定义
Builder模式是一步一步创建一个复杂对象的创建型模式,它允许用户在不知道内部构建细节的情况下,可以更精细的控制对象的构造过程。该模式是为了将复杂对象的构建过程和它的部件解耦,使得构建过程和部件的表示隔离开来。
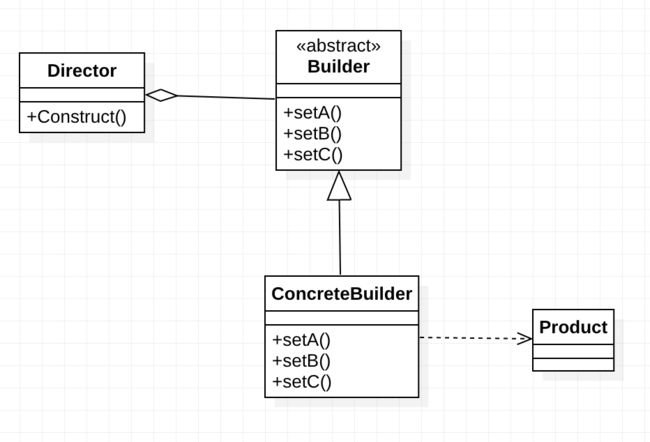
UML图
Builder模式的角色
-
Product
要构造的产品类
-
Builder
抽象构建类,规范产品的组建过程,定义构建方法,具体构建实现由子类完成
-
ConcreteBuilder
具体构建类,完成具体的构建实现
-
Director
统一组装的过程
示例
以组装一辆车为例子,把组装车的流程简化成装配引擎、安装轮胎和组装车身三个步骤。
/**
* 首先定义产品类
* 产品类:汽车
*/
public class Car {
private String engine;
private String tire;
private String body;
public void setEngine(String engine) {
this.engine = engine;
}
public void setTire(String tire) {
this.tire = tire;
}
public void setBody(String body) {
this.body = body;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Car{" +
"engine='" + engine + '\'' +
", tire='" + tire + '\'' +
", body='" + body + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
/**
* Builder类
* 规范构建流程
*/
public abstract class Builder {
public abstract void buildEngine(String engine);
public abstract void buildTire(String tire);
public abstract void buildBody(String body);
public abstract Car create();
}
/**
* 具体的Builder类
* 实现具体的构建流程
*/
public class CarBuilder extends Builder {
Car car = new Car();
@Override
public void buildEngine(String engine) {
car.setEngine(engine);
}
@Override
public void buildTire(String tire) {
car.setTire(tire);
}
@Override
public void buildBody(String body) {
car.setBody(body);
}
@Override
public Car create() {
return car;
}
}
/**
* Director类
* 封装了构建产品对象的过程,对外隐藏构建细节
*/
public class Director {
private Builder builder;
public Director(Builder builder) {
this.builder = builder;
}
public void construct(String engine, String tire, String body) {
builder.buildEngine(engine);
builder.buildTire(tire);
builder.buildBody(body);
}
}
public static void main(String[]args){
Builder builder = new CarBuilder();
Director director = new Director(builder);
director.construct("4AG","马牌轮胎","钢化车身");
Car car = builder.create();
System.out.println(car.toString());
}
Car{engine='4AG', tire='马牌轮胎', body='钢化车身'}
Android源码中的Builder模式
AlterDialog对话框的构建就是用的Builder模式。如下在使用AlterDialog时,需要先初始化AlertDialog.Builder对象,然后通过这个Builder对象设置Dialog的相关参数,调用create方法创建AlterDialog对象,并调用show方法显示。
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(this);
builder.setTitle("title")
.setMessage("message")
.setPositiveButton("confirm", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "confirm click", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
AlertDialog alertDialog = builder.create();
alertDialog.show();
AlertDialog.Builder是AlterDialog的静态内部类,代码如下
public static class Builder {
private final AlertParams P;
private final int mTheme;
public Builder(@NonNull Context context) {
this(context, AlertDialog.resolveDialogTheme(context, 0));
}
public Builder(@NonNull Context context, @StyleRes int themeResId) {
this.P = new AlertParams(new ContextThemeWrapper(context, AlertDialog.resolveDialogTheme(context, themeResId)));
this.mTheme = themeResId;
}
@NonNull
public Context getContext() {
return this.P.mContext;
}
public AlertDialog.Builder setTitle(@Nullable CharSequence title) {
this.P.mTitle = title;
return this;
}
public AlertDialog.Builder setMessage(@Nullable CharSequence message) {
this.P.mMessage = message;
return this;
}
// ...
}
在Builder对象的各个set方法中,又将值赋给了AlertParams对象的属性,AlertParams是AlterController的静态内部类,代码如下
public static class AlertParams {
public final Context mContext;
public final LayoutInflater mInflater;
public int mIconId = 0;
public Drawable mIcon;
public int mIconAttrId = 0;
public CharSequence mTitle;
public View mCustomTitleView;
public CharSequence mMessage;
public CharSequence mPositiveButtonText;
public Drawable mPositiveButtonIcon;
//...
}
在Builder对象的相关构建方法完成后,调用了create方法生成AlterDialog对象,create方法如下
public AlertDialog create() {
AlertDialog dialog = new AlertDialog(this.P.mContext, this.mTheme);
this.P.apply(dialog.mAlert);
dialog.setCancelable(this.P.mCancelable);
if (this.P.mCancelable) {
dialog.setCanceledOnTouchOutside(true);
}
dialog.setOnCancelListener(this.P.mOnCancelListener);
dialog.setOnDismissListener(this.P.mOnDismissListener);
if (this.P.mOnKeyListener != null) {
dialog.setOnKeyListener(this.P.mOnKeyListener);
}
return dialog;
}
create方法中首先初始化AlertDialog对象,AlterDialog的构造方法如下
protected AlertDialog(@NonNull Context context, @StyleRes int themeResId) {
super(context, resolveDialogTheme(context, themeResId));
this.mAlert = new AlertController(this.getContext(), this, this.getWindow());
}
在AlertDialog构造方法中会调用到其父类Dialog的构造方法
Dialog(@NonNull Context context, @StyleRes int themeResId, boolean createContextThemeWrapper) {
if (createContextThemeWrapper) {
if (themeResId == ResourceId.ID_NULL) {
final TypedValue outValue = new TypedValue();
context.getTheme().resolveAttribute(R.attr.dialogTheme, outValue, true);
themeResId = outValue.resourceId;
}
mContext = new ContextThemeWrapper(context, themeResId);
} else {
mContext = context;
}
mWindowManager = (WindowManager) context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
final Window w = new PhoneWindow(mContext);
mWindow = w;
w.setCallback(this);
w.setOnWindowDismissedCallback(this);
w.setOnWindowSwipeDismissedCallback(() -> {
if (mCancelable) {
cancel();
}
});
w.setWindowManager(mWindowManager, null, null);
w.setGravity(Gravity.CENTER);
mListenersHandler = new ListenersHandler(this);
}
在Dialog构造方法中首先初始化PhoneWindow对象,然后将mWindowManager对象设置给mWindow对象。继续回到AlertDialog的构造方法中,传入context对象和window对象初始化了AlertController对象mAlert。AlertDialog构造方法中逻辑分析完了,回到create方法中,调用AlertParams的apply方法传入mAlter对象,代码如下
public void apply(AlertController dialog) {
if (this.mCustomTitleView != null) {
dialog.setCustomTitle(this.mCustomTitleView);
} else {
if (this.mTitle != null) {
dialog.setTitle(this.mTitle);
}
if (this.mIcon != null) {
dialog.setIcon(this.mIcon);
}
if (this.mIconId != 0) {
dialog.setIcon(this.mIconId);
}
if (this.mIconAttrId != 0) {
dialog.setIcon(dialog.getIconAttributeResId(this.mIconAttrId));
}
}
if (this.mMessage != null) {
dialog.setMessage(this.mMessage);
}
//...
}
在这个方法中,将AlertParams成员变量的值如mMessage等设值给了mAlter对象的成员变量。现在AlterDialog对象已经创建,并且相关参数已经设置到mAlter对象中,但是AlterDialog还没显示出来,而且相关参数值还未设置到AlterDialog的布局上,那接下来看下show方法显示AlterDialog的流程
public void show() {
//...
mCanceled = false;
if (!mCreated) {
dispatchOnCreate(null);
} else {
// Fill the DecorView in on any configuration changes that
// may have occured while it was removed from the WindowManager.
final Configuration config = mContext.getResources().getConfiguration();
mWindow.getDecorView().dispatchConfigurationChanged(config);
}
onStart();
mDecor = mWindow.getDecorView();
//...
mWindowManager.addView(mDecor, l);
//...
}
dispatchOnCreate中回调Dialog的onCreate方法,该方法为空实现,具体实现由AlterDialog的onCreate完成,代码如下
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
this.mAlert.installContent();
}
这里具体逻辑交由mAlert的installContent方法处理
public void installContent() {
int contentView = this.selectContentView();
this.mDialog.setContentView(contentView);
this.setupView();
}
方法中先是得到AlterDialog的布局,继而将通过setContentView将布局设置给AlterDialog,最后setupView方法就是将mAlert中的各成员变量设置到AlterDialog对应的view中
private void setupView() {
//...
ViewGroup contentPanel = this.resolvePanel(customContentPanel, defaultContentPanel);
this.setupContent(contentPanel);
//...
}
这里以设置mMessage属性为例,以下为setupContent代码,这里首先查找到mMessageView这个TextView,然后将mAlert的成员变量设置给了mMessageView。
private void setupContent(ViewGroup contentPanel) {
//...
this.mMessageView = (TextView)contentPanel.findViewById(16908299);
if (this.mMessageView != null) {
if (this.mMessage != null) {
this.mMessageView.setText(this.mMessage);
} else {
//...
}
}
}
show方法中最后调用WindowManager.addView方法添加了AlterDialog的Window,这样AlterDialog就显示出来了。