卷积im2col函数
1、im2col函数
一个图像 input_num=1;
图像通道 input_channel=1;
图像高 input_h=4;
图像宽 input_w=4;
kernel高 kernel_h=3;
kernel宽 kernel_w=3;
stride=1;pad=0;
卷积后,输出图像的计算公式:
output_h=(input_h-kernel_h)/stride+1;
output_w=(input_w-kernel_w)/stride+1;
原图(图a)按照从左到右、从上到下的过程,将(a)中大小为33(因为kernel大小为33)的矩阵拉成右图(图b)中的一列。具体过程如下图所示:

二:多通道的im2col
假设有三个通道(R、G、B)图像通道 input_channel=3;
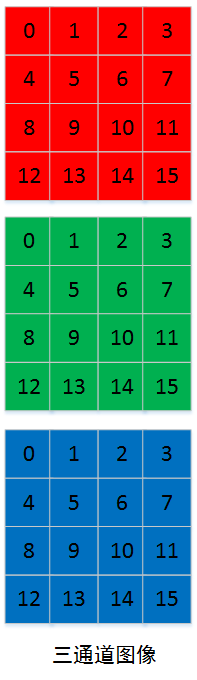
图像在内存中的存储是:首先是连续存储第一通道的数据,然后再存储第二通道的数据,最后存储第三通道的数据。如下图:

多通道的im2col的过程如下图所示
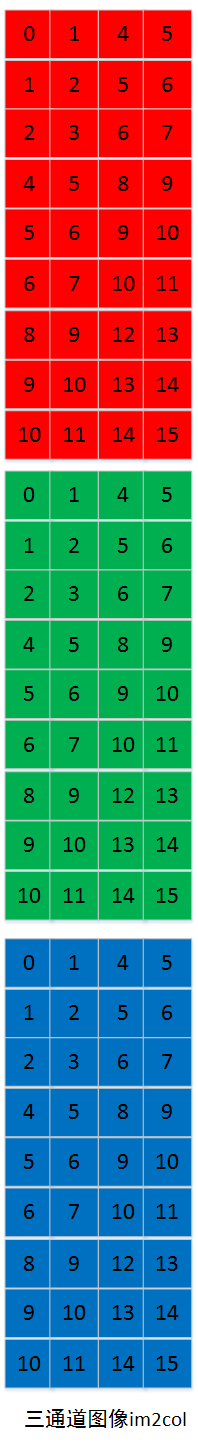
内存中的存储是首先im2col第一通道,然后在im2col第二通道,最后im2col第三通道。各通道im2col的数据在内存中也是连续存储的。如下图:
三:kernel
图像的每个通道对应一个kernel通道,如下图(注:为计算简单,将kernel的值设置为1,同样此值不代表颜色数值。)

kernel的通道数据在内存中也是连续存储的。所以上面的kernel图像也可以表示为下图:

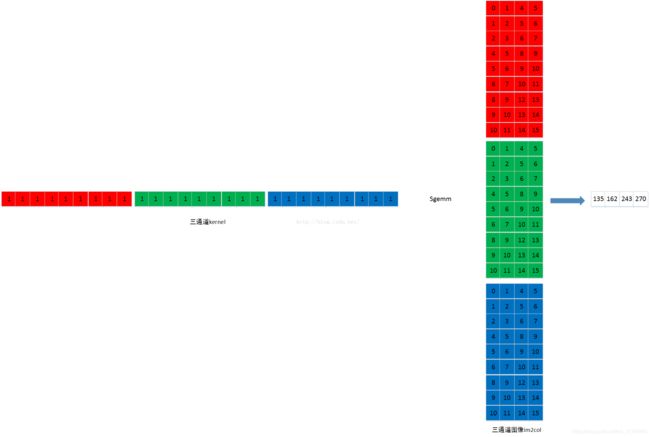
四:矩阵乘 sgemm
在caffe中图像与kernel的矩阵乘,是kernel*img。即:在矩阵乘法中
M=1 ,
N=output_h * output_w
K=input_channels * kernel_h * kernel_w
如下图所示:
图像数据是连续存储,因此输出图像也可以如下图所示【output_h * output_w】=【2*2】:

五:多通道图像输出
在caffe中图像与kernel的矩阵乘中:
M=output_channels ,
N=output_h * output_w
K=input_channels * kernel_h * kernel_w
如下图:

同样,多个输出通道图像的数据是连续存储,因此输出图像也可以如下图所示【output_channelsoutput_h * output_w】=【32*2】,

六、实现程序
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include