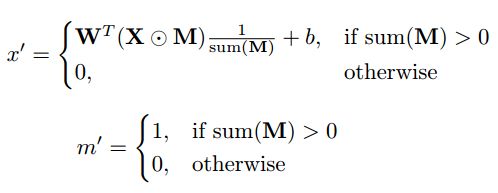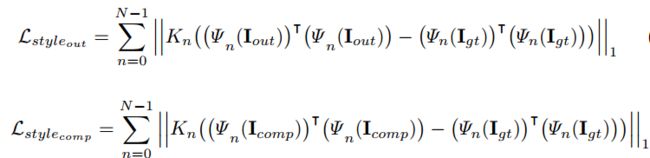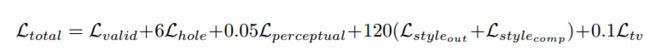基于部分卷积Pconv的图片修复
论文:Image Inpainting for Irregular Holes Using Partial Convolutions
Github:
https://github.com/MathiasGruber/PConv-Keras
https://github.com/deeppomf/DeepCreamPy#dependencies-for-running-the-code-yourself
https://github.com/deeppomf/DeepCreamPy/releases/tag/v1.2.1-beta
英伟达的论文,非常值得阅读,PConv和loss func都很有特点。
论文贡献:
- 提出了部分卷积(partial convolutions),使得在每一层都使用上一层跟新后的mask,在图片修复上取得了state-of-the-art 的结果。
- 提出了U-net类型的网络结构,区别在于将传统u-net中的卷积层替换为部分卷积层,解码模块的RELU替换为LeakyRELU。
- 首次提出对于非规则孔洞的图片修复
- 提出了一个大的非规则的带mask的图片修复数据集。
网络结构:
网络采用U-Net结构,分为编码模块(PConv1-PConv8)和解码模块(PConv9-PConv16)两部分。
Partial Convolutional(PConv):
部分卷积将卷积分为了输入图片的卷积和输入掩码mask的卷积。之前的论文都是只在第一层使用mask,mask也不会得到跟新,本文的partial convolutions,每次都使用跟新后的mask,随着网络层数的增加,mask输出m’中为0的像素越来越少,输出的结果x’中有效区域的面积越来越大,mask对整体loss的影响会越来越小(如上图所示,表示了不同层的mask输出)。
如上式所示,W表示卷积层滤波器的weights,b表示卷积层滤波器的bias,X表示输入的图片,M表示掩码mask,⊙ 表示element-wise点乘运算,x'表示输入图片经过卷积后的输出,m’表示输入掩码经过卷积后的输出。
Keras实现:
def call(self, inputs, mask=None):
# Both image and mask must be supplied
if type(inputs) is not list or len(inputs) != 2:
raise Exception('PartialConvolution2D must be called on a list of two tensors [img, mask]. Instead got: ' + str(inputs))
# Create normalization. Slight change here compared to paper, using mean mask value instead of sum
normalization = K.mean(inputs[1], axis=[1,2], keepdims=True)
normalization = K.repeat_elements(normalization, inputs[1].shape[1], axis=1)
normalization = K.repeat_elements(normalization, inputs[1].shape[2], axis=2)
# Apply convolutions to image
img_output = K.conv2d(
(inputs[0]*inputs[1]) / normalization, self.kernel,
strides=self.strides,
padding=self.padding,
data_format=self.data_format,
dilation_rate=self.dilation_rate
)
# Apply convolutions to mask
mask_output = K.conv2d(
inputs[1], self.kernel_mask,
strides=self.strides,
padding=self.padding,
data_format=self.data_format,
dilation_rate=self.dilation_rate
)
# Where something happened, set 1, otherwise 0
mask_output = K.cast(K.greater(mask_output, 0), 'float32')
# Apply bias only to the image (if chosen to do so)
if self.use_bias:
img_output = K.bias_add(
img_output,
self.bias,
data_format=self.data_format)
# Apply activations on the image
if self.activation is not None:
img_output = self.activation(img_output)
return [img_output, mask_output]Loss:
Iin:输入的图片
Iout:网络的预测输出
M :掩码,孔洞为0,有效像素为1
Igt:label,即ground truth
Icomp :孔洞像素的输出
Ψn :第n层激活后的特征图,本文取pool1, pool2, pool3
孔洞的损失:
![]()
1-M表示孔洞区域,整体表示了孔洞区域的输出和ground truth的L1 loss。
Keras实现:
def loss_hole(self, mask, y_true, y_pred):
"""Pixel L1 loss within the hole / mask"""
return self.l1((1-mask) * y_true, (1-mask) * y_pred)非孔洞的有效像素的损失:
![]()
M表示非孔洞区域,整体表示非孔洞区域的网络预测输出和ground truth的L1 loss。
Keras实现:
def loss_valid(self, mask, y_true, y_pred):
"""Pixel L1 loss outside the hole / mask"""
return self.l1(mask * y_true, mask * y_pred)感知的损失:
感知的损失,或者内容的损失,表示了pool1, pool2, pool3层的输出和ground truth的L1 损失。表示了width,height,channel三个方面的差异。
Keras实现:
def loss_perceptual(self, vgg_out, vgg_gt, vgg_comp):
"""Perceptual loss based on VGG16, see. eq. 3 in paper"""
loss = 0
for o, c, g in zip(vgg_out, vgg_comp, vgg_gt):
loss += self.l1(o, g) + self.l1(c, g)
return loss风格的损失:
Kn :归一化参数,表示为1/CnHnWn
Ψn 的形状为(HnWn) × Cn ,因此Ψn 的转置和Ψn 的矩阵乘积后输出的矩阵大小为Cn × Cn 。
整体公式表示了pool1, pool2, pool3层的输出和输出的转置与ground truth和ground truth的转置的差异。表示了channel方面的差异。
Keras实现:
def loss_style(self, output, vgg_gt):
"""Style loss based on output/computation, used for both eq. 4 & 5 in paper"""
loss = 0
for o, g in zip(output, vgg_gt):
loss += self.l1(self.gram_matrix(o), self.gram_matrix(g))
return loss平滑性的损失:
P表示经过1个像素的膨胀后的孔洞区域。
平滑性损失total variation (TV) 表示为孔洞区域内一个像素和该像素的右侧像素和下面像素的L1 loss。总体来看衡量了2个孔洞区域(一个为原始孔洞区域,另一个为在水平方向右移一个像素的区域,或者在垂直方向下移一个像素的区域)在水平方向和垂直方向的差异。
Keras实现:
def loss_tv(self, mask, y_comp):
"""Total variation loss, used for smoothing the hole region, see. eq. 6"""
# Create dilated hole region using a 3x3 kernel of all 1s.
kernel = K.ones(shape=(3, 3, mask.shape[3], mask.shape[3]))
dilated_mask = K.conv2d(1-mask, kernel, data_format='channels_last', padding='same')
# Cast values to be [0., 1.], and compute dilated hole region of y_comp
dilated_mask = K.cast(K.greater(dilated_mask, 0), 'float32')
P = dilated_mask * y_comp
# Calculate total variation loss
a = self.l1(P[:,1:,:,:], P[:,:-1,:,:])
b = self.l1(P[:,:,1:,:], P[:,:,:-1,:])
return a+b总的loss:
每个loss前面的权重大小是在100个验证图片上使用参数搜索得到的。
实验结果:
本文的Pconv方法优于PM(PatchMatch),GL,GntIpt 等方法。
总结:
- PConv的提出,动态的使得不同层的mask对loss表现出不同的贡献,使得训练学习过程表现出从孔洞外面逐渐缩小孔洞学习的机制。底层网络学习孔洞外围,高层网络学习孔洞里面。与整个网络都学习整个孔洞相比具有明显的优势。
- loss设计上与阿里的这篇Pyramid Embedded Generative Adversarial Network for Automated Font Generation一样都采用了感知loss。区别在于本文只使用了其中3个特征层,而阿里这篇使用了vgg-19的所有层。