B树详解
一,B树的定义
B-树,即为B树。因为B树的原英文名称为B树,而国内很多人喜欢把B树译作B-树,其实,这是个非常不好的直译,很容易让人产生误解。如人们可能会以为B-树是一种树,而B树又是一种树。而事实上是,B-树就是指的B树。
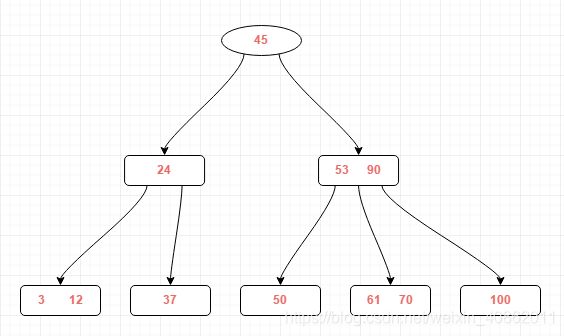
一棵简单的三阶B树如下图:
一棵m阶B树,或为空树,或为满足下列特性对的m叉树。
- 树中每个结点最多含有m棵子树。
- 若根结点不是叶子结点,则至少有2个子树。
- 除根结点之外的所有非终端结点至少有⌈m/2⌉棵子树。
- 如果一个结点有n-1个关键字,则该结点有n个分支,且这n-1个关键字按照递增顺序排列。
- 每个非终端结点中包含信息:(N,A0,K1,A1,K2,A2,...,KN,一)其中:
- Ki(1≤i≤n)为关键字,且关键字按升序排序。
- 指针Ai(0≤i≤n)指向子树的根结点,Ai-1指向子树中所有结点的关键字均小于Ki,且大于Ki-1;
- 关键字的个数n必须满足:⌈m/2⌉-1≤n≤m-1。
- 结点内关键字各不相等且按从小到大排列。
- 结点结构如下:
n
K1
K2
...
Kn
A0
A1
A2
...
An
- 所有的叶子节点都在同一层,子叶结点不包含任何信息。叶子结点处于同一层,可以用空指针表示,是查找失败到达的位置。
注:平衡m叉查找树是指每个关键字的左侧子树与右侧子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1的查找树,其结点结构与上面提到的B-树结点结构相同,由此可见,B-树是平衡m叉查找树,但限制更强,要求所有叶结点都在同一层。
二,B树的存储结构
#define m 3 // B树的阶,此设为3
typedef int KeyType;
typedef struct {
KeyType key;
char data;
} Record;
typedef struct BTNode {
int keynum; // 结点中关键字个数,即结点的大小
struct BTNode *parent; // 指向双亲结点
KeyType key[m+1]; // 关键字向量,0号单元未用
struct BTNode *ptr[m+1]; // 子树指针向量
Record *recptr[m+1]; // 记录指针向量,0号单元未用
} BTNode, *BTree; // B树结点和B树的类型
typedef struct {
BTree pt; // 指向找到的结点
int i; // 1..m,在结点中的关键字序号
int tag; // 1:查找成功,0:查找失败
} Result; // 在B树的查找结果类型三,B树的查找操作
B-树的查找很简单,是二叉排序树的扩展,二叉排序树是二路查找,B-树是多路查找,因为B-树结点内的关键字是有序的,在结点内进行查找时除了顺序查找外,还可以用折半查找来提升效率.B-树的具体查找步骤如下(假设查找的关键字为key):
- 先让key与根结点中的关键字比较,如果key等于K [i](K []为结点内的关键字数组),则查找成功。
- 若key
- 若key> K [n]的,则到P [n]所指示的子树中继续查找。
- 若k [i]
- 如果最后遇到空指针,则证明查找不成功。
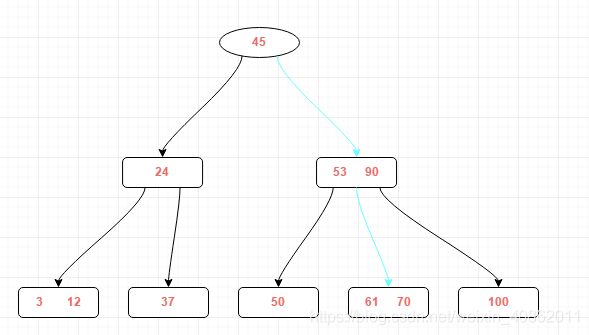
拿上面的B树举例,假如我们想要查找关键字61,下面即显示了查找的路径
实现代码
/**
* 在B-树t查找关键字key,用r返回(pt, i, tag)
* 若查找成功,则tag=1,指针pt所指结点中第i个关键字等于key
* 否则tag=0,若要插入关键字key,应位于pt结点中第i-1和第i个关键字之间
*
* @param t B-树
* @param key 待查找的关键字
* @param r B-树的查找结果类型
*/
void SearchBTree(BTree t, KeyType key, Result &r) {
int i = 0;
int found = 0;
BTree p = t; // 一开始指向根结点,之后指向待查结点
BTree q = NULL; // 指向待查结点的双亲
while (p != NULL && found == 0) {
i = Search(p, key);
if (i <= p->keynum && p->key[i] == key) {
found = 1;
} else {
q = p;
p = p->ptr[i - 1]; // 指针下移
}
}
if (1 == found) { // 查找成功,返回key的位置p和i
r.pt = p;
r.i = i;
r.tag = 1;
} else { // 查找失败,返回key的插入位置q和i
r.pt = q;
r.i = i;
r.tag = 0;
}
}
/**
* 在p->key[1 .. p->keynum]找key,并返回位序
*
* @param p B-树的结点p
* @param key 关键字
* @return key在p结点的位序
*/
int Search(BTree p, KeyType key) {
int i = 1;
while (i <= p->keynum && key > p->key[i]) {
i++;
}
return i;
}
四,B树的插入操作
与二叉排序树一样,B-树的创建过程也是将关键字逐个插入到树中的过程。
乙树的插入首先利用了B树的查找操作查找关键字ķ的插入位置。若该关键字存在于B树中,则不用插入直接返回,否则查找操作必定失败于某个最底层的非终端结点上,也就是要插入的位置。插入分两种情况讨论。
- 插入关键字后该结点的关键字数小于等于m - 1,插入操作结束。
- 插入关键字后该结点的关键字数等于m,则应该进行分裂操作,分裂操作如下:
- 生成一个新结点,从中间位置把结点(不包括中间位置的关键字)分为两部分。
- 前半部分留在旧结点中,后半部分复制到新结点中。
- 中间位置的关键字连同新结点的存储位置插入到父结点中,如果插入后父结点的关键字个数也超过了m-1,则继续分裂。
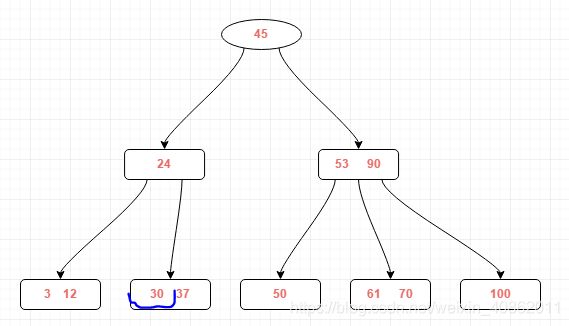
在上图B树中插入30,可以得到如下的结果:
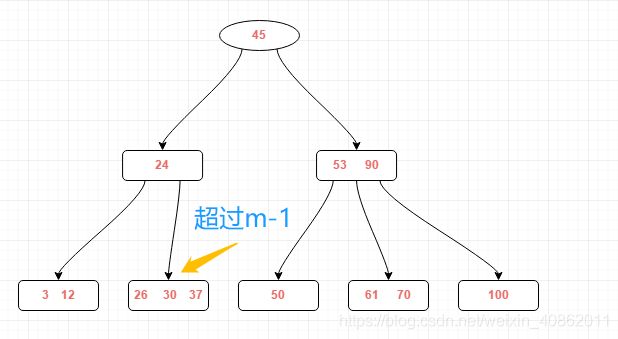
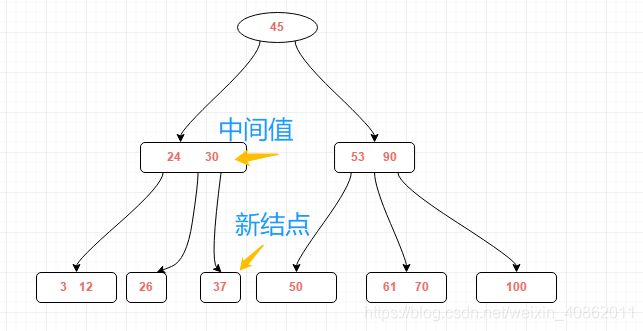
再插入26,得到下图结果,插入后的终端结点中的关键字数大于m-1,需对结点进行分裂
左部26,中间值为30,右部为37,左部放在原来的结点,右部放入新的结点,中间值则插入到父结点中,并且父结点会产生一个新的指针,指向新的结点的位置,如下图所示:
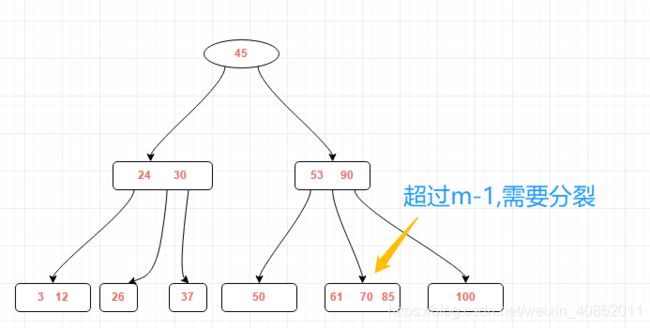
继续插入新的关键字85,如图所示
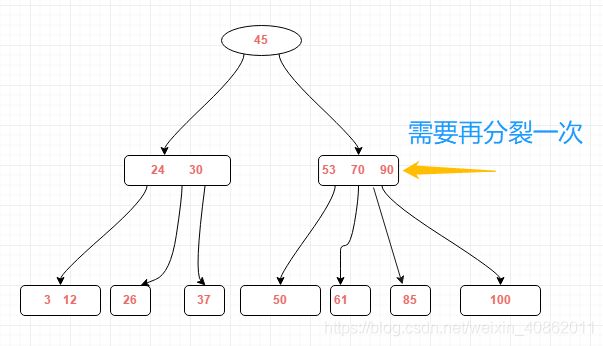
需对刚才插入的结点进行分裂操作,操作方式和之前一样得到结果如下:(分裂完后发现原来结点的父结点也需要分裂)
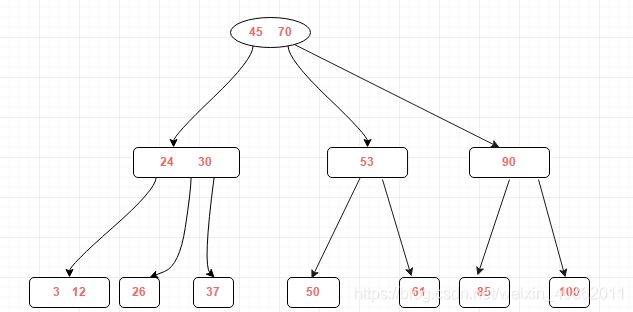
再进行分裂操作后的结果如下:
实现代码
/**
* 在B-树t中q结点的key[i - 1]和key[i]之间插入关键字key
* 若插入后结点关键字个数等于B-树的阶,则沿双亲指针链进行结点分裂
*
* @param t B-树
* @param key 待插入的关键字
* @param q 关键字插入的结点
* @param i 插入位序
*/
void InsertBTree(BTree &t, KeyType key, BTree q, int i) {
KeyType x;
int s;
int finished = FALSE;
int needNewRoot = FALSE;
BTree ap;
if (NULL == q) {
newRoot(t, NULL, key, NULL);
} else {
x = key;
ap = NULL;
while (FALSE == needNewRoot && FALSE == finished) {
Insert(q, i, x, ap); // x和ap分别插入到q->key[i]和q->ptr[i]
if (q->keynum < m) {
finished = TRUE;
} else {
s = (m + 1) / 2; // 得到中间结点位置
split(q, s, ap); // 分裂q结点
x = q->key[s];
// 在双亲位置插入关键字x
if (q->parent != NULL) {
q = q->parent;
i = Search(q, x); // 寻找插入的位置
} else {
needNewRoot = TRUE;
}
}
}
if (TRUE == needNewRoot) {
newRoot(t, q, x, ap);
}
}
}
/**
* 将q结点分裂成两个结点,前一半保留在原结点,后一半移入ap所指新结点
*
* @param q B-树结点
* @param s 中间位序
* @param ap 新结点,用来存放原结点的后一半关键字
*/
void split(BTree &q, int s, BTree &ap) {
int i, j;
int n = q->keynum; // 关键字数量
ap = (BTree)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
ap->ptr[0] = q->ptr[s];
for (i = s + 1, j = 1; i <= n; i++, j++) {
ap->key[j] = q->key[i];
ap->ptr[j] = q->ptr[i];
}
ap->keynum = n - s;
ap->parent = q->parent;
for (i = 0; i <= n - s; i++) {
// 修改新结点的子结点的parent域
if (ap->ptr[i] != NULL) {
ap->ptr[i]->parent = ap;
}
}
q->keynum = s - 1; // 修改q结点的关键字数量
}
/**
* 生成新的根结点
*
* @param t B-树
* @param p B-树结点
* @param key 关键字
* @param ap B-树结点
*/
void newRoot(BTree &t, BTree p, KeyType key, BTree ap) {
t = (BTree)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
t->keynum = 1;
t->ptr[0] = p;
t->ptr[1] = ap;
t->key[1] = key;
if (p != NULL) {
p->parent = t;
}
if (ap != NULL) {
ap->parent = t;
}
t->parent = NULL;
}
/**
* 关键字key和新结点指针ap分别插入到q->key[i]和q->ptr[i]
*
* @param q 插入目标结点
* @param i 插入位序
* @param key 待插入的关键字
* @param ap 新结点指针
*/
void Insert(BTree &q, int i, KeyType key, BTree ap) {
int j;
int n = q->keynum;
for (j = n; j >= i; j--) {
q->key[j + 1] = q->key[j]; // 后移
q->ptr[j + 1] = q->ptr[j]; // 后移
}
q->key[i] = key;
q->ptr[i] = ap;
if (ap != NULL) {
ap->parent = q;
}
q->keynum++;
}五,B树的删除操作
对于B-树关键字的删除,需要找到待删除的关键字,在结点中删除关键字的过程也有可能破坏B-树的特性,如旧关键字的删除可能使得结点中关键字的个数少于规定个数,的英文这可能需要向其兄弟结点借关键字或者其状语从句:结孩子点进行关键字的交换,可能也。需要进行结点的合并,其中,和当前结点的孩子进行关键字交换的操作可以保证删除操作总是发生在终端结点上。
该结点为最下层非终端结点
- 如果被删关键字所在结点的原关键字个数n≥⌈m/2⌉,则删去该关键字后结点仍满足B树的定义。
- 如果被删关键字所在结点的关键字个数n等于⌈m/2⌉-1,则删除该关键字后该结点将不满足B树的定义,需要调整:如果其左右兄弟结点中有富余的关键字,即与该结点相邻的右(或左)兄弟结点中的关键字数目大于⌈m/2⌉-1,则可将右(或左)兄弟结点中最小(大)关键字上移至双亲结点。而将双亲结点中小(大)于该上移关键字的关键字下移至被删关键字所在结点中。
- 如果左右兄弟结点都没有多余的关键字,则需要把要删除关键字的结点与其左(或右)兄弟结点以及双亲结点中分割两者的关键字合并成一个结点,即在删除关键字后,该结点中剩余的关键字和指针,加上双亲结点中的关键字的Ki一起,合并到Ai-1或(Ai)结点,即删除该关键字结点的左(右)兄弟结点。如果导致双亲结点中关键字个数小于⌈m/2⌉-1,则对此双亲结点做同样处理。如果知道根结点也做了合并,则整棵树减少一层。
该结点不是最下层非终端结点
- 假设被删关键字为该结点中第我个关键字的Ki,则可从指针Ai所指的子树中找出位于最下层非终端结点的最小关键字替代Ki,并将其删除,即可转换为上面的情况进行操作。
下面给出删除叶子结点的几种情况:
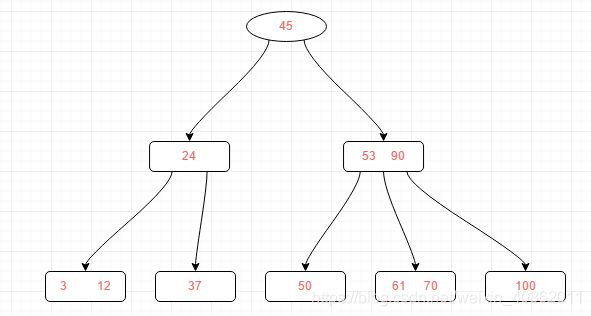
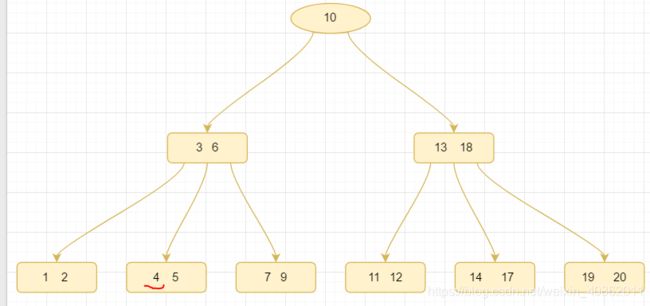
第一种:关键字的数量不小于⌈m/2⌉,如下图删除关键字12
删除12后的结果如下,只是简单的删除关键字和其对应的指针
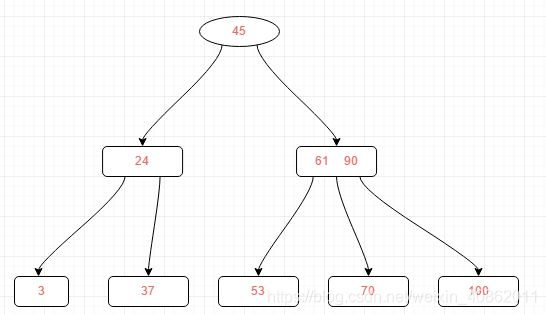
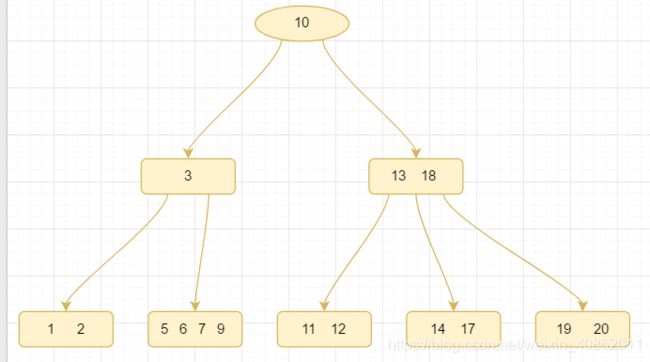
第二种:关键字个数等于⌈m/2⌉-1,而且该结点相邻的右兄弟(或左兄弟)结点中的关键字数目大于⌈m/2⌉-1
在上图中删除50关键字
我们需要把50的右兄弟中最小的关键字:61上移到其父结点,然后替换小于61的关键字53的位置,53则放至50的结点中然后,我们可以得到如下的结果:
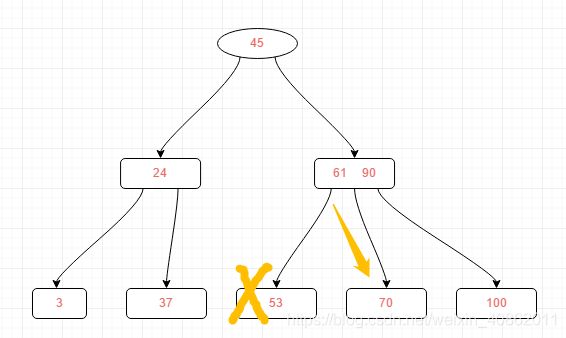
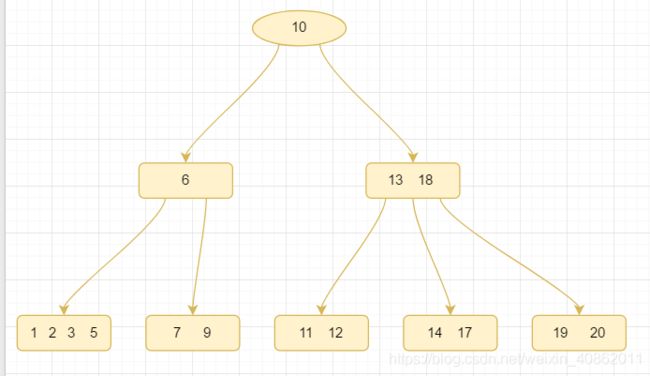
第三种:关键字个数Ñ等于⌈m/2⌉-1,而且被删除关键字所在结点和其相邻的兄弟结点中的关键字数目均等于[M / 2] -1
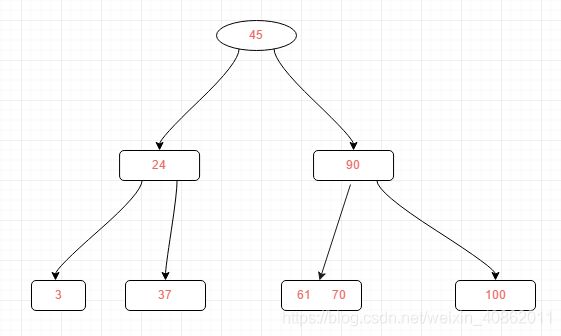
如上图我们删除53,需要将53外的关键字(空)和父亲结点的61关键字一起合并到70这个关键字的结点中,结果如下
第四种:如下图所示
删除关键字4,4在终端结点上,但是此时4所在的结点的关键字个数已经到下限,需要借关键字,可以看到其左右兄弟结点的关键字个数也不够借,因此需要进行关键字的合并,合并的方法有两种,如下图所示
实现代码
/**
* 删除B-树上p结点的第i个关键字
*
* @param t B-树
* @param p 目标关键字所在结点
* @param i 关键字位序
*/
void DeleteBTree(BTree &t, BTree &p, int i) {
if (p->ptr[i] != NULL) { // 不是最下层非终端结点
Successor(p, i); // 找到后继最下层非终端结点的最小关键字代替它
DeleteBTree(t, p, 1); // 删除最下层非终端结点中的最小关键字
} else {
Remove(p, i); // 从结点p中删除key[i]
if (p->keynum < (m-1) / 2) {
Restore(t, p); // 调整B树
}
}
}
/**
* 在Ai子树中找出最下层非终端结点的最小关键字代替Ki
*
* @param p B-树结点
* @param i 关键字位序
*/
void Successor(BTree &p, int i) {
BTree leaf = p;
if (NULL == p) {
return;
}
leaf = leaf->ptr[i]; // 指向子树
while (NULL != leaf->ptr[0]) {
// 找到最下层非终端结点
leaf = leaf->ptr[0];
}
p->key[i] = leaf->key[1];
p = leaf;
}
/**
* 从结点p移除关键字key[i]
*
* @param p B-树结点
* @param i 关键字位序
*/
void Remove(BTree &p, int i) {
int k;
// 指针与key都向左移
for (k = i; k < p->keynum; k++) {
p->key[k] = p->key[k + 1];
p->ptr[k] = p->ptr[k + 1];
}
p->keynum--;
}
/**
* 调整B-树
*
* @param t B-树
* @param p B-树结点
*/
void Restore(BTree &t, BTree &p) {
BTree parent, leftBrother, rightBrother; // 被删结点的父结点、左右兄弟
parent = p->parent;
if (parent != NULL) { // 父结点不为空
// 寻找左右兄弟
int i;
for (i = 0; i <= parent->keynum; i++) {
if (parent->ptr[i] == p) {
break;
}
}
if (i > 0) {
leftBrother = parent->ptr[i - 1];
} else {
leftBrother = NULL;
}
if (i < parent->keynum) {
rightBrother = parent->ptr[i + 1];
} else {
rightBrother = NULL;
}
// 左兄弟或右兄弟有富余关键字
if ((leftBrother != NULL && leftBrother->keynum >= (m + 1) / 2) ||
(rightBrother != NULL && rightBrother->keynum >= (m + 1) / 2)) {
BorrowFromBrother(p, leftBrother, rightBrother, parent, i);
} else {
// 左右兄弟都没富余关键字,需要合并
if (leftBrother != NULL) {
MegerWithLeftBrother(leftBrother, parent, p, t, i); // 与左兄弟合并
} else if (rightBrother != NULL) {
MegerWithRightBrother(rightBrother, parent, p, t, i);
} else {
//当左右子树不存在时改变根结点
for (int j = 0; j <= p->keynum + 1; j++) {
if (p->ptr[j] != NULL) {
t = p->ptr[j];
break;
}
}
t->parent = NULL;
}
}
} else {
//根节点,去掉根节点,使树减一层
BTree a;
for (int j = 0; j <= p->keynum + 1; j++) {
if (p->ptr[j] != NULL) {
a = p;
p = p->ptr[j];
a->ptr[j] = NULL;
free(a);
break;
}
}
t = p;
t->parent = NULL;
}
}
/**
* 向兄弟借关键字
*
* @param p B-树结点
* @param leftBrother p结点的左兄弟结点
* @param rightBrother p结点的右兄弟结点
* @param parent p结点的父亲结点
* @param i 位序
*/
void BorrowFromBrother(BTree &p, BTree &leftBrother, BTree &rightBrother, BTree &parent, int &i) {
// 左兄弟有富余关键字,向左兄弟借
if (leftBrother != NULL && leftBrother->keynum >= (m + 1) / 2) {
for (int j = p->keynum + 1; j > 0; j--) {
// 关键字与指针后移,腾出第一个位置
if (j > 1) {
p->key[j] = p->key[j - 1];
}
p->ptr[j] = p->ptr[j - 1];
}
p->ptr[0] = leftBrother->ptr[leftBrother->keynum];
if (p->ptr[0] != NULL) {
p->ptr[0]->parent = p;
}
leftBrother->ptr[leftBrother->keynum] = NULL;
p->key[1] = parent->key[i]; // 被删结点存父结点关键字
parent->key[i] = leftBrother->key[leftBrother->keynum]; // 父结点的key变为被删结点左兄弟的最大关键字
leftBrother->keynum--;
p->keynum++;
} else if (rightBrother != NULL && rightBrother->keynum >= (m + 1) / 2) { // 右兄弟有富余关键字
p->key[p->keynum + 1] = parent->key[i + 1];
p->ptr[p->keynum + 1] = rightBrother->ptr[0]; // 子树指针指向右兄弟最左边的子树指针
if (p->ptr[p->keynum + 1] != NULL) {
p->ptr[p->keynum + 1]->parent = p;
}
p->keynum++;
parent->key[i + 1] = rightBrother->key[1]; // 父结点从右兄弟借关键字
for (int j = 0; j < rightBrother->keynum; j++) {
if (j > 0) {
rightBrother->key[j] = rightBrother->key[j + 1];
}
rightBrother->ptr[j] = rightBrother->ptr[j + 1];
}
rightBrother->ptr[rightBrother->keynum] = NULL;
rightBrother->keynum--;
}
}
/**
* 与左兄弟合并
*
* @param leftBrother p结点的左兄弟结点
* @param parent p结点的父亲结点
* @param p B-树结点
* @param t B-树
* @param i 位序
*/
void MegerWithLeftBrother(BTree &leftBrother, BTree &parent, BTree &p, BTree &t, int &i) {
// 与左兄弟合并
leftBrother->key[leftBrother->keynum + 1] = parent->key[i]; // 从父结点拿下分割本节点与左兄弟的关键字
leftBrother->ptr[leftBrother->keynum + 1] = p->ptr[0];
if (leftBrother->ptr[leftBrother->keynum + 1] != NULL) {
leftBrother->ptr[leftBrother->keynum + 1]->parent = leftBrother; // 给左兄弟的结点,当此结点存在时需要把其父亲指向指向左结点
}
leftBrother->keynum++; //左兄弟关键数加1
for (int j = 1; j <= p->keynum; j++) {
// 把本结点的关键字和子树指针赋给左兄弟
leftBrother->key[leftBrother->keynum + j] = p->key[j];
leftBrother->ptr[leftBrother->keynum + j] = p->ptr[j];
if (leftBrother->ptr[leftBrother->keynum + j] != NULL) {
leftBrother->ptr[leftBrother->keynum + j]->parent = leftBrother;
}
}
leftBrother->keynum += p->keynum;
parent->ptr[i] = NULL;
free(p); // 释放p结点
for (int j = i;j < parent->keynum; j++) {
// 左移
parent->key[j] = parent->key[j + 1];
parent->ptr[j] = parent->ptr[j + 1];
}
parent->ptr[parent->keynum] = NULL;
parent->keynum--; // 父结点关键字个数减1
if (t == parent) {
// 如果此时父结点为根,则当父结点没有关键字时才调整
if (0 == parent->keynum) {
for (int j = 0;j <= parent->keynum + 1; j++) {
if (parent->ptr[j] != NULL) {
t = parent->ptr[j];
break;
}
t->parent = NULL;
}
}
} else {
// 如果父结点不为根,则需要判断是否需要重新调整
if (parent->keynum < (m - 1) / 2) {
Restore(t, parent);
}
}
}
/**
* 与右兄弟合并
*
* @param rightBrother p结点的右兄弟结点
* @param parent p结点的父亲结点
* @param p B-树结点
* @param t B-树
* @param i 位序
*/
void MegerWithRightBrother(BTree &rightBrother, BTree &parent, BTree &p, BTree &t, int &i) {
// 与右兄弟合并
for (int j = (rightBrother->keynum); j > 0; j--) {
if (j > 0) {
rightBrother->key[j + 1 + p->keynum] = rightBrother->key[j];
}
rightBrother->ptr[j + 1 + p->keynum] = rightBrother->ptr[j];
}
rightBrother->key[p->keynum + 1] = parent->key[i + 1]; // 把父结点的分割两个本兄弟和右兄弟的关键字拿下来使用
for (int j = 0; j <= p->keynum; j++) {
// 把本结点的关键字及子树指针移动右兄弟中去
if (j > 0) {
rightBrother->key[j] = p->key[j];
}
rightBrother->ptr[j] = p->ptr[j];
if (rightBrother->ptr[j] != NULL) {
rightBrother->ptr[j]->parent = rightBrother; // 给右兄弟的结点需要把其父结点指向右兄弟
}
}
rightBrother->keynum += (p->keynum + 1);
parent->ptr[i] = NULL;
free(p); // 释放p结点
for (int j = i;j < parent->keynum;j++) {
if (j > i) {
parent->key[j] = parent->key[j + 1];
}
parent->ptr[j] = parent->ptr[j + 1];
}
if (1 == parent->keynum) {
// 如果父结点在关键字减少之前只有一个结点,那么需要把父结点的右孩子赋值给左孩子
parent->ptr[0] = parent->ptr[1];
}
parent->ptr[parent->keynum] = NULL;
parent->keynum--; // 父结点关键字数减1
if (t == parent) {
//如果此时父结点为根,则当父结点没有关键字时才调整
if (0 == parent->keynum) {
for (int j = 0; j <= parent->keynum + 1; j++) {
if (parent->ptr[j] != NULL) {
t = parent->ptr[j];
break;
}
}
t->parent = NULL;
}
} else {
//如果父结点不为根,则需要判断是否需要重新调整
if (parent->keynum < (m - 1) / 2) {
Restore(t, parent);
}
}
}
更详细的B树删除操作请参考----> B树的删除操作(五种情况图解)