MPC实现自动驾驶轨迹跟踪
本文继MPC运动学方法实现轨迹跟踪推导进行matlab代码实现,虽然你们找到的参考书都是simulink carsim联仿,我却坚持使用纯代码仿真,因为牛逼。
代码模板沿用了LQR轨迹跟踪算法Python/Matlab算法实现,LQR轨迹跟踪算法Python/Matlab算法实现2, LQR轨迹跟踪算法Python算法实现3。代码直接复制下来就能用,拿去爽。
clc
clear all
Kp = 1.0 ;
dt = 0.1 ;% [s]
Length = 2.9 ;% [m] wheel base of vehicle
Nx=3;%状态量的个数
Nu =2;%控制量的个数
Np =60;%预测步长
Nc=30;%控制步长
Row=10;%松弛因子
Q=100*eye(Nx*Np,Nx*Np);
R=1*eye(Nc*Nu);
max_steer =60 * pi/180; % in rad
target_v =30.0 / 3.6;
cx = 0:0.1:200; % sampling interception from 0 to 100, with step 0.1
for i = 1:500% here we create a original reference line, which the vehicle should always follow when there is no obstacles;
cy(i) = -sin(cx(i)/10)*cx(i)/8;
end
for i = 501: length(cx)
cy(i) = -sin(cx(i)/10)*cx(i)/8; %cy(500);
end
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% here we provide another reference line for testing, now you dont need to
% use it
% %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
p = [cx', cy'];
%计算一阶导数
for i = 1:length(cx)-1
pd(i) = (p(i+1,2)-p(i,2))/(p(i+1,1)-p(i,1));
end
pd(end+1) = pd(end);
%计算二阶导数
for i =2: length(cx)-1
pdd(i) = (p(i+1,2)-2*p(i,2) + p(i-1,2))/(0.5*(-p(i-1,1)+p(i+1,1)))^2;
end
pdd(1) = pdd(2);
pdd(length(cx)) = pdd(length(cx)-1);
%计算曲率
for i = 1:length(cx)-1
k(i) = (pdd(i))/(1+pd(i)^2)^(1.5);
end
cx= cx';
cy =cy';
cyaw = atan(pd');
ck = k';
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% above things are preprocessing %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
i = 1;
T = 80;
lastIndex = length(cx);
x = 0.1; y = -0.1; yaw = 0.1; v = 0.1;
U = [0.01;0.01];
vd1_p = 0;
vd2_p = 0;
vd_p = [vd1_p; vd2_p];
ind =0;
figure
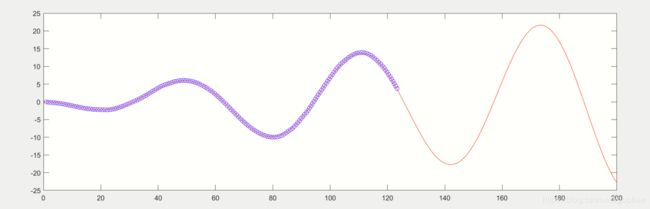
plot(cx,cy,'r-')
hold on
while ind < length(cx)
[delta,v,ind,e,U, vd_p ] = mpc_control(x,y,yaw,cx,cy,cyaw,ck,dt,Length,Q,R,U,target_v,vd_p) ;
if abs(e)> 3% we do not allow the vehicle deviation larger than 4
fprintf('diviation too big!\n')
break;
end
delta
[x,y,yaw,v] = update(x,y,yaw,v, delta, dt,Length, max_steer); %update the vehicle state for next iteration
posx(i) = x;
posy(i) =y;
i = i+1;
plot(posx(i-1),posy(i-1),'bo')
pause(0.01);
hold on
end
%% supplimented functions are as follows:
% function"Update" updates vehicle states
function [x, y, yaw, v] = update(x, y, yaw, v, delta,dt,Length,max_steer)% update x, y, yaw, and velocity
delta = max(min(max_steer, delta), -max_steer);
x = x + v * cos(yaw) * dt + randn(1)* 0;
y = y + v * sin(yaw) * dt + randn(1)* 0;
yaw = yaw + v / Length * tan(delta) * dt ;
v = v ;
end
function [a] = PIDcontrol(target_v, current_v, Kp) %we originally control v separately
a = Kp * (target_v - current_v);
end
function [angle] = pipi(angle) % the unit of angle is in rad, but in this case, you dont need to use it ;
if (angle > pi)
angle = angle - 2*pi;
elseif (angle < -pi)
angle = angle + 2*pi;
else
angle = angle;
end
end
function [delta,v,ind,e,U, vd_p ] = ...
mpc_control(x,y,yaw,cx,cy,cyaw,ck,dt,Length,Q,R,U,target_v,vd_p)
u = [x,y,yaw];
[ind, e] = calc_target_index(x,y,cx,cy,cyaw); % find current vehicle location, it is represented by reference index
vd1=target_v ;
k =ck(ind);
vd2=atan(Length * k);
r = [cx(ind), cy(ind), cyaw(ind)];
Nx=3;%状态量的个数
Nu =2;%控制量的个数
Np =60;%预测步长
Nc=30;%控制步长
Row=10;%松弛因子
t_d =u(3);%角度为弧度
kesi=zeros(Nx+Nu,1);
kesi(1)=u(1)-r(1);%u(1)==X(1)
kesi(2)=u(2)-r(2);%u(2)==X(2)
kesi(3)=t_d-r(3); %u(3)==X(3)
kesi(4)=U(1);
kesi(5)=U(2);
% fprintf('Update start, u(1)=%4.2f\n',U(1))
% fprintf('Update start, u(2)=%4.2f\n',U(2))
T=dt;
% Mobile Robot Parameters
L = Length;
% Mobile Robot variable
%矩阵初始化
delta_u=zeros(Nx,Nu);
a=[1 0 -vd1*sin(t_d)*T;
0 1 vd1*cos(t_d)*T;
0 0 1;];
b=[cos(t_d)*T 0;
sin(t_d)*T 0;
tan(vd2)*T/L vd1*T/(L * (cos(vd2)^2))];
A_cell=cell(2,2);
B_cell=cell(2,1);
A_cell{1,1}=a;
A_cell{1,2}=b;
A_cell{2,1}=zeros(Nu,Nx);
A_cell{2,2}=eye(Nu);
B_cell{1,1}=b;
B_cell{2,1}=eye(Nu);
A=cell2mat(A_cell);
B=cell2mat(B_cell);
C=[1 0 0 0 0;0 1 0 0 0;0 0 1 0 0;];
PHI_cell=cell(Np,1);
THETA_cell=cell(Np,Nc);
for j=1:1:Np
PHI_cell{j,1}=C*A^j;
for k=1:1:Nc
if k<=j
THETA_cell{j,k}=C*A^(j-k)*B;
else
THETA_cell{j,k}=zeros(Nx,Nu);
end
end
end
PHI=cell2mat(PHI_cell);%size(PHI)=[Nx*Np Nx+Nu]
THETA=cell2mat(THETA_cell);%size(THETA)=[Nx*Np Nu*(Nc+1)]
H_cell=cell(2,2);
H_cell{1,1}=THETA'*Q*THETA+R;
H_cell{1,2}=zeros(Nu*Nc,1);
H_cell{2,1}=zeros(1,Nu*Nc);
H_cell{2,2}=Row;
H=cell2mat(H_cell);
H = 1/2*(H+ H');
error=PHI*kesi;
f_cell=cell(1,2);
f_cell{1,1}=2*error'*Q*THETA;
f_cell{1,2}=0;
% f=(cell2mat(f_cell))';
f=cell2mat(f_cell);
%% 以下为约束生成区域
%不等式约束
A_t=zeros(Nc,Nc);%见falcone论文 P181
for p=1:1:Nc
for q=1:1:Nc
if q<=p
A_t(p,q)=1;
else
A_t(p,q)=0;
end
end
end
A_I=kron(A_t,eye(Nu));%对应于falcone论文约束处理的矩阵A,求克罗内克积
Ut=kron(ones(Nc,1),U);%此处感觉论文里的克罗内科积有问题,暂时交换顺序
umin=[-0.2;-0.54;];%维数与控制变量的个数相同
umax=[0.2;0.332];
% delta_umin=[0.05;-0.0082;];
% delta_umax=[0.05;0.0082];
delta_umin = [ -2.2 ; -0.64];
delta_umax = [ 0.2 ; 0.64];
Umin=kron(ones(Nc,1),umin);
Umax=kron(ones(Nc,1),umax);
A_cons_cell={A_I zeros(Nu*Nc,1);-A_I zeros(Nu*Nc,1)};
b_cons_cell={Umax-Ut;-Umin+Ut};
A_cons=cell2mat(A_cons_cell);%(求解方程)状态量不等式约束增益矩阵,转换为绝对值的取值范围
b_cons=cell2mat(b_cons_cell);%(求解方程)状态量不等式约束的取值
% 状态量约束
M=10;
delta_Umin=kron(ones(Nc,1),delta_umin);
delta_Umax=kron(ones(Nc,1),delta_umax);
lb=[delta_Umin;0];%(求解方程)状态量下界,包含控制时域内控制增量和松弛因子
ub=[delta_Umax;M];%(求解方程)状态量上界,包含控制时域内控制增量和松弛因子
%% 开始求解过程
% options = optimset('Algorithm','interior-point-convex');
options = optimoptions('quadprog','Display','iter','MaxIterations',100,'TolFun',1e-16);
%options = optimset('Algorithm','interior-point-convex');
[X,fval,exitflag]=quadprog(H,f,A_cons,b_cons,[],[],lb,ub,[],options);
%% 计算输出
% for i = 1:length(X)
% if X == []
% delta_u(1)=randn(1)*0.01;
% delta_u(2)=randn(1)*0.01;
% elseif X(i) == 0
% delta_u(1)=randn(1)*0.01;
% delta_u(2)=randn(1)*0.01;
% else
% delta_u(1)=X(1);
% delta_u(2)=X(2);
% end
% end
delta_u(1)=X(1);
delta_u(2)=X(2);
U(1)=kesi(4)+delta_u(1) ;%用于存储上一个时刻的控制量
U(2)=kesi(5)+delta_u(2); %kesi here is previous step U
u_real(1)=U(1)+vd1; % vd1 and vd2 here is U_ref
u_real(2)=U(2)+vd2;
delta= u_real(2);
v = u_real(1);
% U(1)=kesi(4)+delta_u(1) + vd1 - vd_p(1);%用于存储上一个时刻的控制量
% U(2)=kesi(5)+delta_u(2) + vd2 - vd_p(2); %kesi here is previous step U
kesi(4) = U(1);
kesi(5) = U(2);
vd_p = [vd1;vd2 ];
% delta = U(2)
% v = 3
end
function [ind, error] = calc_target_index(x,y, cx,cy,cyaw)% find my location, and lateral error
N = length(cx);
Distance = zeros(N,1);
for i = 1:N
Distance(i) = sqrt((cx(i)-x)^2 + (cy(i)-y)^2);
end
[value, location]= min(Distance);
ind = location
dx1 = cx(ind) - x;
dy1 = cy(ind) - y ;
angle = pipi(cyaw(ind)-atan(dy1/dx1));
heading = cyaw(ind)*180/pi
if y<cy(ind)
error = -value;
else
error = value;
end
% error = value;
end