cf.D.Domino for Young
D. Domino for Young
You are given a Young diagram.
Given diagram is a histogram with n columns of lengths a 1 , a 2 , … , a n ( a 1 ≥ a 2 ≥ … ≥ a n ≥ 1 ) . a_1,a_2,…,a_n (a_1≥a_2≥…≥a_n≥1). a1,a2,…,an(a1≥a2≥…≥an≥1).
Young diagram for a=[3,2,2,2,1].
Your goal is to find the largest number of non-overlapping dominos that you can draw inside of this histogram, a domino is a 1×2 or 2×1 rectangle.
Input
The first line of input contain one integer n (1≤n≤300000): the number of columns in the given histogram.
The next line of input contains n integers a 1 , a 2 , … , a n ( 1 ≤ a i ≤ 300000 , a i ≥ a i + 1 ) a_1,a_2,…,a_n (1≤a_i≤300000,a_i≥a_{i+1}) a1,a2,…,an(1≤ai≤300000,ai≥ai+1): the lengths of columns.
Output
Output one integer: the largest number of non-overlapping dominos that you can draw inside of the given Young diagram.
Example
inputCopy
5
3 2 2 2 1
outputCopy
4
Note
Some of the possible solutions for the example:
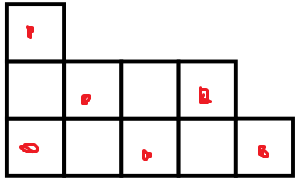
如上图, 考虑二分图匹配, 红点和旁边白点连边, 但是 n < 9 e 10 n<9e^{10} n<9e10, 跑不动
手动模拟匹配
假设红点数小于等于白点数且当前有红点h未匹配(显然还有白点b未匹配) 那么,
- 如果h旁边有白点为匹配, 匹配数+1
- 如果h旁边所有白点都匹配了, 则h->b的路径必然是
h —>B->H->B …->H->B->H------->b路径,那么,这就是一条可增广路,匹配数+1
所以, 只要有足够多的的红点, 所有白点都能匹配
红白点可以互换.则求红白点数的最小值
#includeinline
TT bool read(T &x){
x=0;char c=gc();bool f=0;
while(c<48||c>57){if(c==EOF)return 0;f^=(c=='-'),c=gc();}
while(47<c&&c<58)x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+(c^48),c=gc();
if(f)x=-x;return 1;
}
TT bool read(T&a,T&b){return read(a)&&read(b);}
TT bool read(T&a,T&b,T&c){return read(a)&&read(b)&&read(c);}
typedef long long ll;
const ll MAXN=1e1+8,mod=1e9+7,inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
int main() {
ll n,x,f=0,res1=0,res2=0;//红白点数量.
read(n);
while(n--){
read(x);
if(f){
res1+=(x+1)>>1;
res2+=x>>1;
}
else{
res1+=x>>1;
res2+=(x+1)>>1;
}
f^=1;
}
cout<<min(res1,res2);
return 0;
}