ImportResource标注在一个配置类上
@ImportResource(locations = {"classpath:beans.xml"})
导入Spring的配置文件让其生效
编写Spring的配置文件
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="helloService" class="com.atguigu.springboot.service.HelloService">bean>
beans>
SpringBoot推荐给容器中添加组件的方式;推荐使用全注解的方式
1、配置类 @Configuration相当于Spring配置文件
2、使用@Bean给容器中添加组件
/**
* @Configuration:指明当前类是一个配置类;就是来替代之前的Spring配置文件
* 在配置文件中用Profile
1、多Profile文件
我们在主配置文件编写的时候,文件名可以是 application-{profile}.properties/yml
默认使用application.properties的配置;
2、yml支持多文档块方式
server:
port: 8080
spring:
profiles:
active: prod
---
spring:
profiles: dev
server:
port: 8081
---
spring:
profiles: prod
server:
port: 8082
激活指定profile
1、在配置文件中指定 spring.profiles.active=dev
2、命令行:
java -jar spring-boot-02-config-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --spring.profiles.active=dev;
可以直接在测试的时候,配置传入命令行参数
3、虚拟机参数;
-Dspring.profiles.active=dev
配置文件加载位置
springboot 启动会扫描以下位置的application.properties或者application.yml文件作为Spring boot的默认配置文件
–file:./config/
–file:./
–classpath:/config/
–classpath:/
优先级由高到底,高优先级的配置会覆盖低优先级的配置;
SpringBoot会从这四个位置全部加载主配置文件;互补配置;
对同一级别的配置文件,properties配置文件的级别高于yml配置文件的级别
项目打包好以后,我们可以使用命令行参数的形式,启动项目的时候来指定配置文件的新位置;指定配置文件和默认加载的这些配置文件共同起作用形成互补配置;
java -jar spring-boot-02-config-02-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --spring.config.location=G:/application.properties
外部配置加载顺序
SpringBoot也可以从以下位置加载配置; 优先级从高到低;高优先级的配置覆盖低优先级的配置,所有的配置会形成互补配置
1.命令行参数
所有的配置都可以在命令行上进行指定
java -jar spring-boot-02-config-02-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --server.port=8087 --server.context-path=/abc
多个配置用空格分开; --配置项=值
2.来自java:comp/env的JNDI属性
3.Java系统属性(System.getProperties())
4.操作系统环境变量
5.RandomValuePropertySource配置的random.*属性值
由jar包外向jar包内进行寻找;
优先加载带profile
6.jar包外部的application-{profile}.properties或application.yml(带spring.profile)配置文件
7.jar包内部的application-{profile}.properties或application.yml(带spring.profile)配置文件
再来加载不带profile
8.jar包外部的application.properties或application.yml(不带spring.profile)配置文件
9.jar包内部的application.properties或application.yml(不带spring.profile)配置文件
10.@Configuration注解类上的@PropertySource
11.通过SpringApplication.setDefaultProperties指定的默认属性