MobileNet结构简单讲解及其实现
已经使用tensorflow2实现了MobileNet系列的网络结构,在此做个记录。
MobileNet v1
本节首先描述MobileNet的核心部分也就是深度可分离卷积。它其实就是将原来的卷积层分成了两部分,分解成深度卷积以及一个1x1的卷积即逐点卷积。也就是Depthwise+Pointwise两部分(注意Depthwise,不求不同channel的和)。以下是两部分图像:

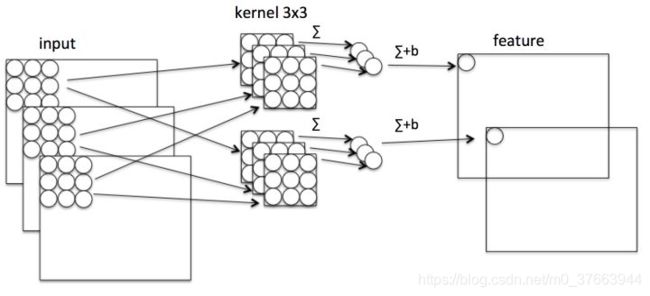
我们看下普通卷积的图示:
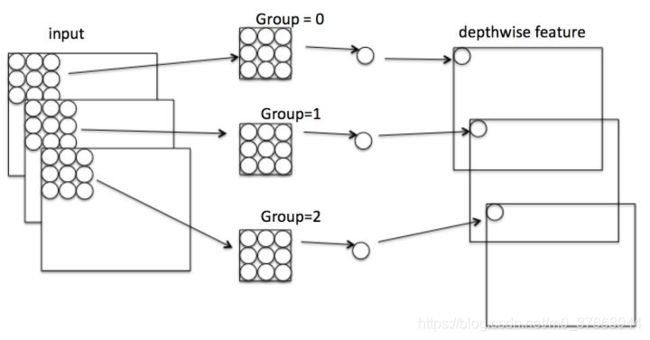
看下Depthwise图示:
Pointwise:
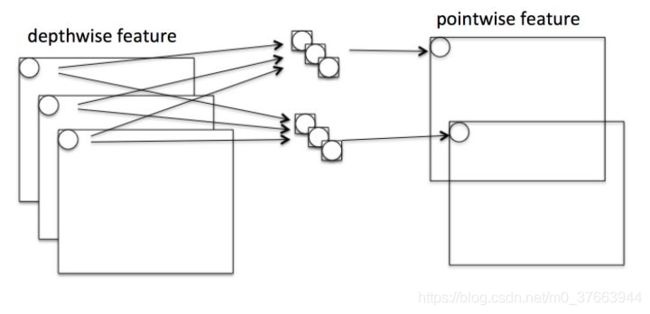
我们将普通卷积拆分成了Depthwise+Pointwise。这样的好处是可以减少参数量,从上面的三幅图中也可以看出。
这就是MobileNet v1最重要的内容,代替了普通卷积层。
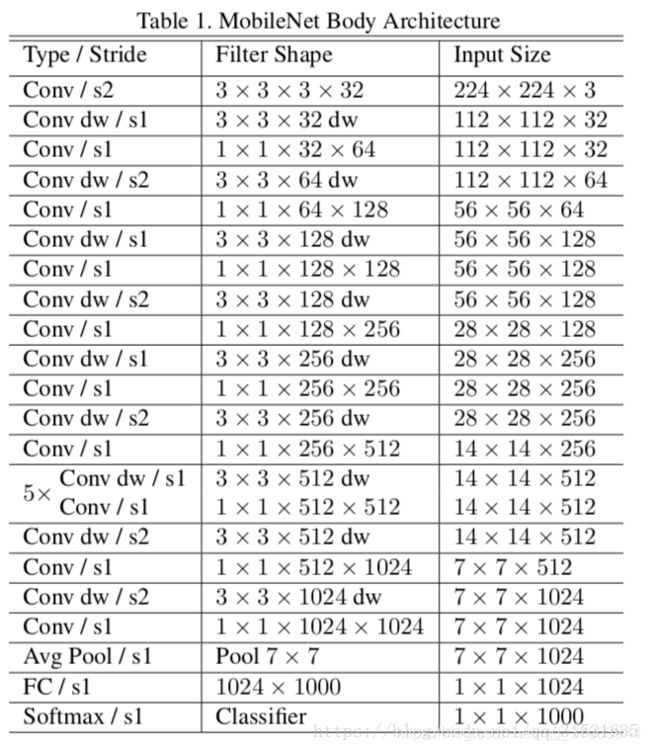
主体结构如下(dw表示depthwise):
结构代码如下:
from __future__ import absolute_import, division, print_function, unicode_literals
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Flatten, Conv2D, SeparableConv2D,
BatchNormalization, ReLU, AveragePooling2D
from tensorflow.keras import Model
img_h = 224
img_w = 224
inputs = tf.keras.Input((img_h, img_w, 3))
image = np.random.normal(size=(1, 224, 224, 3))
def _conv2d(net, filters, kernel_size, stride):
outputs = Conv2D(filters, kernel_size, stride, padding="same")(net)
# 非线性激活之前进行BN批标准化
outputs = BatchNormalization()(outputs)
outputs = ReLU()(outputs)
return outputs
def _depthwise_conv2d(inputs, pointwise_conv_filters, depthwise_conv_kernel_size, stride):
outputs = SeparableConv2D(inputs.shape[3], depthwise_conv_kernel_size, stride, padding='same')(inputs)
outputs = BatchNormalization()(outputs)
outputs = ReLU()(outputs)
outputs = Conv2D(pointwise_conv_filters,
1,
padding='same')(outputs)
outputs = BatchNormalization()(outputs)
outputs = ReLU()(outputs)
return outputs
def _avg_pool2d(inputs):
inputs_shape = inputs.get_shape().as_list()
assert len(inputs_shape) == 4
pool_height = inputs_shape[1]
pool_width = inputs_shape[2]
outputs = AveragePooling2D(pool_size = (pool_height, pool_width), strides=1, padding='valid')(inputs)
return outputs
def mobilenet_v1(inputs):
net = inputs
net = _conv2d(net, 32, 3, stride=2)
net = _depthwise_conv2d(net, 64, 3, stride=1)
net = _depthwise_conv2d(net, 128, 3, stride=2)
net = _depthwise_conv2d(net, 128, 3, stride=1)
net = _depthwise_conv2d(net, 256, 3, stride=2)
net = _depthwise_conv2d(net, 256, 3, stride=1)
net = _depthwise_conv2d(net, 512, 3, stride=2)
net = _depthwise_conv2d(net, 512, 3, stride=1)
net = _depthwise_conv2d(net, 512, 3, stride=1)
net = _depthwise_conv2d(net, 512, 3, stride=1)
net = _depthwise_conv2d(net, 512, 3, stride=1)
net = _depthwise_conv2d(net, 512, 3, stride=1)
net = _depthwise_conv2d(net, 1024, 3, stride=2)
net = _depthwise_conv2d(net, 1024, 3, stride=1)
output = _avg_pool2d(net)
return output
def mobilenet_v1_model(inputs):
outputs = mobilenet_v1(inputs)
outputs = Flatten()(outputs)
outputs = Dense(1000, activation="softmax")(outputs)
return outputs
t = mobilenet_v1_model(image)
MobileNet v2
MobileNet v2在v1的基础上加入了shortcut结构(残差)。
如图:
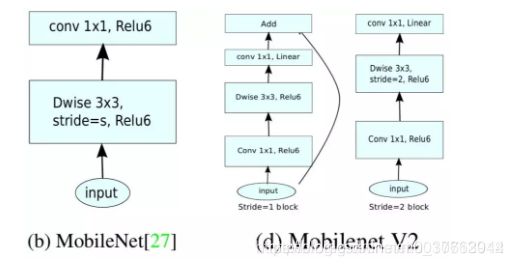
从上图可以看出MobileNet v2中有两种基本结构,加了残差和不加的。
主体结构如下:
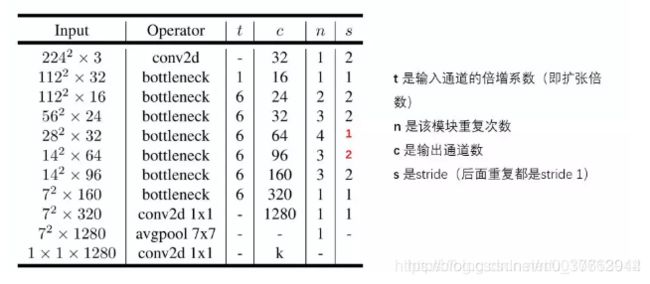
具体实现如下:
from __future__ import absolute_import, division, print_function, unicode_literals
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Flatten, Conv2D, SeparableConv2D, BatchNormalization, ReLU, AveragePooling2D
from tensorflow.keras import Model, Input
image = np.random.normal(size=(1, 224, 224, 3))
# mobilenet_v2网络定义
def mobilenet_v2_func_blocks():
filter_initializer = tf.random_uniform_initializer()
activation_func = tf.nn.relu6
def conv2d(inputs, filters, kernel_size, stride):
outputs = Conv2D(filters, kernel_size, strides=(stride, stride),
padding='same', use_bias=False,
kernel_initializer=filter_initializer)(inputs)
outputs = BatchNormalization()(outputs)
outputs = ReLU()(outputs)
return outputs
def _1x1_conv2d(inputs, filters, stride):
kernel_size = 1
outputs = Conv2D(filters, kernel_size, strides=(stride, stride),
padding='same', use_bias=False,
kernel_initializer=filter_initializer)(inputs)
outputs = BatchNormalization()(outputs)
return outputs
def expansion_conv2d(inputs, expansion, stride):
input_shape = inputs.get_shape().as_list()
assert len(input_shape) == 4
filters = input_shape[3] * expansion
kernel_size = 1
outputs = Conv2D(filters, kernel_size, strides=(stride, stride),
padding='same', use_bias=False,
kernel_initializer=filter_initializer)(inputs)
outputs = BatchNormalization()(outputs)
outputs = activation_func(outputs)
return outputs
def projection_conv2d(inputs, filters, stride):
kernel_size = 1
outputs = Conv2D(filters, kernel_size, strides=(stride, stride),
padding='same', use_bias=False,
kernel_initializer=filter_initializer)(inputs)
outputs = BatchNormalization()(outputs)
return outputs
def depthwise_conv2d(inputs, depthwise_conv_kernel_size, stride):
outputs = SeparableConv2D(inputs.shape[3], depthwise_conv_kernel_size,
stride, padding='same', depth_multiplier=1)(inputs)
outputs = BatchNormalization()(outputs)
outputs = ReLU()(outputs)
return outputs
def _avg_pool2d(inputs):
inputs_shape = inputs.get_shape().as_list()
assert len(inputs_shape) == 4
pool_height = inputs_shape[1]
pool_width = inputs_shape[2]
outputs = AveragePooling2D(pool_size = (pool_height, pool_width), strides=1, padding='valid')(inputs)
return outputs
def inverted_residual_block(inputs, filters, stride, expansion=6):
assert stride == 1 or stride == 2
depthwise_conv_kernel_size = 3
pointwise_conv_filters = filters
net = inputs
net = expansion_conv2d(net, expansion, stride=1)
net = depthwise_conv2d(net, depthwise_conv_kernel_size, stride=stride)
net = projection_conv2d(net, pointwise_conv_filters, stride=1)
if stride == 1:
# print('----------------- test, net.get_shape().as_list()[3] = %r' % net.get_shape().as_list()[3])
# print('----------------- test, inputs.get_shape().as_list()[3] = %r' % inputs.get_shape().as_list()[3])
# 如果 net.get_shape().as_list()[3] != inputs.get_shape().as_list()[3]
# 借助一个 1x1 的卷积让他们的 channels 相等,然后再相加
if net.shape[3] != inputs.shape[3]:
inputs = _1x1_conv2d(inputs, net.shape[3], stride=1)
net = net + inputs
return net
else:
# stride == 2
return net
func_blocks = {}
func_blocks['conv2d'] = conv2d
func_blocks['inverted_residual_block'] = inverted_residual_block
func_blocks['avg_pool2d'] = _avg_pool2d
func_blocks['filter_initializer'] = filter_initializer
func_blocks['activation_func'] = activation_func
return func_blocks
def mobilenet_v2(inputs):
func_blocks = mobilenet_v2_func_blocks()
_conv2d = func_blocks['conv2d']
_inverted_residual_block = func_blocks['inverted_residual_block']
_avg_pool2d = func_blocks['avg_pool2d']
net = inputs
net = _conv2d(net, 32, 3, stride=2) # size/2
net = _inverted_residual_block(net, 16, stride=1, expansion=1)
net = _inverted_residual_block(net, 24, stride=2) # size/4
net = _inverted_residual_block(net, 24, stride=1)
net = _inverted_residual_block(net, 32, stride=2) # size/8
net = _inverted_residual_block(net, 32, stride=1)
net = _inverted_residual_block(net, 32, stride=1)
net = _inverted_residual_block(net, 64, stride=2) # size/16
net = _inverted_residual_block(net, 64, stride=1)
net = _inverted_residual_block(net, 64, stride=1)
net = _inverted_residual_block(net, 64, stride=1)
net = _inverted_residual_block(net, 96, stride=1)
net = _inverted_residual_block(net, 96, stride=1)
net = _inverted_residual_block(net, 96, stride=1)
net = _inverted_residual_block(net, 160, stride=2) # size/32
net = _inverted_residual_block(net, 160, stride=1)
net = _inverted_residual_block(net, 160, stride=1)
net = _inverted_residual_block(net, 320, stride=1)
net = _conv2d(net, 1280, [1, 1], stride=1)
output = _avg_pool2d(net)
return output
def mobilenet_v1_model(inputs):
func_blocks = mobilenet_v2_func_blocks()
_conv2d = func_blocks['conv2d']
outputs = mobilenet_v2(inputs)
outputs = _conv2d(outputs, 10, [1, 1], stride=1)
return outputs
out = mobilenet_v1_model(image)
MobileNet v3
v3在v2的版本上有以下的改进:
1.结构调整:
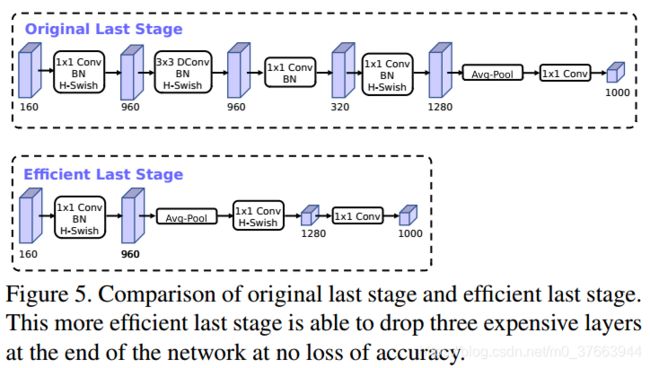
2.由于嵌入式设备计算sigmoid是会耗费相当大的计算资源的,因此作者提出了h-switch作为激活函数。且随着网络的加深,非线性激活函数的成本也会随之减少。所以,只有在较深的层使用h-switch才能获得更大的优势。
h − s w i s h [ x ] = x R e L U 6 ( x + 3 ) ) 6 h-swish[x]=x\frac{ReLU6(x+3))}{6} h−swish[x]=x6ReLU6(x+3))
3.在v2的block上引入SE模块,SE模块是一种轻量级的通道注意力模块。在depthwise之后,经过池化层,然后第一个fc层,通道数缩小4倍,再经过第二个fc层,通道数变换回去(扩大4倍),然后与depthwise进行按位相加。
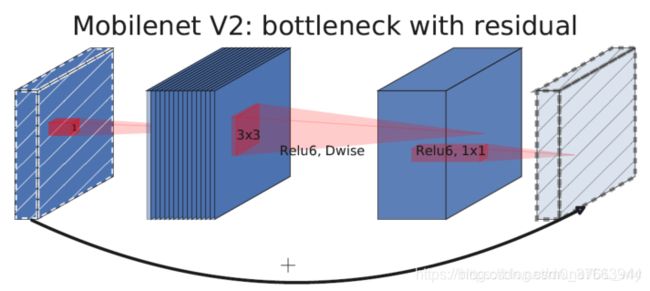
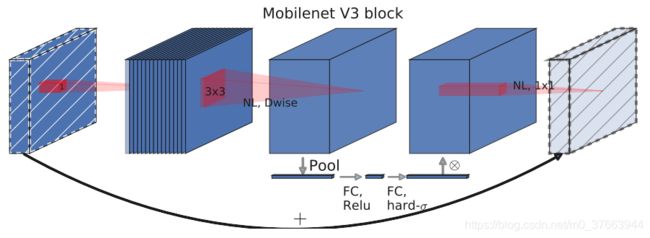
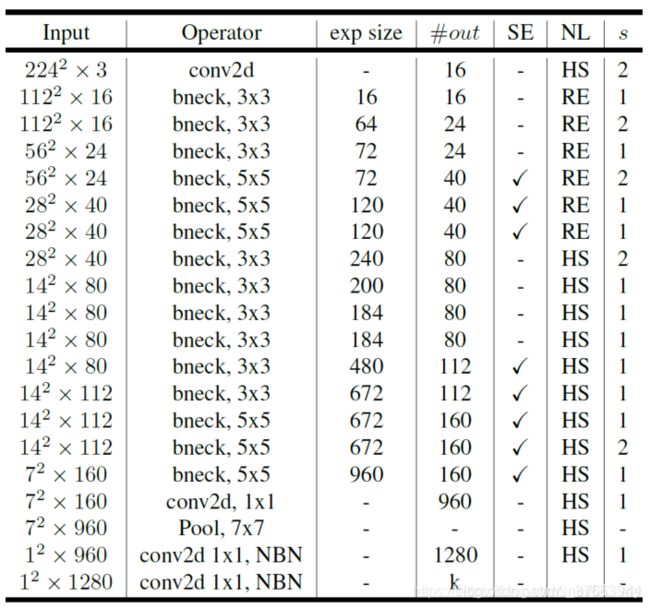
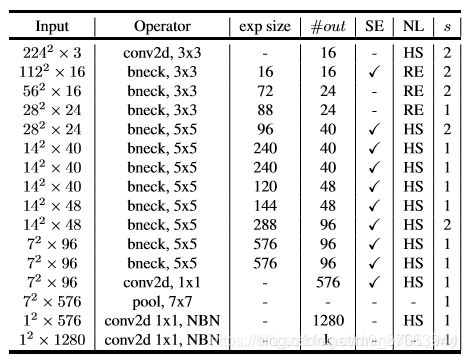
主体结构图示(作者提出了MobileNetV3-Large和MobileNetV3-Small两种不同大小的网络结构。如下图所示):
large
small
from __future__ import absolute_import, division, print_function, unicode_literals
import tensorflow as tf
import os
from tensorflow import keras
import numpy as np
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Flatten, Conv2D, SeparableConv2D,\
BatchNormalization, ReLU, AveragePooling2D, ZeroPadding2D,\
Activation, Softmax, DepthwiseConv2D, Dropout
from tensorflow.keras import Model, Input
from tensorflow.keras.backend import squeeze
from tensorflow.keras.regularizers import l2
image = np.random.normal(size=(1, 224, 224, 3))
def _relu6(inputs):
return ReLU(max_value=6)(inputs)
def _hardsigmoid(inputs):
return _relu6(inputs + 3.0)/6.0
def _hardswish(inputs):
return inputs * _hardsigmoid(inputs)
def _squeeze(inputs):
print(inputs)
return squeeze(squeeze(inputs, 1), 1)
def _globalaveragepooling2D(inputs):
input_shape = inputs.shape[1:3]
return AveragePooling2D(input_shape)(inputs)
def convnormact(inputs, filters, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=0, norm_layer=False, act_layer='relu',\
use_bias=True, l2_reg=1e-5):
x = inputs
if padding>0:
x = ZeroPadding2D(padding)(inputs)
x = Conv2D(filters, kernel_size, stride, kernel_regularizer=l2(l2_reg),
use_bias=use_bias)(x)
if norm_layer:
x = BatchNormalization()(x)
_available_activation = {
"relu": ReLU(),
"relu6": _relu6,
"hswish": _hardswish,
"hsigmoid": _hardsigmoid,
"softmax": Softmax(),
}
if act_layer:
x = _available_activation[act_layer](x)
return x
def sebottleneck(inputs, reduction=4, l2_reg=0.01):
input_channels = inputs.shape[3]
x = _globalaveragepooling2D(inputs)
x = convnormact(x,
input_channels // reduction,
kernel_size=1,
norm_layer=None,
act_layer="relu",
use_bias=False,
l2_reg=l2_reg,
)
x = convnormact(x,
input_channels,
kernel_size=1,
norm_layer=None,
act_layer="hsigmoid",
use_bias=False,
l2_reg=l2_reg
)
return inputs*x
def _make_divisible(v, divisor, min_value=None):
if min_value is None:
min_value = divisor
new_v = max(min_value, int(v + divisor / 2) // divisor * divisor)
if new_v < 0.9 * v:
new_v += divisor
return new_v
def bneck(inputs, out_channels, exp_channels, kernel_size, stride, use_se,\
act_layer, l2_reg=1e-5):
"""
#exp_channels: Integer, expansion factor.
t is always applied to the input size.
#out_channels: Integer, the dimensionality of the output space.
"""
print("inputs_shape:", inputs.shape)
in_channels = int(inputs.shape[3])
x = convnormact(inputs, exp_channels, kernel_size=1, norm_layer="bn", act_layer=act_layer,\
use_bias=False, l2_reg=l2_reg)
dw_padding = (kernel_size - 1) // 2
x = ZeroPadding2D(dw_padding)(x)
x = DepthwiseConv2D(kernel_size, stride,\
depthwise_regularizer=l2(l2_reg), use_bias=False)(x)
x = BatchNormalization()(x)
if use_se:
x = sebottleneck(x, l2_reg=l2_reg)
_available_activation = {
"relu": ReLU(),
"hswish": _hardswish,
}
if act_layer:
x = _available_activation[act_layer](x)
x = convnormact(x,
out_channels,
kernel_size=1,
norm_layer="bn",
act_layer=None,
use_bias=False,
l2_reg=l2_reg
)
if stride == 1 and in_channels == out_channels:
return inputs + x
return x
def laststage(inputs, penultimate_channels, last_channels, num_classes,\
l2_reg):
x = convnormact(inputs,
penultimate_channels,
kernel_size=1,
stride=1,
norm_layer="bn",
act_layer="hswish",
use_bias=False,
l2_reg=l2_reg
)
x = _globalaveragepooling2D(x)
x= convnormact(x,
last_channels,
kernel_size=1,
norm_layer=None,
act_layer="hswish",
l2_reg=l2_reg,
)
x = Dropout(rate=0.2)(x)
x = convnormact(x,
num_classes,
kernel_size=1,
norm_layer=None,
act_layer="softmax",
l2_reg=l2_reg,
)
x = _squeeze(x)
return x
def mobilenetv3(inputs,
num_classes=1001,
width_multiplier=1.0,
divisible_by=8,
l2_reg=1e-5,):
x = convnormact(inputs, 16, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, norm_layer="bn",\
act_layer="hswish", use_bias=False, l2_reg=l2_reg)
# Bottleneck layers
bneck_settings = [
# k exp out SE NL s
[ 3, 16, 16, False, "relu", 1 ],
[ 3, 64, 24, False, "relu", 2 ],
[ 3, 72, 24, False, "relu", 1 ],
[ 5, 72, 40, True, "relu", 2 ],
[ 5, 120, 40, True, "relu", 1 ],
[ 5, 120, 40, True, "relu", 1 ],
[ 3, 240, 80, False, "hswish", 2 ],
[ 3, 200, 80, False, "hswish", 1 ],
[ 3, 184, 80, False, "hswish", 1 ],
[ 3, 184, 80, False, "hswish", 1 ],
[ 3, 480, 112, True, "hswish", 1 ],
[ 3, 672, 112, True, "hswish", 1 ],
[ 5, 672, 160, True, "hswish", 2 ],
[ 5, 960, 160, True, "hswish", 1 ],
[ 5, 960, 160, True, "hswish", 1 ],
]
for idx, (k, exp, out, SE, NL, s) in enumerate(bneck_settings):
out_channels = _make_divisible(out * width_multiplier, divisible_by)
exp_channels = _make_divisible(exp * width_multiplier, divisible_by)
x = bneck(x,
out_channels=out_channels,
exp_channels=exp_channels,
kernel_size=k,
stride=s,
use_se=SE,
act_layer=NL)
penultimate_channels = _make_divisible(960 * width_multiplier, divisible_by)
last_channels = _make_divisible(1280 * width_multiplier, divisible_by)
out = laststage(x,
penultimate_channels,
last_channels,
num_classes,
l2_reg=l2_reg,)
return out
inputs = Input(shape=(224, 224, 3))
out = mobilenetv3(inputs)
model = Model(inputs, out)
参考文献:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/35405071
https://blog.csdn.net/DL_wly/article/details/90168883
https://www.cnblogs.com/dengshunge/p/11334640.html