【小家Spring】Spring MVC容器的web九大组件之---ViewResolver源码详解---视图View详解
每篇一句
学好模式比具体学一门技术来得更重要。因为技术是战术,设计模式(策略)才是战略。战术是经常变的,但战略是基本不变的。 所以建议学会站在一个更好的角度去看待问题
相关阅读
【小家Spring】Spring MVC容器的web九大组件之—ViewResolver源码详解—视图解析器ViewResolver详解
【小家Spring】Spring MVC容器的web九大组件之—HandlerAdapter源码详解—HttpMessageConverter 消息转换器详解
【小家Spring】Spring MVC容器的web九大组件之—HandlerAdapter源码详解—HttpMessageConverter的匹配规则(选择原理)
前言
上篇文章已经重点讲解过了:ViewResolver视图解析器
【小家Spring】Spring MVC容器的web九大组件之—ViewResolver源码详解—视图解析器ViewResolver详解
SpringMVC用于处理视图最重要的两个接口是ViewResolver和View。ViewResolver的主要作用 是把一个逻辑上的视图名称解析为一个真正的视图,SpringMVC中用于把View对象呈现给客户端的 是View对象本身,而ViewResolver只是把逻辑视图名称解析为对象的View对象。View接口的主要 作用是用于处理视图,然后返回给客户端。
View
View是用于MVC交互的Web视图。实现负责呈现内容,并公开模型。单个视图可显示多个模型属性
视图实现可能差异很大,比如我们最基础的实现:JSP就是一种视图展示方式。当然还有后面的Jstl以及FreeMarker等。此接口旨在避免限制可能的实现范围
视图应该是bean(但不一定需要放进容器)。它们很可能被viewresolver实例化为bean。
由于这个接口是无状态的,视图实现应该是线程安全的。
public interface View {
// @since 3.0
// HttpStatus的key,可议根据此key去获取。备注:并不是每个视图都需要实现的。目前只有`RedirectView`有处理
String RESPONSE_STATUS_ATTRIBUTE = View.class.getName() + ".responseStatus";
// @since 3.1 也会这样去拿:request.getAttribute(View.PATH_VARIABLES)
String PATH_VARIABLES = View.class.getName() + ".pathVariables";
// The {@link org.springframework.http.MediaType} selected during content negotiation
// @since 3.2
// MediaType mediaType = (MediaType) request.getAttribute(View.SELECTED_CONTENT_TYPE)
String SELECTED_CONTENT_TYPE = View.class.getName() + ".selectedContentType";
// Return the content type of the view, if predetermined(预定的)
@Nullable
default String getContentType() {
return null;
}
// 这是最重要的 根据model里面的数据,request等 把渲染好的数据写进response里~
void render(@Nullable Map<String, ?> model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception;
}
看看它的继承树:

可以看出来它只有两个分支:AbstractView和SmartView,而SmartView的唯一实现为:RedirectView并且它也继承自AbstractView。
我们可以粗略的认为:Spring MVC内置的所有的View都是
AbstractView的子类
AbstractView
AbstractView实现了render方法,主要做的操作是将model中的参数和request中的参数全部都放到Request中,然后就转发Request就可以了
public abstract class AbstractView extends WebApplicationObjectSupport implements View, BeanNameAware {
/** Default content type. Overridable as bean property. */
public static final String DEFAULT_CONTENT_TYPE = "text/html;charset=ISO-8859-1";
/** Initial size for the temporary output byte array (if any). */
private static final int OUTPUT_BYTE_ARRAY_INITIAL_SIZE = 4096;
// 这几个属性值,没有陌生的。在视图解析器章节里面都有解释过~~~
@Nullable
private String contentType = DEFAULT_CONTENT_TYPE;
@Nullable
private String requestContextAttribute;
// "Static" attributes are fixed attributes that are specified in the View instance configuration
// "Dynamic" attributes, on the other hand,are values passed in as part of the model.
private final Map<String, Object> staticAttributes = new LinkedHashMap<>();
private boolean exposePathVariables = true;
private boolean exposeContextBeansAsAttributes = false;
@Nullable
private Set<String> exposedContextBeanNames;
@Nullable
private String beanName;
// 把你传进俩的Properties 都合并进来~~~
public void setAttributes(Properties attributes) {
CollectionUtils.mergePropertiesIntoMap(attributes, this.staticAttributes);
}
...
@Override
public void render(@Nullable Map<String, ?> model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// 合并staticAttributes、pathVars、model数据到一个Map里来
// 其中:后者覆盖前者的值(若有相同key的话~~)也就是所谓的model的值优先级最高~~~~
// 最终还会暴露RequestContext对象到Model里,因此model里可以直接访问RequestContext对象哦~~~~
Map<String, Object> mergedModel = createMergedOutputModel(model, request, response);
// 默认实现为设置几个响应头~~~
// 备注:默认情况下pdf的view、xstl的view会触发下载~~~
prepareResponse(request, response);
// getRequestToExpose表示吧request暴露成:ContextExposingHttpServletRequest(和容器相关,以及容器内的BeanNames)
// renderMergedOutputModel是个抽象方法 由子类去实现~~~~
renderMergedOutputModel(mergedModel, getRequestToExpose(request), response);
}
//================下面是一些方法,父类提供 子类可以直接使用的方法==============
// 一个temp输出流,缓冲区大小为4096 字节流
protected ByteArrayOutputStream createTemporaryOutputStream() {
return new ByteArrayOutputStream(OUTPUT_BYTE_ARRAY_INITIAL_SIZE);
}
// 把字节流写进response里面~~~
protected void writeToResponse(HttpServletResponse response, ByteArrayOutputStream baos) throws IOException {
// Write content type and also length (determined via byte array).
response.setContentType(getContentType());
response.setContentLength(baos.size());
// Flush byte array to servlet output stream.
ServletOutputStream out = response.getOutputStream();
baos.writeTo(out);
out.flush();
}
// 相当于如果request.getAttribute(View.SELECTED_CONTENT_TYPE) 指定了就以它为准~
protected void setResponseContentType(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
MediaType mediaType = (MediaType) request.getAttribute(View.SELECTED_CONTENT_TYPE);
if (mediaType != null && mediaType.isConcrete()) {
response.setContentType(mediaType.toString());
}
else {
response.setContentType(getContentType());
}
}
...
}
该抽象类主要是提供了对render方法的模版实现,以及提供一些基础方法供给子类来使用,比如createTemporaryOutputStream()等等
AbstractJackson2View
这个是一个比较新的Viw(@since 4.1),它是基于Jackson渲染的视图。
//@since 4.1
// Compatible with Jackson 2.6 and higher, as of Spring 4.3.
public abstract class AbstractJackson2View extends AbstractView {
private ObjectMapper objectMapper;
private JsonEncoding encoding = JsonEncoding.UTF8;
@Nullable
private Boolean prettyPrint;
private boolean disableCaching = true;
protected boolean updateContentLength = false;
// 唯一构造函数,并且还是protected的~~
protected AbstractJackson2View(ObjectMapper objectMapper, String contentType) {
this.objectMapper = objectMapper;
configurePrettyPrint();
setContentType(contentType);
setExposePathVariables(false);
}
... // get/set方法
// 复写了父类的此方法~~~ setResponseContentType是父类的哟~~~~
@Override
protected void prepareResponse(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
setResponseContentType(request, response);
// 设置编码格式,默认是UTF-8
response.setCharacterEncoding(this.encoding.getJavaName());
if (this.disableCaching) {
response.addHeader("Cache-Control", "no-store");
}
}
// 实现了父类的渲染方法~~~~
@Override
protected void renderMergedOutputModel(Map<String, Object> model, HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
ByteArrayOutputStream temporaryStream = null;
OutputStream stream;
// 注意此处:updateContentLength默认值是false 所以会直接从response里面吧输出流拿出来 而不用temp流
if (this.updateContentLength) {
temporaryStream = createTemporaryOutputStream();
stream = temporaryStream;
}
else {
stream = response.getOutputStream();
}
Object value = filterAndWrapModel(model, request);
// value是最终的从model中出来的~~~~这里就是把value值写进去~~~~
// 先通过stream得到一个JsonGenerator,然后先writePrefix(generator, object)
// 然后objectMapper.writerWithView
// 最后writeSuffix(generator, object); 然后flush即可~
writeContent(stream, value);
if (temporaryStream != null) {
writeToResponse(response, temporaryStream);
}
}
// 筛选Model并可选地将其包装在@link mappingjacksonvalue容器中
protected Object filterAndWrapModel(Map<String, Object> model, HttpServletRequest request) {
// filterModel抽象方法,从指定的model中筛选出不需要的属性值~~~~~
Object value = filterModel(model);
// 把这两个属性值,选择性的放进container容器里面 最终返回~~~~
Class<?> serializationView = (Class<?>) model.get(JsonView.class.getName());
FilterProvider filters = (FilterProvider) model.get(FilterProvider.class.getName());
if (serializationView != null || filters != null) {
MappingJacksonValue container = new MappingJacksonValue(value);
if (serializationView != null) {
container.setSerializationView(serializationView);
}
if (filters != null) {
container.setFilters(filters);
}
value = container;
}
return value;
}
}
MappingJackson2JsonView
它是用于返回Json视图的(下面会介绍Spring MVC返回json的三种方式)
// @since 3.1.2 可议看到它出现得还是比较早的~
public class MappingJackson2JsonView extends AbstractJackson2View {
public static final String DEFAULT_CONTENT_TYPE = "application/json";
@Nullable
private String jsonPrefix;
@Nullable
private Set<String> modelKeys;
private boolean extractValueFromSingleKeyModel = false;
@Override
protected Object filterModel(Map<String, Object> model) {
Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>(model.size());
Set<String> modelKeys = (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.modelKeys) ? this.modelKeys : model.keySet());
// 遍历model所有内容~
model.forEach((clazz, value) -> {
// 符合下列条件的会给排除掉~~~
// 不是BindingResult类型 并且 modelKeys包含此key 并且此key不是JsonView和FilterProvider 这种key就排除掉~~~
if (!(value instanceof BindingResult) && modelKeys.contains(clazz) &&
!clazz.equals(JsonView.class.getName()) &&
!clazz.equals(FilterProvider.class.getName())) {
result.put(clazz, value);
}
});
// 如果只需要排除singleKey,那就返回第一个即可,否则result全部返回
return (this.extractValueFromSingleKeyModel && result.size() == 1 ? result.values().iterator().next() : result);
}
// 如果配置了前缀,把前缀写进去~~~
@Override
protected void writePrefix(JsonGenerator generator, Object object) throws IOException {
if (this.jsonPrefix != null) {
generator.writeRaw(this.jsonPrefix);
}
}
}
此视图是专门来处理作为一个json视图格式进行返回的。那么接下里有必要举例说明一下,Spring MVC返回Json格式数据的多种方式:
Spring MVC返回json的三种方式
- 使用
MappingJackson2JsonView,其实它是相对来说比较新的一种返回json数据的放置,主要是用到了这个视图的能力。
直接使用它相对来说还是比较麻烦点的,一般都需要结合内容协商视图解析器来使用(比如把它设置默认处理json的视图),但是本文就做一个Demo,所以还是简单的处理一下吧:使用BeanNameViewResolver执行我们定义的这个视图去即可:
@RequestMapping(value = "/json")
public String testView(Model model) {
// 注意Model不添加数据,将会是一个空的JSON串
model.addAttribute("name", "fsx");
model.addAttribute("age", 18);
return "mappingJackson2JsonView";
}
// 配置视图:
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
public class WebMvcConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
// 此处为配置了一个前缀,发现前缀可以解决jsonp的问题~~~
@Bean
public MappingJackson2JsonView mappingJackson2JsonView() {
MappingJackson2JsonView mappingJackson2JsonView = new MappingJackson2JsonView();
mappingJackson2JsonView.setJsonPrefix("prefix");
return mappingJackson2JsonView;
}
@Override
public void configureViewResolvers(ViewResolverRegistry registry) {
BeanNameViewResolver viewResolver = new BeanNameViewResolver();
viewResolver.setOrder(10); // 这样能保证在InternalResourceViewResolver之前执行
registry.viewResolver(viewResolver);
}
}
浏览器访问:http://localhost:8080/demo_war_war/json可看到如下:
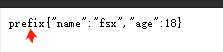
它提供的前缀能力,在某些特殊的场景会有用
- 利用
HttpServletResponse,然后获取response.getOutputStream()或response.getWriter()自己写json串
@RequestMapping(value = "/json")
public void testView(PrintWriter printWriter) {
printWriter.write("{\"name\":\"fsx\",\"age\":18}");
}
显然这种方式最为原始的方式,一般情况下我是不推荐这么使用的~
插一句:我曾经看到过有项目在使用Spring MVC框架的时候,还大量的使用到了Servlet规范的东西,其实这个真的是非常非常不好的做法~~
@ResponseBody这种方式是当下平时我们书写使用最多的方式
相信这种方式我说一个字:“略”,应该没有人有意见吧~~~
MappingJackson2XmlView
它主要处理:
public static final String DEFAULT_CONTENT_TYPE = "application/xml";
大致逻辑是同上。只不过它用的是XmlMapper而已~~~
AbstractPdfView
处理PDF:"application/pdf"。依赖jar是com.lowagie
MarshallingView
Marshaller在国内使用非常少,忽略
AbstractXlsView
这个依赖于Apache的POI库,处理Excel等。
Spring MVC 中对于输出格式为pdf和xsl的view,提供了两个abstract的view类供继承分别为AbstractPdfView和AbstractXlsView。
AbstractFeedView
和com.rometools包的WireFeed有关,忽略。
FastJsonJsonView
它不是位于Spring包内,位于aliabba包内。因为它也是一个json视图,所以没有太多可说的:
public class FastJsonJsonView extends AbstractView {
public static final String DEFAULT_CONTENT_TYPE = "application/json;charset=UTF-8";
// 这个是专门处理jsonp的
public static final String DEFAULT_JSONP_CONTENT_TYPE = "application/javascript";
private static final Pattern CALLBACK_PARAM_PATTERN = Pattern.compile("[0-9A-Za-z_\\.]*");
...
@Override
protected void renderMergedOutputModel(Map<String, Object> model, //
HttpServletRequest request, //
HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
Object value = filterModel(model);
String jsonpParameterValue = getJsonpParameterValue(request);
if (jsonpParameterValue != null) {
JSONPObject jsonpObject = new JSONPObject(jsonpParameterValue);
jsonpObject.addParameter(value);
value = jsonpObject;
}
ByteArrayOutputStream outnew = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
// 它依赖的是这个静态方法,把value值写进去的~~~~
int len = JSON.writeJSONString(outnew, //
fastJsonConfig.getCharset(), //
value, //
fastJsonConfig.getSerializeConfig(), //
fastJsonConfig.getSerializeFilters(), //
fastJsonConfig.getDateFormat(), //
JSON.DEFAULT_GENERATE_FEATURE, //
fastJsonConfig.getSerializerFeatures());
if (this.updateContentLength) {
// Write content length (determined via byte array).
response.setContentLength(len);
}
// Flush byte array to servlet output stream.
ServletOutputStream out = response.getOutputStream();
outnew.writeTo(out);
outnew.close();
out.flush();
}
}
AbstractUrlBasedView
下面来到我们最为重要的一个分支:AbstractUrlBasedView。因为前面讲到过UrlBasedViewResolver这个分支是最重要的视图处理器,所以自然而然这个相关的视图也是最为重要的~~~
AbstractPdfStamperView
这个和AbstractPdfView有点类似,不过它出来相对较晚。因为它可以基于URL去渲染PDF,它也是个抽象类,Spring MVC并没有PDF的具体的视图实现~~
RedirectView(SmartView)
这个视图和SmartView一起讲解一下。首先SmartView是一个子接口,增加了一个方法:
// @since 3.1 接口出来较晚,但是RedirectView早就有了的~~~
public interface SmartView extends View {
boolean isRedirectView();
}
顾名思义RedirectView是用于页面跳转使用的。重定向我们都不陌生,因此我们下面主要看看RedirectView它的实现:
重定向在浏览器可议看到两个毫不相关的request请求。跳转的请求会丢失原请求的所有数据,一般的解决方法是将原请求中的数据放到跳转请求的URL中这样来传递,下面来看看
RediectView是怎么优雅的帮我们解决这个问题的~~~
我们的重定向例子:
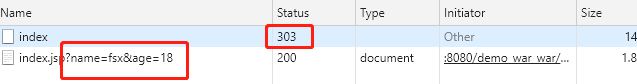
@GetMapping("/index")
public Object index(Model model) {
RedirectView redirectView = new RedirectView("/index.jsp");
redirectView.setContextRelative(true); //因为我们希望加上ServletContext 所以这个设置为true 并且以/打头
redirectView.setHttp10Compatible(false); //不需要兼容http1.0 所以http状态码一般返回303
// 给些参数 最终会拼接到URL后面去~
model.addAttribute("name", "fsx");
model.addAttribute("age", 18);
return redirectView;
}
public class RedirectView extends AbstractUrlBasedView implements SmartView {
private static final Pattern URI_TEMPLATE_VARIABLE_PATTERN = Pattern.compile("\\{([^/]+?)\\}");
private boolean contextRelative = false;
// 是否兼容http1.0
private boolean http10Compatible = true;
private boolean exposeModelAttributes = true;
// 如果你不设置,默认就是ISO-8859-1
@Nullable
private String encodingScheme;
@Nullable
private HttpStatus statusCode;
private boolean expandUriTemplateVariables = true;
// 当设置为@code true时,将追加当前URL的查询字符串,从而传播到重定向的URL。
private boolean propagateQueryParams = false;
@Nullable
private String[] hosts;
// 此处exposePathVariables设置为了true
public RedirectView() {
setExposePathVariables(false);
}
// 此处需要注意的是:给定的URL将被视为相对于Web服务器,而不是相对于当前Servletcontext
public RedirectView(String url) {
super(url);
setExposePathVariables(false);
}
// contextRelative:true表示为将URL解释为相对于当前ServletContext上下文 它的默认这是false
public RedirectView(String url, boolean contextRelative) {
super(url);
this.contextRelative = contextRelative;
setExposePathVariables(false);
}
...
// 配置与应用程序关联的一个或多个主机。所有其他主机都将被视为外部主机。
public void setHosts(@Nullable String... hosts) {
this.hosts = hosts;
}
// 显然此复写 永远返回true
@Override
public boolean isRedirectView() {
return true;
}
// 父类ApplicationObjectSupport的方法
// 此视图并不要求有ApplicationContext
@Override
protected boolean isContextRequired() {
return false;
}
// 这个就是吧Model里的数据 转换到 request parameters去~
@Override
protected void renderMergedOutputModel(Map<String, Object> model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
// 构建目标URL,若以/开头并且contextRelative=true,那就自动会拼上getContextPath(request)前缀 否则不拼
// encoding以自己set的为准,否则以request的为准,若都为null。那就取值:WebUtils.DEFAULT_CHARACTER_ENCODING
// 2、从当前request里面拿到UriVariables,然后fill到新的url里面去~
// 3、把当前request的url后的参数追加到新的url后面(默认是不会追加的~~~) 把propagateQueryParams属性值set为true就会追加了~~
// 4、exposeModelAttributes默认值是true,会吧model里的参数都合理的拼接到URL后面去~~~(这步非常重要,处理逻辑也是较为复杂的)
// 注意Bean的名字必须叫RequestContextUtils.REQUEST_DATA_VALUE_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME 否则此处也不会执行的~~~
String targetUrl = createTargetUrl(model, request);
// 它主要是找Spring容器里是否有`RequestDataValueProcessor`的实现类,然后`processUrl`处理一下
// 备注Spring环境默认没有它的实现,但是`Spring Security`对他是有实现的。比如大名鼎鼎的:`CsrfRequestDataValueProcessor`
targetUrl = updateTargetUrl(targetUrl, model, request, response);
// Save flash attributes
// 此处因为request.getAttribute(DispatcherServlet.OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE)拿到的Map都是空的,所以此处也不会像里放了
// FlashMap主要是用来解决`post/redrect/get`问题的,而现在都是ajax所以用得很少了~但Spring3.1之后提出了这个方案还是很优秀的
RequestContextUtils.saveOutputFlashMap(targetUrl, request, response);
// Redirect
sendRedirect(request, response, targetUrl, this.http10Compatible);
}
protected void sendRedirect(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
String targetUrl, boolean http10Compatible) throws IOException {
// 这个isRemoteHost很有意思。若getHosts()为空,就直接返回false了
// 然后看它是否有host,若没有host(相对路径)那就直接返回false
// 若有host再看看这个host是否在我们自己的getHosts()里面,若在里面也返回fasle(表示还是内部的嘛)
// 只有上面都没有return 就返回true
// 比如此处值为:/demo_war_war/index.jsp
String encodedURL = (isRemoteHost(targetUrl) ? targetUrl : response.encodeRedirectURL(targetUrl));
// 这里是兼容Http1.0的做法 看一下即可~~~
if (http10Compatible) {
HttpStatus attributeStatusCode = (HttpStatus) request.getAttribute(View.RESPONSE_STATUS_ATTRIBUTE);
if (this.statusCode != null) {
response.setStatus(this.statusCode.value());
response.setHeader("Location", encodedURL);
}
else if (attributeStatusCode != null) {
response.setStatus(attributeStatusCode.value());
response.setHeader("Location", encodedURL);
}
else {
// Send status code 302 by default.
// 大部分情况下我们都会走这里,所以我们看到的Http状态码都是302~~~~
response.sendRedirect(encodedURL);
}
}
// Http1.1
else {
// getHttp11StatusCode:若我们自己指定了status就以指定的为准
// 否则看这里有没有:request.getAttribute(View.RESPONSE_STATUS_ATTRIBUTE)
// 最后都没有,就是默认值HttpStatus.SEE_OTHER 303
HttpStatus statusCode = getHttp11StatusCode(request, response, targetUrl);
response.setStatus(statusCode.value());
response.setHeader("Location", encodedURL);
}
}
}
备注:若你方法只是:
redirect:xxx这种形式,最终都会转换成一个RedirectView,所以不再去单独说明。参见:ViewNameMethodReturnValueHandler有这个转化过程
这样整个RedirectView就算是看完了。刚到这,就有小伙伴问:如何重定向到POST请求?
what还能这么玩?于是乎 我研究了一番:不可能
我在想为何为问出这样的问题呢?302属于浏览器客户端的行为,咋可能发POST请求呢?原来我百度了一下,是网上有不少误导性的文章,比如:

纠正:exposeModelAttributes属性表示是否吧model里的值拼接到URL后面,默认是true会拼接的。若你改成fasle,最多也就是不拼接而已,浏览器还是会给你发送一个GET请求的。
关于Spring MVC中的Flash Attribute,可参考文章:
Spring MVC Flash Attribute 的讲解与使用示例
但其实现在的ajax承担了很大一部分原来的工作,几乎没有post/redirect/get这种问题了~~~
提问:重定向传值普通值我们好解决,但如果是一个对象呢?比如User对象里面有很多属性?
方案一:序列化成json串传递
方案二:使用RedirectAttributes#addFlashAttribute + @ModelAttribute的方式(具体做法小伙伴们可议尝试尝试,其原理是基于FlashMapManager和FlashMap的)
提示一点,方案二默认是基于sesson的,所以分布式环境需谨慎使用。
其实像这种重定向还需要传大量数据的方案,一般本身就存在问题,建议遇上此问题的选手多思考,是否合理???
AbstractTemplateView
关于模版引擎渲染的抽象。它主要做两件事:
public abstract class AbstractTemplateView extends AbstractUrlBasedView {
@Override
protected final void renderMergedOutputModel(
Map<String, Object> model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
//1、exposeRequestAttributes,通过request.getAttributeNames()把请求域里面的attr都暴露出去
//2、exposeSessionAttributes,session.getAttributeNames()把session域里面所有的attr都暴露出去
//3、exposeSpringMacroHelpers,把RequestContext暴露出去(上两个默认值都是false,这个默认值是true)
...
renderMergedTemplateModel(model, request, response);
}
// 模版方法 各个模版自己去实现~~~
protected abstract void renderMergedTemplateModel(
Map<String, Object> model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception;
}
FreeMarkerView
下面就以老牌模版引擎FreeMarker为例,窥探一下实现的思路:
public class FreeMarkerView extends AbstractTemplateView {
// FreeMarker Configuration: "ISO-8859-1" if not specified otherwise
@Nullable
private String encoding;
// FreeMarker的配置文件 里面极其多的配置信息~~比如文件后缀名、编码等
@Nullable
private Configuration configuration;
@Nullable
private TaglibFactory taglibFactory;
@Nullable
private ServletContextHashModel servletContextHashModel;
// 就是检查这个模版存不存在~~~
@Override
public boolean checkResource(Locale locale) throws Exception {
String url = getUrl();
Assert.state(url != null, "'url' not set");
try {
// Check that we can get the template, even if we might subsequently get it again.
getTemplate(url, locale);
return true;
}
catch (FileNotFoundException ex) {
// Allow for ViewResolver chaining...
return false;
}
catch (ParseException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Failed to parse [" + url + "]", ex);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Failed to load [" + url + "]", ex);
}
}
...
// 最终会根据此模版去渲染~~~这是FreeMarker真正去做的事~~~~
protected void processTemplate(Template template, SimpleHash model, HttpServletResponse response)
throws IOException, TemplateException {
template.process(model, response.getWriter());
}
}
此处我贴一个直接使用FreeMarker的使用案例,方便小伙伴对它的使用步骤有个感性的认识~~~
@Test
public void testFreeMarker() throws Exception{
// 第0步,创建模板文件(自己找个目录创建,文件一般都以.ftl结尾)
// 第一步:创建一个Configuration对象,直接new一个对象。构造方法的参数就是freemarker对于的版本号。
Configuration configuration = new Configuration(Configuration.getVersion());
// 第二步:设置模板文件所在的路径。
configuration.setDirectoryForTemplateLoading(new File("D:\\workspace\\e3-item-web\\src\\main\\webapp\\WEB-INF\\ftl"));
// 第三步:设置模板文件使用的字符集。一般就是utf-8.
configuration.setDefaultEncoding("utf-8");
// 第四步:加载一个模板,创建一个模板对象。
Template template = configuration.getTemplate("hello.ftl");
// 第五步:创建一个模板使用的数据集,可以是pojo也可以是map。一般是Map。
Map data = new HashMap<>();
//向数据集中添加数据
data.put("hello", "this is my first freemarker test!");
// 第六步:创建一个Writer对象,一般创建一FileWriter对象,指定生成的文件名。
Writer out = new FileWriter(new File("D:\\Freemarker\\hello.txt"));
// 第七步:调用模板对象的process方法输出文件,生成静态页面。
template.process(data, out);
// 第八步:关闭流。
out.close();
}
TilesView
略
XsltView
略
InternalResourceView:最重要的一个视图
Internal:内部的。所以该视图表示:内部资源视图。
// @since 17.02.2003 第一版就有了
public class InternalResourceView extends AbstractUrlBasedView {
// 指定是否始终包含视图而不是转发到视图
//默认值为“false”。打开此标志以强制使用servlet include,即使可以进行转发
private boolean alwaysInclude = false;
// 设置是否显式阻止分派回当前处理程序路径 表示是否组织循环转发,比如自己转发自己
// 我个人认为这里默认值用true反而更好~~~因为需要递归的情况毕竟是极少数~
// 其实可以看到InternalResourceViewResolver的buildView方法里是把这个属性显示的设置为true了的~~~
private boolean preventDispatchLoop = false;
public InternalResourceView(String url, boolean alwaysInclude) {
super(url);
this.alwaysInclude = alwaysInclude;
}
@Override
protected boolean isContextRequired() {
return false;
}
// 请求包含、请求转发是它特有的~~~~~
@Override
protected void renderMergedOutputModel(Map<String, Object> model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// Expose the model object as request attributes.
// 把model里的数据都request.setAttribute里
// 因为最终JSP里面取值其实都是从request等域对象里面取~
exposeModelAsRequestAttributes(model, request);
// Expose helpers as request attributes, if any.
// JstlView有实现此protected方法~
exposeHelpers(request);
// Determine the path for the request dispatcher.
String dispatcherPath = prepareForRendering(request, response);
// Obtain a RequestDispatcher for the target resource (typically a JSP). 注意:此处特指JSP
// 就是一句话:request.getRequestDispatcher(path)
RequestDispatcher rd = getRequestDispatcher(request, dispatcherPath);
if (rd == null) {
throw new ServletException("Could not get RequestDispatcher for [" + getUrl() +
"]: Check that the corresponding file exists within your web application archive!");
}
// If already included or response already committed, perform include, else forward.
//useInclude:若alwaysInclude==true或者该request是incluse请求或者response.isCommitted()==true
// 那就走incluse,否则走forward~~~~~
if (useInclude(request, response)) {
response.setContentType(getContentType());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Including [" + getUrl() + "]");
}
rd.include(request, response);
}
else {
// Note: The forwarded resource is supposed to determine the content type itself.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Forwarding to [" + getUrl() + "]");
}
rd.forward(request, response);
}
}
// 拿到URL,做一个循环检查~~~ 若是循环转发就报错~~
protected String prepareForRendering(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws Exception {
String path = getUrl();
Assert.state(path != null, "'url' not set");
if (this.preventDispatchLoop) {
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
if (path.startsWith("/") ? uri.equals(path) : uri.equals(StringUtils.applyRelativePath(uri, path))) {
throw new ServletException("Circular view path [" + path + "]: would dispatch back " +
"to the current handler URL [" + uri + "] again. Check your ViewResolver setup! " +
"(Hint: This may be the result of an unspecified view, due to default view name generation.)");
}
}
return path;
}
}
这样我们的InternalResourceView这个视图就渲染完成了,为何这么简单呢?因为它最终要么是include,要么forward掉了。交给别的Servlet去处理了。
而我们知道JSP的本质其实就是一个servlet,所以转发给它处理其实就是定位到了我们的JSP页面,它完成的对response写入动作。
比如:
@GetMapping("/index")
public Object index() {
InternalResourceView view = new InternalResourceView();
view.setUrl("/index.jsp");
view.setPreventDispatchLoop(true);
return view;
}
注意:直接返回一个View是不会经过
ViewResolver处理的
这样是能够正常展示出我们的jsp页面的。但是,但是,但是如果我们是一个html页面呢?比如如下:
@GetMapping("/index")
public Object index() {
InternalResourceView view = new InternalResourceView();
view.setUrl("/index.html");
view.setPreventDispatchLoop(true);
return view;
}
访问直接报错:
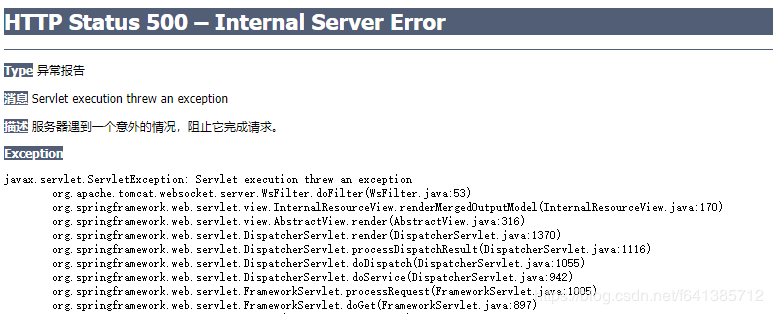
原因很简单,因为你是HTML页面,所以它并没有对应的Servlet,所以你转发的时候肯定就报错了。所以接下里的问题变成了:
如何让我们的Controller跳转到HTML页面呢???其实这个涉及到Spring MVC中对静态资源的访问问题
说在前面:因为html属于静态数据,所以一般我们需要访问的话都是通过
mvc:resources等这种配置去达到目的让可议直接访问。但是不乏业务中可能也存在通过controller方法跳转到html页面的需求(虽然你可以JSP里面全是html页面),本文就实现这个效果,能加深对此视图的了解~~
参考:【小家Spring】Spring MVC控制器中Handler的四种实现方式:Controller、HttpRequestHandler、Servlet、@RequestMapping
的最后半段来了解Spring MVC对静态资源的处理
JstlView
它继承自InternalResourceView,所以还是和JSP相关的。jstl相关的jar为:jstl.jar和standard.jar。它哥俩已经老久都没有更新过了,不过可以理解。毕竟JSP都快寿终正寝了。
它还可以和国际化有关,若使用Jstl的fmt标签,需要在SpringMVC的配置文件中配置国际化资源文件。
public class JstlView extends InternalResourceView {
...
public JstlView(String url, MessageSource messageSource) {
this(url);
this.messageSource = messageSource;
}
// 导出一些JSTL需要的东西
@Override
protected void exposeHelpers(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (this.messageSource != null) {
JstlUtils.exposeLocalizationContext(request, this.messageSource);
}
else {
JstlUtils.exposeLocalizationContext(new RequestContext(request, getServletContext()));
}
}
}
因为JSTL技术比较古老了,现在很少人使用(当然JSP的使用人群还是有不少的,需要较重点的了解一下,毕竟是java嫡系技术,在历史进程中还是很重要的存在的),所以这里也不做演示了~
ScriptTemplateView
这个是脚本渲染引擎,从Spring4.2开始提供了一个ScriptTemplateView作为脚本模版视图。
脚本渲染引擎,据我目前了解,是为Kotlin而准备的,此处一个大写的:略
总结
视图就是展示给用户看的结果。可以是很多形式,例如:html、JSP、excel表单、Word文档、PDF文档、JSON数据、freemarker模板视图等等。
视图(解析器)作为Spring MVC设计中非常优秀的一环,最重要的是这种设计思想、作者的设计意图,值得我们深思和学习
关注A哥
| Author | A哥(YourBatman) |
|---|---|
| 个人站点 | www.yourbatman.cn |
| [email protected] | |
| 微 信 | fsx641385712 |
活跃平台 |
|
| 公众号 | BAT的乌托邦(ID:BAT-utopia) |
| 知识星球 | BAT的乌托邦 |
| 每日文章推荐 | 每日文章推荐 |