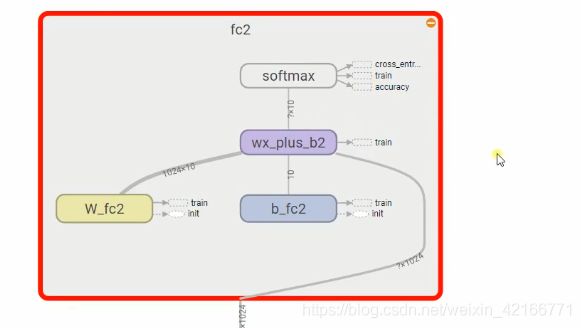
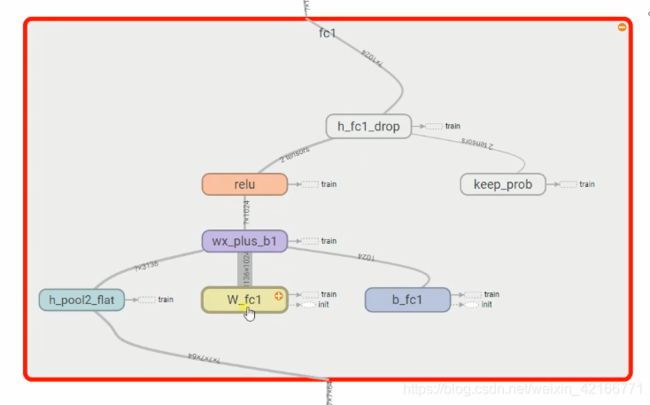
卷积神经网络CNN,以及用CNN解决MNIST分类问题。
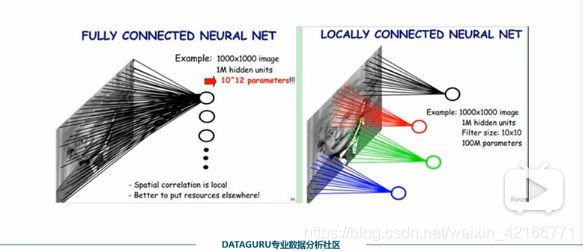
传统的神经网络存在的问题:
权值太多,计算量太大
权值太多,需要大量样本进行训练
CNN通过感受野和权值共享减少了神经网络需要训练的参数个数
感受野:后面的神经元只能接到前面图片的一部分
权值共享:权值个数相同,相同颜色的 权值值也相同
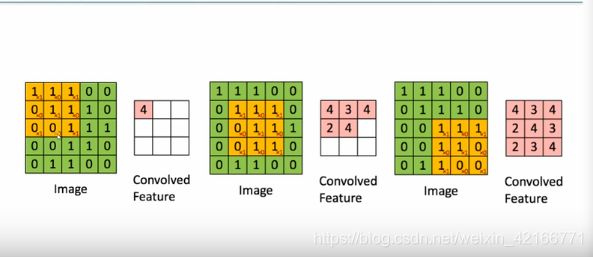
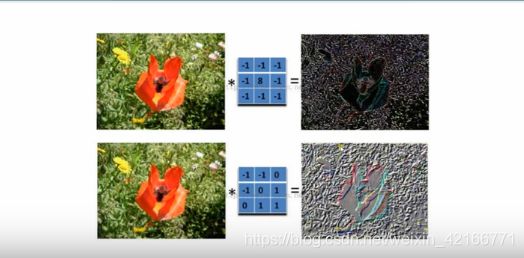
卷积核的定义:
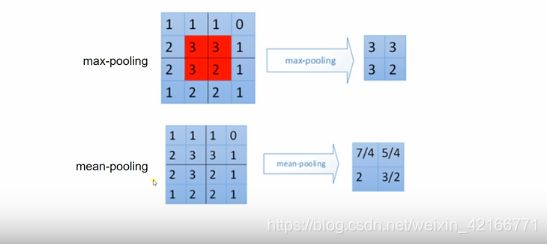
池化层:
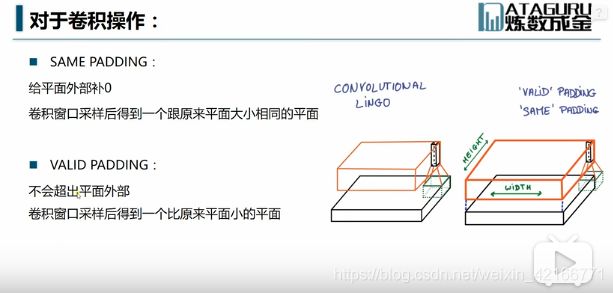
卷积操作 same padding 和 valid padding
池化操作:same padding 和 valid padding
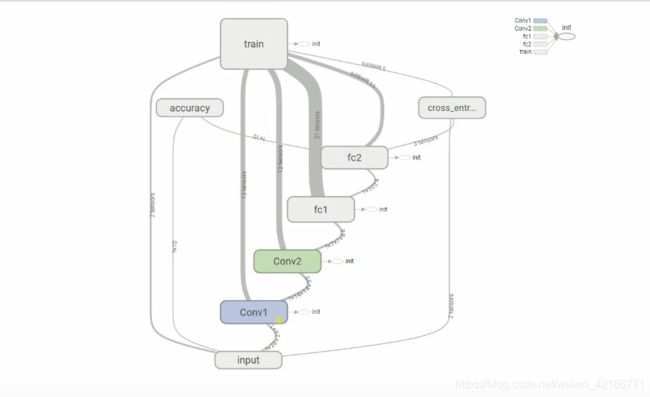
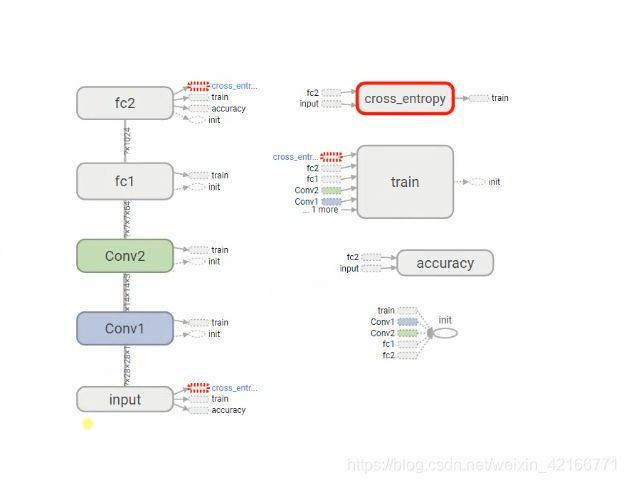
卷积神经网络结构图:
输入层 → 第一个卷积层 → 第二个卷积层 → 第一个全连接层 →第二个全连接层 → 交叉熵代价函数 → 求准确率 → 训练→ 输出层
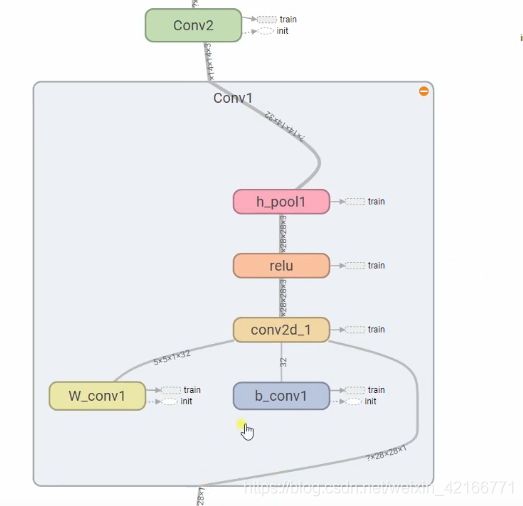
卷积层的结构:
初始化权值和偏置值 → 卷积处理 → relu 激活函数 → 池化层处理 →下一个卷积层
全连接层:
值转换 →初始化权值和偏值值 → relu 激活函数 → dropout函数(让一部分神经元工作) → 输出
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
#载入数据库
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/",one_hot=True)
#每个批次的大小
batch_size = 100
#计算一共 有多少个批次
n_batch = mnist.train.num_examples//batch_size
#初始化权值
def weight_variable(shape):
initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape,stddev = 0.1) #生成一个截断的正态分布
return tf.Variable(initial)
#初始化权值
def bias_variable(shape):
initial = tf.constant(0.1,shape = shape)
return tf.Variable(initial)
#卷积层
def conv2d(x,w):
# x input tensor of shape [batch,in_height,in_width,in_channels]
#w fileter/kernel tensor of shape [filter_heigth,filter_width,in_channel,put_channels]
#strides[0] = strides[3] = 1,strides[1]代表 x方向的步长 ,strides[2]表示 y 方向的步长
#padding:A string from: "same","valid"
return tf.nn.conv2d(x,w,strides = [1,1,1,1],padding = 'SAME')
#池化层
def max_pool_2x2(x):
#kize[1,x,y,1]
return tf.nn.max_pool(x,ksize = [1,2,2,1],strides = [1,2,2,1],padding = "SAME")
#定义两个placeholder
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,784])#28x28
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,10])
#改变x的格式转为4D事务向量[batch,in_height,in_width,in_channels]
x_image = tf.reshape(x,[-1,28,28,1])
#初始化第一个卷积层的权值和偏值
W_conv1 = weight_variable([5,5,1,32])#5x5的采样窗口,32个卷积核从1个平面抽取特征
b_conv1 = bias_variable([32]) #每一个卷积核一个偏值
#把x_image和权值向量进行卷积,再加上偏值值,然后应用于relu激活函数
b_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x_image,W_conv1)+b_conv1)
h_pool1 =max_pool_2x2(b_conv1) #进行max_pooling
#初始化第二个卷积层的权值和偏值
W_conv2 = weight_variable([5,5,32,64]) #5x5的采样窗口,64个卷积核从32个平面抽取特征
b_conv2 = bias_variable([64]) #每一个卷积核一个偏值
#把h_pool1和权值向量进行卷积,再加上偏值值,然后应用于relu激活函数
b_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1,W_conv2)+b_conv2)
h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(b_conv2) #进行max_pooling
#28*28的图片第一次卷积后还是28*28,第一次池化后变为14*14
#第二次卷积后为14*14,第二次池化后变成了7*7
#通过上面的操作后得到64张7*7的平面
#初始化第一个全连接层的权值
W_fcl = weight_variable([7*7*64,1024])#上异常有7*7*64个神经元,全连接层有1024个神经元
b_fcl = bias_variable([1024])#1024个节点
#把池化层2的输出扁平化为1维
h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2,[-1,7*7*64])
#求第一个全连接层的输出
b_fcl = tf.nn.relu (tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat,W_fcl)+b_fcl)
#keep_prob用来表示神经元的输出概率
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
b_fcl_drop = tf.nn.dropout(b_fcl,keep_prob)
#初始化第二个全连接层
W_fc2 = weight_variable([1024,10])
b_fc2 = bias_variable([10])
#计算输出
prediction = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(b_fcl_drop,W_fc2)+b_fc2)
#交叉熵代价函数
cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels= y,logits =prediction))
#使用AdamOptimizer进行优化
train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-4).minimize(cross_entropy)
#结果存放在一个布尔型列表中
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(prediction,1),tf.argmax(y,1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,tf.float32))
with tf.Session () as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for epoch in range(21):
for batch in range (n_batch):
batch_xs,batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
sess.run(train_step,feed_dict = {x:batch_xs,y:batch_ys,keep_prob:0.7})
acc= sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict = {x:mnist.test.images,y:mnist.test.labels,keep_prob:1.0})
print("Iter"+str(epoch)+",Testing Accuracy ="+str(acc))