JAVA 的IO流(异常&File文件类)及一些常用流
IO流:IO流用来处理设备之间的数据传输,上传文件和下载文件因为IO流操作的对象就是File文件,而且操作过程中会出现很多的异常,所以还要学习异常和File文件类
异常:Java程序在运行过程中出现的错误
Throwable是所有异常的顶层父类
异常分为两种:
1。Error严重问题:不用处理,因为问题非常严重,例如内存溢出
2。Exception非严重问题:可解决也可以不解决
(1):编译期异常:非RuntimeException(异常必须解决)发生在编译期间,必须处理,不处理,程序就无法运行,此时有两种处理方法
-1)抛出异常给调用者,谁调用谁就来处理 ,throws一般只抛出到 main方法 ,就要处理 -2)自己处理,使用try catch方式
(2):运行期异常:RuntimeException,可解决可不解决
发生在程序运行过程中
一旦发生异常JVM有自己默认的处理方式:打印异常信息,结束JVM
但一般不采用默认的处理方式,而是捕获异常自己去处理
try catch finally方法
try一般放一些有问题的代码
catch一旦try发生异常了,就会进入catc里面
finally不管前面是否执行,finally都会执行,一般做一些收尾工作,比如释放资源
package org.westos.demo2;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a=2;
int b=0;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入第一个整数");
a = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入第二个整数");
b = sc.nextInt();
try {//
一般放一些有问题的代码 System.out.println(a/b);
System.out.println("一般放一些有问题的代码");
}
catch (Exception e) {
//
一旦try发生异常了,就会进入catch里面
System.out.println("一旦try发生异常了,就会进入catch里面");
}
finally {
//finally 最后的 //finally 不管try里面遇不遇到异常
//finally 都会执行,一般做一些首尾工作,比如释放资源
sc.close();
}
}
}
throws方法
private static void hehe() throws ParseException {
String dateStr="2018-02-04";
SimpleDateFormat simp = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy:MM-dd");
//编译期异常有处理方式.抛出异常给调用者(甩锅) //ParseException 解析异常
simp.parse(dateStr);
Throwable常见方法
getMessage()获取异常信息,返回字符串
toString()获取异常类名和异常信息,返回字符串
printStackTrace()获取异常类名和异常信息,以及异常出现在程序中的位置返回值void
throw和throws的区别
1。throws用在方法声明后面,跟的是异常类名,可以跟多个异常类名,用逗号隔开
表示抛出异常,由该方法的调用者来处理throws表示出现异常的一种可能性,
并不一定会发生这些异常
2。throw用在方法体内,跟的是异常对象名,只能抛出一个异常对象名
这个异常对象可以是编译期异常对象,可以是运行期异常对象
表示抛出异常,由方法体内的语句处理
throw则是抛出了异常,执行throw则一定抛出了某种异常
自定义异常
开发过程中,会遇到很多的问题,而有的问题并没有对应的异常与之对应,
所以就需要自己定义常量,而我们自己定义的常量必须继承自Exception
package org.westos.demo4;
//自定义异常类
public class MyException extends RuntimeException{
public MyException() {
super();
}
public MyException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
package org.westos.demo4;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test {
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入你的取款金额");
int money = sc.nextInt();
if(money>200) {
throw new MyException("余额不足");
}else {
System.out.println("取款成功");
}
}
}
当异常出现父子关系时
1.父类的方法如果没有抛出异常,那子类在重写父类的方法时也不能抛出异常
2.父类如果抛出了异常,子类也可以抛出异常,但是不能比父类的大,但是可以跟父类一样,或者比父类小
3.如果说父类抛出了多个异常,那子类只能抛出父类中的异常的 一个 或几个,但是不能抛出父类中没有的异常
File文件类:对目录和文件的封装
文件类的功能和方法
三种构造方法
File(String pathname):根据一个路径得到File对象
File(String parent, String child):根据一个目录和一个子文件/目录得到File对象
File(File parent, String child):根据一个父File对象和一个子文件/目录得到File对象
File file = new File("D:\\abc");
File file4 = new File(file,"a.txt");
File file2 = new File("D:\\abc\\a.txt");
File file3=new File("D:\\abc","a.txt");1。创建功能
public boolean createNewFile():创建一个新的文件 如果存在这样的文件,就不创建了
public boolean mkdirs():创建文件夹,如果父文件夹不存在,会帮你创建出来
可以创建多层目录 当然也可以创建单层目录
如果创建文件或文件夹时没有写盘符路径,默认在项目路径下
相对路径:没有带盘符的路径
绝对路径:带有盘符的路径
2。删除功能
public boolean delete():删除文件或者文件夹
注意:删除文件夹时 这个文件夹是空文件夹 如果这个文件夹里面有文件,则不能删除
3。重命名功能
public boolean renameTo(File dest):把文件重命名为指定的文件路径
如果路径名相同,就是改名。
如果路径名不同,就是改名并剪切。
4。判断功能
public boolean isDirectory():判断是否是目录
public boolean isFile(): 判断是否是文件
public boolean exists(): 判断是否存在
public boolean canRead(): 判断是否可读
public boolean canWrite(): 判断是否可写
public boolean isHidden(): 判断是否隐藏
5。获取功能
public String getAbsolutePath(): 获取绝对路径
public String getPath(): 获取相对路径
public String getParent() 返回此抽象路径名父目录的路径名字符串;如果此路径名没有指定父目录,则返回 null
public File getParentFile() 返回此抽象路径名父目录的抽象路径名;如果此路径名没有指定父目录,则返回 null
public long getTotalSpace() 返回此抽象路径名指定的分区大小。 返回总容量 单位字节
public long getFreeSpace() 返回此抽象路径名指定的分区中未分配的字节数。返回剩余容量 单位字节
public String getName(): 获取名称
public long length(): 获取长度。字节数
public long lastModified(): 获取最后一次的修改时间,毫秒值
public String[] list(): 获取指定目录下的所有文件或者文件夹的名称数组
public File[] listFiles(): 获取指定目录下的所有文件或者文件夹的File数组
获取指定目录下的所有文件或文件夹的名称数组或者File数组
package org.westos.demo4;
import java.io.File;
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// public String[] list(): 获取指定目录下的所有文件或者文件夹的名称数组
// public File[] listFiles(): 获取指定目录下的所有文件或者文件夹的File数组
File file = new File("E:\\eclipse");
String[] list = file.list();
for(String name:list) {
System.out.println(name);
}
System.out.println("------------------------------------------");
File file2 = new File("E:\\aaa");
File[] listFiles = file2.listFiles();
for(File f:listFiles) {
System.out.println(f.getName());
if(f.isFile()) {
if(f.getName().endsWith(".txt")) {
f.delete();
}
}
}
}
}
判断指定盘下是否有指定格式结尾的文件并输出名称
方法1
package org.westos.demo5;
import java.io.File;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//需求:判断E盘目录下是否有后缀名为.jpg的文件
//如果有,就输出该文件名称
File file = new File("E:\\demo");
//获取此目录下的所有的文件或文件夹的数组
File[] files = file.listFiles();
for(File f:files) {
if(f.isFile()) {
if(f.getName().endsWith(".jpg")) {
System.out.println(f.getName());
}
}
}
}
}
方法2
package org.westos.demo5;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FilenameFilter;
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//需求:判断E盘目录下是否有后缀名为.jpg的文件
//如果有,就输出该文件名称
File file = new File("E:\\demo");
File[] listFiles = file.listFiles(new FilenameFilter() {
@Override
public boolean accept(File dir, String name) {
//System.out.println(dir);
//System.out.println(name);
File file2 = new File(dir,name);
if(file2.isFile()&&file2.getName().endsWith(".jpg")) {
return true;
}else {
return false;
}
}
});
System.out.println(listFiles.length);
for(File f:listFiles) {
System.out.println(f.getName());
}
}
}
删除多级目录(递归调用)
package org.westos.demo6;
import java.io.File;
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 删除多级目录
File file = new File("E:\\demo");
// boolean f = file.delete();
// 获取此目录下所有的文件或文件夹
delFile(file);
}
private static void delFile(File file) {
File[] listFiles = file.listFiles();
for (File f : listFiles) {
if (f.isDirectory()) {
delFile(f);// 递归调用 :方法内部调用方法本身
} else {
f.delete();
}
}
file.delete();
}
}
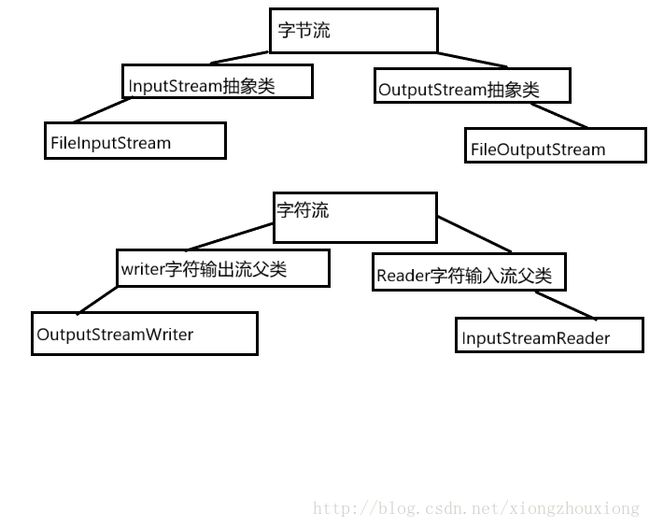
IO流
IO流的分类
按流向分:分为输入流和输出流
按类型分:分为字节流和字符流
IO流的继承图
字节流
FileOutputStream字节输出流
两种构造方法:
FileOutputStream(File file)
FileOutputStream(String name)
fos2.write('a');字符型
fos2.write("c".getBytes());字符串应该转换为字符型
流用完之后一定要释放资源 .close()
例如: FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("hehe2.txt", true);
三种write方法
public void write(int b):写一个字节 超过一个字节 砍掉前面的字节
public void write(byte[] b):写一个字节数组
public void write(byte[] b,int off,int len):写一个字节数组的一部分
GBK编码:一个汉字占两个字节
UTF-8:一个汉字占三个字节
FileInputStream字节输入流
int len = 0 ; // 作用: 记录读取到的有效的字节个数
for(byte b:bytes){
System.out.print(new String(b);
package org.westos.demo2;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("E:\\20180204-JavaSE-File类的介绍5.exe");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\\b.exe");
//模版代码
byte[] by = new byte[1024];//数据缓冲区
int len = 0;//读取到的字节有效个数
while ((len = fis.read(by)) != -1) {
fos.write(by, 0, len);
}
fis.close();
fos.close();
}
}
流用完之后一定要释放资源 .close()
package org.westos.demo4;
import java.io.*;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.time.Instant;
public class MyTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
// BufferedInputStream BufferedOutputStream 底层引入了这个缓冲区的思想
Instant start = Instant.now();
// test();//耗时12271毫秒 耗时2132毫秒
test2();//耗时41776毫秒 耗时3345毫秒
Instant end = Instant.now();
long time = Duration.between(start, end).toMillis();
System.out.println("耗时"+time+"毫秒");
}
private static void test2() throws IOException{
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\test.zip");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("E:\\test.zip");
byte[] by=new byte[1024];//充当缓冲区
int len=0;
while ((len=fis.read(by))!=-1){
fos.write(by,0,len);
fos.flush();
}
fis.close();
fos.close();
}
private static void test() throws IOException{
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:\\test.zip"));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("E:\\test.zip"));
//读一个字节 写一个字节
byte[] by=new byte[1024];//充当缓冲区
int len=0;
while ((len=bis.read(by))!=-1){
bos.write(by,0,len);
bos.flush();
}
//释放资源
bis.close();
bos.close();
}
}
package org.westos.demo5;
import java.io.*;
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//复制单级文件夹
//1.封装源文件夹
File srcFile = new File("D:\\demo2");
//2.封装目标文件夹
File mbFile = new File("E:\\demo2");
//3.如果目标文件夹没有
if (!mbFile.exists()) {
mbFile.mkdirs();
}
//4.复制文件
copyFiles(srcFile, mbFile);
}
private static void copyFiles(File srcFile, File mbFile) {
//文件的复制
File[] files = srcFile.listFiles();
for (File f : files) {
if(f.isFile()){
//如果是文件
//开始复制
copySingleFile(f, mbFile);
}else{
//递归调用
//封装源文件夹
System.out.println(f.toString());
//封装目标文件夹
String mbfilePath=mbFile+"\\"+f.getName();
System.out.println(mbfilePath);
//System.out.println(mbfilePaht);
File mb = new File(mbfilePath);
if(!mb.exists()){
mb.mkdirs();
}
//递归调用
copyFiles(f,mb);
}
}
}
private static void copySingleFile(File f, File mbFile) {
try {
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(f));
//D:\\demo2\\a.txt
//E:\\demo2\\a.txt
String mbFilePath = mbFile + "\\" + f.getName();
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(mbFilePath));
//频繁的读写
byte[] by = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while ((len = bis.read(by)) != -1) {
bos.write(by, 0, len);
bos.flush();
}
bis.close();
bos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
字符流
字节流的五种写入方式
public void write(char[] cbuf) 写一个字符数组
public void write(char[] cbuf,int off,int len) 写一个字符数组的 一部分
public void write(String str) 写一个字符串
public void write(String str,int off,int len) 写一个字符串的一部分
输出流所关联的文件如果不存在会自动创建
输入流所关联的文件如果不存在就会报错
转换流,字符输入流InputStreamReader
构造方法:
InputStreamReader(InputStream is)
用默认的编码(GBK)读取数据
InputStreamReader(InputStream is,String charsetName)
用指定的编码读取数据
字符流的两种读取方法
public int read() 一次读取一个字符
public int read(char[] cbuf) 一次读取一个字符数组 如果没有读到 返回-1
一次读取一个数组时需要一个缓冲区char[] chs = new char[1024]
案例:字符流复制文本文件
package org.westos.demo2;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
public class MyTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
//我们一次读取一个字符数组来复制文本文件
//一次读取一个字符来复制文本文件
InputStreamReader is=new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("MyTest4.java"));
OutputStreamWriter os=new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("E:\\MyTest4.java"));
char[] chs=new char[1024];
int len=0;
while((len=is.read(chs))!=-1) {
os.write(chs, 0, len);
os.flush();
}
is.close();
os.close();
}
}
package org.westos.demo2;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//一次读取一个字符来复制文本文件
InputStreamReader is=new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("MyTest4.java"));
OutputStreamWriter os=new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("E:\\MyTest4.java"));
int len=0;
while((len=is.read())!=-1) {
os.write(len);
os.flush();
}
//释放资源
is.close();
os.close();
}
}
字符流便捷类FileWriter和FileReader
转换流的名字比较长,而我们常见的操作都是按照本地默认编码实现的,所以,为了简化我们的书写,转换流提供了对应的子类FileWriter和FileReader
这两个类不能指定编码方式,所以使用默认编码,具有追加功能
案例:FileWriter和FileReader复制文本文件
注意事项:
一般情况下,如果想要对流复制的文件进行增删等操作,应该在流close之后再操作,否则不起作用
序列化:把内存中的数据,写到硬盘上
反序列化:把硬盘中的数据,读到内存中
高效的字符流
BufferedReader(Reader in)高效字符输入流
readline()一次读一行,读不到返回null
BufferedWriter(Writer out)高效字符输出流
newline()高效字符流独有的具有平台兼容性的换行符
package org.westos.demo;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 采用高效的字符流进行文本文件的复制
BufferedReader bfr = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("a.java"));
BufferedWriter bfw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("E:\\b.txt"));
char[] chs = new char[1024];
int len = 0;
while ((len = bfr.read(chs)) != -1) {
bfw.write(chs, 0, len);
bfw.flush();
}
// 频繁的读写文件
String line = null;
while ((line = bfr.readLine()) != null) {
bfw.write(line);
bfw.flush();
bfw.newLine();
}
bfr.close();
bfw.close();
}
}
案例:把集合中的数据存储到文本文件
package org.westos.demo4;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//把ArrayList集合中的字符串数据存储到文本文件
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
list.add("张三");
list.add("李四");
list.add("王五");
list.add("赵六");
//把集合中的数据保存到文本文件中
BufferedWriter bfw=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("学生名单.txt"));
for(String name:list) {
bfw.write(name);
bfw.newLine();
bfw.flush();
}
bfw.close();
}
}
案例:复制单级文件夹
package org.westos.demo;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 从文本文件中读取数据(每一行为一个字符串数据)到集合中,并遍历集合
BufferedReader bfr = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("学生名单.txt"));
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
String line = null;
while ((line = bfr.readLine()) != null) {
list.add(line);
}
bfr.close();
for (String name : list) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
}
package org.westos.demo;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Random;
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 有一个文本文件,每一行是一个学生的名字,请写一个程序,每次允许随机获取一个学生名称
BufferedReader bfr = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("学生名单.txt"));
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
String line = null;
while ((line = bfr.readLine()) != null) {
list.add(line);
}
bfr.close();
Random random = new Random();
int index = random.nextInt(list.size());
System.out.println(list.get(index));
new File("abc.txt").createNewFile();
}
} package org.westos.demo;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.FilenameFilter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 复制D:\\demo目录下所有以.java结尾的文件到E:\\demo .并且将其后缀名更改文.txt
File srcfile = new File("D:\\demo");
File mbfile = new File("E:\\demo");
if (!mbfile.exists()) {
mbfile.mkdirs();
}
// 复制文件
copyFiles(srcfile, mbfile);
//这里改名
File[] listFiles = mbfile.listFiles();
for (File file : listFiles) {
File file2=new File(mbfile,file.getName().replaceAll(".java", ".txt"));
file.renameTo(file2);
}
}
private static void copyFiles(File srcfile, File mbfile) throws IOException {
File[] files = srcfile.listFiles(new FilenameFilter() {
@Override
public boolean accept(File dir, String name) {
File file = new File(dir, name);
if (file.isFile() && file.getName().endsWith(".java")) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
});
// 遍历文件数组,复制文件
for (File f : files) {
copySingleFile(f, mbfile);
}
}
// 复制文件
private static void copySingleFile(File f, File mbfile) throws IOException {
BufferedReader bfr = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(f));
String fileName = mbfile + "\\" + f.getName();
BufferedWriter bfw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(fileName));
String line = null;
while ((line = bfr.readLine()) != null) {
bfw.write(line);
bfw.newLine();
bfw.flush();
}
bfw.close();
bfr.close();
}
}
案例:键盘录入学生信息按照总分排序并写入文本文件
学生类:
package org.westos.demo5;
public class Student {
private String name;
private double chineseScore;
private double mathScore;
private double englishScore;
private double totalScore;
public Student() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getChineseScore() {
return chineseScore;
}
public void setChineseScore(double chineseScore) {
this.chineseScore = chineseScore;
}
public double getMathScore() {
return mathScore;
}
public void setMathScore(double mathScore) {
this.mathScore = mathScore;
}
public double getEnglishScore() {
return englishScore;
}
public void setEnglishScore(double englishScore) {
this.englishScore = englishScore;
}
public double getTotalScore() {
return chineseScore + mathScore + englishScore;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [name=" + name + ", chineseScore=" + chineseScore + ", mathScore=" + mathScore
+ ", englishScore=" + englishScore + "]";
}
}
测试类:
package org.westos.demo5;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class MyTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 键盘录入3个学生信息(姓名,语文成绩(chineseScore),数学成绩(mathScore),英语成绩(englishScore)),
// 按照总分从高到低存入文本文件
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
TreeSet treeSet = new TreeSet(new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Student s1, Student s2) {
return (int) (s1.getTotalScore() - s2.getTotalScore());
}
});
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
System.out.println("请输入第" + i + "个学生的姓名");
String name = sc.next();
Student student = new Student();
student.setName(name);
System.out.println("请输入" + name + "的语文成绩");
double chineseScore = sc.nextDouble();
student.setChineseScore(chineseScore);
System.out.println("请输入" + name + "的数学成绩");
double mathScore = sc.nextDouble();
student.setMathScore(mathScore);
System.out.println("请输入" + name + "的英语成绩");
double englishScore = sc.nextDouble();
student.setEnglishScore(englishScore);
treeSet.add(student);
}
// 从集合中拿出数据保存到
BufferedWriter bfw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("学生成绩.txt"));
bfw.write("学生姓名" + "\t" + "语文成绩" + "\t" + "数学成绩" + "\t" + "英语成绩" + "\t" + "总分");
bfw.newLine();
bfw.flush();
for (Student stu : treeSet) {
bfw.write(stu.getName() + "\t" + stu.getChineseScore() + "\t" + stu.getMathScore() + "\t"
+ stu.getEnglishScore() + "\t" + stu.getTotalScore());
bfw.newLine();
bfw.flush();
}
bfw.close();
sc.close();
}
}
数据输出流: DataOutputStream
这个流关闭是无效的,所以就不用关闭了
操作字节数组
ByteArrayOutputStream
ByteArrayInputStream
操作字符数组
CharArrayWrite
CharArrayReader
StringWriter
StringReader
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("a.txt"));
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("a.txt"));
dos.writeInt(100);
dos.writeByte(99);
dos.writeDouble(3.14);
dos.writeBoolean(false);
dis.readInt();
dis.readByte();
dis.readDouble();
dis.readBoolean();
有字符打印流和字节打印流,他不读取文件,只做输出到屏幕上或者输出到文件中
PrintWriter 字符打印流
可以用write写入也可以用print写入
PrintWriter pw=new PrintWriter(new File("d.txt"));
pw.write("b");
pw.write("a");
pw.print("c");
PrintWriter(OutputStream out, boolean autoFlush)
这个构造可以选择是否开启自动刷新功能,比如:
PrintWriter pw2=new PrintWriter(new FileOutputStream("e.txt"),true);
true表示开启自动刷新功能
但是只有在调用println,printf,format的时候才会有用
通过以下方式打印的内容会打印到文件中
PrintStream ps=new PrintStream(new File("c.txt"));
ps.println("abc");
ps.println("ccc");
ps.println("abc");
第一种是我们都很熟悉的scnner方法这里不再细说了
第二种是
String line = bfr.readLine();
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(new File("f.txt"), "rw");rw表示可读可写
方法:
. seek()设定指针的位置
.getFilePointer()得到指针的位置
断点下载简单案例:
package org.westos.demo;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(new File("MyTest.java"), "rw");
RandomAccessFile raf2 = new RandomAccessFile(new File("MyTest2.java"), "rw");
String line=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("cache.txt")).readLine();
long long1 = Long.parseLong(line);
File file = new File("MyTest2.java");
if(file.exists()&&file.length()==long1) {
raf.seek(long1);
}else {
//从头下
raf.seek(0);
}
int len=0;
int length=0;
try {
while ((len=raf.read())!=-1) {
length++;
raf2.write(len);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
//等你遇到异常后
long pointer = raf.getFilePointer();
PrintStream ps=new PrintStream(new File("cache.txt"));
ps.print(pointer);
}
raf.close();
raf2.close();
}
}
序列化与反序列化流
所谓的序列化:就是把对象通过流的方式存储到文件中
有专用的存取方法
存setProperties(key,value)
取getProperties(key)键找值
特殊例子getProperties(key,value)如果这个键key没有找到对应的值就会输出这个value
package org.westos.demo5;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.sound.midi.Soundbank;
public class MyTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("username", "zhangsan");
properties.setProperty("password", "123456");
// 关联一个流写出集合中的数据到文件上
properties.store(new FileWriter(new File("user.txt")), null);
System.out.println("----------------------------------------------");
Properties properties2 = new Properties();
properties2.load(new FileReader(new File("user.txt")));
String user = properties2.getProperty("username");
String pwd = properties2.getProperty("password");
System.out.println(user);
System.out.println(pwd);
System.out.println("================================================");
Properties properties3 = new Properties();
properties3.load(new FileReader(new File("peizhi.properties")));
String s1 = properties3.getProperty("s001");
String s2 = properties3.getProperty("s002");
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s2);
}
}
有一个文本文件,我知道数据是键值对形式的,但是不知道内容是什么。
请写一个程序判断是否有“lisi”这样的键存在,如果有就改变其值为”100”
package org.westos.demo6;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties;
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, IOException {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileReader("demo.txt"));
boolean b = properties.containsKey("lisi");
if (b) {
properties.setProperty("lisi", "100");
properties.store(new FileWriter("demo.txt"), null);
}
}
}