数据结构与算法|前缀、中缀与后缀表达式的转换与计算(Java版与C++版)
目录
- @[TOC](目录)
- 1.何为前缀、中缀、后缀表达式?
- 2.中缀表达式的计算
- 3.中缀表达式转前缀表达式及其计算
- 3.1C++语言实现中缀2前缀
- 3.2Java语言实现中缀2前缀
- 4.中缀表达式转后缀表达式及其计算
- 5.参考博客
目录
- @[TOC](目录)
- 1.何为前缀、中缀、后缀表达式?
- 2.中缀表达式的计算
- 3.中缀表达式转前缀表达式及其计算
- 3.1C++语言实现中缀2前缀
- 3.2Java语言实现中缀2前缀
- 4.中缀表达式转后缀表达式及其计算
- 5.参考博客
1.何为前缀、中缀、后缀表达式?
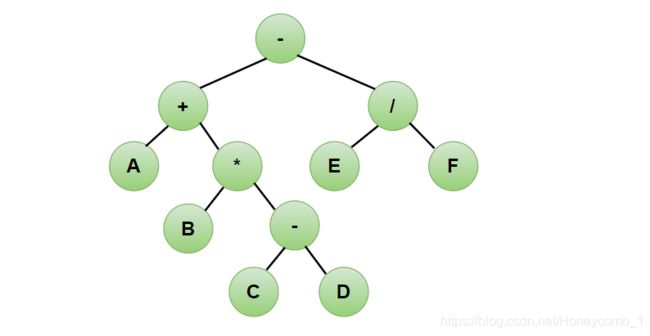
我们可以用上图的二叉树,分别用前序、中序、后序遍历来分别表示表达式,我们会发现它们其实就是前缀、中缀和后缀表达式:
前缀表达式:二叉树的前序遍历,前缀表达式的运算符位于两个相应操作数之前,一种没有括号的算术表达式,前缀表达式又被称为前缀记法或波兰式。
-+A*B-CD/EF
中缀表达式:二叉树的中序遍历,这个表达式也就是我们平常所见的计算表达式。一个通用的算术或逻辑公式表示方法, 操作符是以中缀形式处于操作数的中间,是人们常用的算术表示方法。
A+B*(C-D)-E/F
后缀表达式:二叉树的后序遍历,称为逆波兰表达式。不包含括号,运算符放在两个运算对象的后面,所有的计算按运算符出现的顺序,严格从左向右进行(不再考虑运算符的优先规则)
ABCD-*+EF/-
2.中缀表达式的计算
Java版实现原理: 定义两个栈,一个存储操作数,一个存储运算符。
通过遍历表达式,判断遇到的是操作数还是运算符:
- 如果字符是操作数,则直接入栈;
- 如果字符是运算符,则判断优先级:
- 如果是"(",直接入栈;
- 如果是")",则运算符出栈并计算,直到栈顶元素为"(";
- 如果是"+"、"-"、"*"、"/",则用它跟栈顶运算符比较
1)如果当前运算符的优先级 <= 栈顶运算符的优先级,则栈顶运算符出栈并计算;
2)如果当前运算符的优先级 > 栈顶运算符的优先级,则当前运算符入栈;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
String expression = "15+20+3*(4-2)-35";
try{
System.out.println(expression+"="+CalculateInfix(expression));
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
public static boolean isOper(char op){///判断是否为运算符
return op == '+'||op == '-'||op == '*'||op == '/';
}
public static int calculate(int num1,String op,int num2){
int res = 0;
switch (op){
case "+":
res = num1 + num2;
break;
case "-":
res = num1 - num2;
break;
case "*":
res = num1 * num2;
break;
case "/":
res = num1 / num2;
break;
default:
break;
}
return res;
}
public static int priority(String op){///判断优先级
String str = "+-*/";
return str.indexOf(op);
}///如果是在编程中尽量用case分情况设置,提高运行效率
}
中缀表达式计算的主要代码:
public static int CalculateInfix(String expression){
Stack<String> numstr = new Stack<>();
Stack<String> chstr = new Stack<>();
int i = 0;
int len = expression.length();
char ch;
String op;
int num1,num2;
int res;
while(i<len){
ch = expression.charAt(i);
if(ch >= 48 && ch <= 57){
String str = "" + ch;
while(i+1<len){
ch = expression.charAt(i+1);
if(ch < 48||ch>57) break;
else {///针对的是多位数情况
i++;
str +=ch;
}
}
numstr.push(str);
}else{
if(ch == '(') chstr.push(""+ch);///入栈
else if(ch == ')'){
while(!chstr.peek().equals("(")){///没遇到")"前
op = chstr.pop();///运算符出栈
num1 = Integer.parseInt(numstr.pop());
num2 = Integer.parseInt(numstr.pop());
res = calculate(num2,op,num1);
numstr.push(""+res);
}
chstr.pop();
}else if(isOper(ch)){///判断当前运算符是否合法
if(chstr.empty()) chstr.push(""+ch);
else{
String curop = ""+ch;
String stacktop = chstr.peek();
if(priority(curop) > priority(stacktop)) chstr.push(curop);///当前运算符优先级大的入栈
else {
while(!chstr.empty() && priority(curop) <= priority(chstr.peek())){
op = chstr.pop();
num1 = Integer.parseInt(numstr.pop());
num2 = Integer.parseInt(numstr.pop());
res = calculate(num2,op,num1);
numstr.push(""+res);
}
chstr.push(curop);
}
}
}else throw new RuntimeException("无法识别的运算符"+ch);
}
i++;
}///while
while(!chstr.empty()){///如果运算符栈还没空的话,继续出栈运算
op = chstr.pop();
num1 = Integer.parseInt(numstr.pop());
num2 = Integer.parseInt(numstr.pop());
res = calculate(num2,op,num1);
numstr.push(""+res);
}
res = Integer.parseInt(numstr.pop());
return res;
}
C++语言版实现原理: 跟Java版的原理差不多,唯一不同的就是优先级判断有所区别。
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
stack<int>num;
stack<char>ch;
void caculate(){
int a = num.top(); num.pop();
int b = num.top(); num.pop();
char c = ch.top(); ch.pop();
int d;
switch(c){
case '-':
d = b-a; break;
case '+':
d = a+b; break;
case '*':
d = a*b; break;
case '/':
d = b/a; break;
default:break;
}
num.push(d);
}
int main(){
string str = "3+4*(5-2)-4/2";
str = '('+str+')';///为了方便计算
for(int i=0; i<str.size();i++){
if(str[i] >= '0'&&str[i] <= '9'){
int j = i;
int n = 0;
while(str[j] >= '0'&&str[j]<='9'){///解决多位数的情况
n *= 10;
n += str[j] - '0';
j++;
}
i = j-1;
num.push(n);
}else if(str[i] == '-'){
if(i && !(str[i-1] >= '0'&& str[i-1] <= '9')&&str[i-1] != ')'){
int j = i+1;
int n = 0;
while(str[j] >= '0'&&str[j]<='9'){
n *= 10;
n += str[j] - '0';
j++;
}
i = j-1;
num.push(-n);
}else{
while(ch.top()!= '(') caculate();
ch.push(str[i]);
}
}else if(str[i]=='+'){
while(ch.top()!='(') caculate();
ch.push(str[i]);
}else if(str[i] == '*'|| str[i] == '/'){
while(ch.top()=='*'||ch.top()=='/') caculate();
ch.push(str[i]);
}else if(str[i]==')'){
while(ch.top() != '(') caculate();
ch.pop();
}else if(str[i] == '(')
ch.push(str[i]);
}
cout<< num.top() <<endl;
return 0;
}
3.中缀表达式转前缀表达式及其计算
中缀表达式转前缀表达式的规则:从右到左扫描中缀表达式,最后反转字符串。
3.1C++语言实现中缀2前缀
- 如果当前字符为
操作数,直接将操作数放到prefix中 - 如果当前字符为
操作符:
如果符号栈为空,直接加入符号栈中
如果符号栈不为空,则判断当前栈顶元素:
1)如果当前栈顶元素为')',直接将操作符放入符号栈中;
2)如果当前栈顶元素的优先级>当前操作符的优先级,则将栈顶元素出栈,并加入prefix中,再此重复执行2),直到当前栈顶元素<=当前操作符的优先级,然后操作符入栈 - 如果当前字符为’)’,直接将其入符号栈
- 如果当前字符为’(’,将右括号和左括号之间元素出栈并加入prefix中,最后’)'出栈
- 重复前4步,直到最后一个字符被读入
- 判断当前符号栈是否为空,如果不为空,将栈中元素出栈并加到prefix中
- 反转字符串
例如:中缀表达式:3+4*(5-2)+4/2,其对应的前缀表达式:++3*4-52/42
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
bool isOper(char ch){
return ch=='+'||ch=='-'||ch=='*'||ch=='/';
}
int prior(char ch){
int d;
switch(ch){
case '+':
d = 0; break;
case '-':
d = 0; break;
case '*':
d = 1; break;
case '/':
d = 1; break;
default:break;
}
return d;
}
void infixtoprefix(string infix,string &prefix);
int main(){
string infix = "3+4*(5-2)+4/2";
string prefix;
cout<<infix<<"前缀表达式为"<<endl;
infixtoprefix(infix,prefix);
cout<<prefix<<endl;
return 0;
}
///++3*4-52/42
void infixtoprefix(string infix,string &prefix){
stack<char>opstack;///符号栈
int infixlen = infix.size();
prefix.reserve(infixlen);///为容器预留足够空间
for(int i = infixlen-1; i>=0; i--){///从右到左
if(infix[i]>='0'&&infix[i]<='9') prefix.push_back(infix[i]);///字符存到字串中
else if(isOper(infix[i])){
if(!opstack.empty()){
char optop = opstack.top();
while(optop != ')'&&prior(infix[i])<prior(optop)){
prefix.push_back(optop);
opstack.pop();
if(opstack.empty()) break;
optop = opstack.top();
}
}
opstack.push(infix[i]);///符号栈
}else if(infix[i]==')') opstack.push(infix[i]);
else if(infix[i]=='('){
char optop = opstack.top();
while(optop!=')'){///遇到')'退出
prefix.push_back(optop);
opstack.pop();
optop = opstack.top();
}
opstack.pop();///清除')'
}
}
while(!opstack.empty()){///栈中还剩余元素的话直接加入字符串
prefix.push_back(opstack.top());
opstack.pop();
}
reverse(prefix.begin(),prefix.end());///反转字符串
}
3.2Java语言实现中缀2前缀
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String infix = "3+4*(5-2)+4/2";
System.out.println("中缀表达式:"+infix);
System.out.println("其相应的前缀表达式为");
infixToprefix(infix);
}
public static void infixToprefix(String input){
int len = input.length();
char ch,tempch;
Stack<Character> chstack = new Stack<>();
Stack<Integer> numstack = new Stack<>();
Stack<Object> prestack = new Stack<>();
for(int i = len-1; i>=0; i--){
ch = input.charAt(i);
if(Character.isDigit(ch)){///判断当前字符是否为数字
String s = String.valueOf(ch);///先转为字符串
int j = Integer.parseInt(s);///在转为整型
numstack.push(j);
prestack.push(j);
}else if(isOper(ch)){
while(!chstack.isEmpty()&&chstack.peek()!=')'&&priority(ch)<priority(chstack.peek())){
prestack.push(chstack.peek());
numstack.push(calc(numstack.pop(),numstack.pop(),chstack.pop()));
}
chstack.push(ch);///当栈顶元素优先级小于等于当前元素进栈
}else if(ch == ')') chstack.push(ch);
else if(ch == '('){
while((tempch = chstack.pop())!=')'){
prestack.push(tempch);
numstack.push(calc(numstack.pop(),numstack.pop(),tempch));
if(chstack.isEmpty()){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("遇到右括号");
}
}
}else if(ch == ' ');///遇到空格不处理
else throw new IllegalArgumentException("字符不合法");
}
while(!chstack.isEmpty()){///当符号栈不为空时
tempch = chstack.pop();
prestack.push(tempch);
numstack.push(calc(numstack.pop(),numstack.pop(),tempch));
}
while(!prestack.isEmpty()){
System.out.print(prestack.pop());
}
int result = numstack.pop();
System.out.println("计算结果为"+result);
}
public static Integer calc(int num1,int num2,char op){
switch (op){
case '+':
return num1+num2;
case '-':
return num1-num2;
case '*':
return num1*num2;
case '/':
if(num2==0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("除数不能为0");
return num1/num2;
default:return 0;
}
}
public static boolean isOper(char ch){
return ch == '+'||ch == '-'||ch == '*'||ch == '/';
}
public static int priority(char ch){
//String str="+-*/";
switch (ch){
case '+':return 1;
case '-':return 1;
case '*':return 2;
case '/':return 2;
default:return 0;
}
//return str.indexOf(ch);
}
}
4.中缀表达式转后缀表达式及其计算
相较于中缀转前缀,中缀转后缀是从左到右扫描的,不需要反转。它们的原理都一样。
Java语言的实现:
public class Main {
中缀表达式(1+((2+3)*4)-5转后缀表达式1,2,3,+,4,*,+,5,-
public static void main(String[] args) {
//String expression = "1+((2+3)*4)-5";
String expression = "3+4*(5-2)+4/2";
List<String> infixExpressionList = toInfixExpressionList(expression);
System.out.println("中缀表达式对应的List=" + infixExpressionList);
List<String> suffixExpreesionList = parseSuffixExpreesionList(infixExpressionList);
System.out.println("后缀表达式对应的List" + suffixExpreesionList);
int res = calculate(suffixExpreesionList);
System.out.println("计算的结果是=" + res);
}
public static List<String> parseSuffixExpreesionList(List<String> ls) {
Stack<String> s1 = new Stack<>();
List<String> s2 = new ArrayList<>();
for (String item : ls) {
///如果是一个数,加入s2
if (item.matches("\\d+")) {///读入的是多位数,涉及正则表达式
s2.add(item);
} else if (item.equals("(")) {
s1.push(item);
} else if (item.equals(")")) {
while (!s1.peek().equals("(")) {
s2.add(s1.pop());
}
s1.pop();///将(弹出s1栈,消除小括号
} else {
///当item的优先级小于等于s1栈顶运算符,将s1栈顶的运算符弹出并加入到s2中
while (s1.size() != 0 && Operation.getValue(s1.peek()) >= Operation.getValue(item)) {
s2.add(s1.pop());
}
s1.push(item);
}
}
while (s1.size() != 0) {
s2.add(s1.pop());
}///将剩余的运算符依次弹出并加入s2
return s2;
}
///将中缀表达式存到List中
public static List<String> toInfixExpressionList(String s) {
List<String> ls = new ArrayList<>();
int i = 0;
String str;
char c;
do {
///如果c是一个非数字
if ((c = s.charAt(i)) < 48 || (c = s.charAt(i)) > 57) {
ls.add("" + c);
i++;
} else {
str = "";
while (i < s.length() && ((c = s.charAt(i))>=48&&(c = s.charAt(i)) <= 57)) {
str += c;///多位数时,拼接
i++;
}
ls.add(str);
}
} while (i < s.length());
return ls;
}
public static List<String> getListString(String suffixExpression) {
String[] split = suffixExpression.split(" ");
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
for (String ele : split) {
list.add(ele);
}
return list;
}
public static int calculate(List<String> ls) {
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
for (String item : ls) {
if (item.matches("\\d+")) {
stack.push(item);
} else {
// pop出两个数,并运算, 再入栈
int num2 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());
int num1 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());
int res = 0;
if (item.equals("+")) {
res = num1 + num2;
} else if (item.equals("-")) {
res = num1 - num2;
} else if (item.equals("*")) {
res = num1 * num2;
} else if (item.equals("/")) {
res = num1 / num2;
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("运算符有误");
}
//把res 入栈
stack.push("" + res);
}
}
//最后留在stack中的数据是运算结果
return Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());
}
}
class Operation{
private static int ADD = 1;
private static int SUB = 1;
private static int MUL = 2;
private static int DIV = 2;
public static int getValue(String operation){
int result = 0;
switch(operation){
case "+":
result = ADD;
break;
case "-":
result = SUB;
break;
case "*":
result = MUL;
break;
case "/":
result = DIV;
break;
default:
System.out.println("不存在该运算符:"+operation);
break;
}
return result;
}
}
5.参考博客
1.https://segmentfault.com/q/1010000007089101.
2.https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42662955/article/details/89436453
3.[]