入职Oracle 以后想着把之前写过的《编程之美》中控制CPU使用率曲线的程序再写一边, 可是总是由于入职须要学习的东西太多, 没有时间。
程序早就写好了。 最终有机会贴出来了。o(∩∩)o..
最早的时候我採用C实现的效果并不好。 当时也没有认真调试。 最初的时候採用C#实现的效果反而不错, 由于C#有非常多方便的类库能够获取CPU的占用率, 控制sleep时间等等。事实上在C中也非常easy实现。
整体的算法思想, 这里就不再反复了, 能够參考以下的链接 :
http://blog.csdn.net/watkinsong/article/details/6865775
http://blog.csdn.net/watkinsong/article/details/6867373
http://blog.csdn.net/watkinsong/article/details/6867473
http://blog.csdn.net/watkinsong/article/details/6867666
http://blog.csdn.net/watkinsong/article/details/6870748
http://blog.csdn.net/watkinsong/article/details/6871235
本次算法的实现, 全部的代码都托管到了github, 而且使用了makefile编译文件。
地址: https://github.com/weixsong/aventador
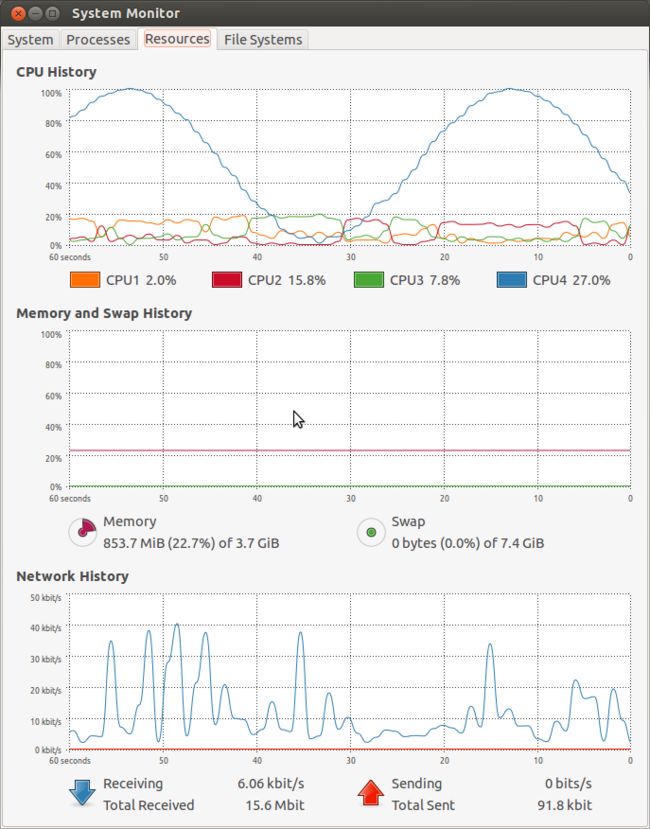
以下简单的给出代码和效果截图。 这里的效果实现比曾经的C#实现的那个sin曲线要好一些。
#define _GNU_SOURCE
#include
#include
#include
#include
extern const double PI = 3.1415926;
// setup the cpu set of this program to run on
int set_cpu(int id)
{
cpu_set_t mask;
CPU_ZERO(&mask);
CPU_SET(id, &mask);
if (sched_setaffinity(0, sizeof(mask), &mask) == -1)
{
fprintf(stderr, "warning: could not set CPU affinity/n");
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "CPUtils.h"
const int CPU_KERNEL_ID = 0x0003;
const int SAMPLE_COUNT = 200;
const int TIME_SLICE = 200; // ms in second
const int TIME_TRANFORM = 1000; // change ms to us
long * busy_span;
// init the busy span, this is used to control the cpu busy time for each sample point
int init_busySpan(int sample_count)
{
busy_span = (long *)malloc(sample_count * sizeof(long));
if(busy_span == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
double radian = 0.0;
double radianIncrement = 2.0 / (double)sample_count;
int amplitude = (int)(TIME_SLICE / 2); // amplitude of sin curves, it means half of the time slice because sin() has negative value
int i;
for(i = 0; i < sample_count; i++)
{
busy_span[i] = (long)(amplitude + sin(radian * PI) * amplitude);
radian = radian + radianIncrement;
}
return 1;
}
int main(void)
{
if(set_cpu(CPU_KERNEL_ID) == 0)
{
printf("cpu affinity set failed\n");
}
else
{
printf("cpu affinity set succeeded\n");
}
printf("clock per second:%ld \n", CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
fflush(stdout);
if(!(init_busySpan(SAMPLE_COUNT)))
{
printf("init error \n");
return 0;
}
int i = 0;
long busy_time; // us
long sleep_time; // us
clock_t begin;
for(i = 0; ; i = (i + 1) % SAMPLE_COUNT)
{
busy_time = busy_span[i] * TIME_TRANFORM;
begin = clock();
while((clock() - begin) < busy_time)
{
// loop
}
sleep_time = (long)((TIME_SLICE - busy_span[i])) * TIME_TRANFORM;
usleep(sleep_time);
}
return 1;
}