1. 词云WordCloud——续
①Python中使用open内置函数进行文件读取
②利用函数jieba.lcut(words)进行分词
③过滤重复词和无关词
④给十个人物出现的次数进行排序
⑤输出图片
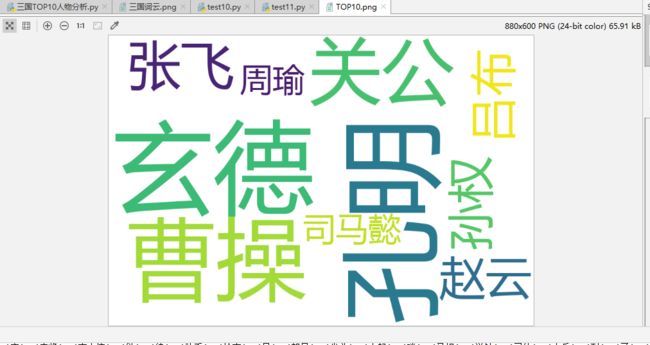
示例一:三国TOP10人物分析
import jieba
from wordcloud import WordCloud
# 1.读取小说内容
with open('./novel/threekingdom.txt','r',encoding='utf-8') as f:
words = f.read()
counts = {} #{‘曹操’:234,‘回寨’:56}
excludes = {"将军", "却说", "丞相", "二人", "不可", "荆州", "不能", "如此", "商议",
"如何", "主公", "军士", "军马", "左右", "次日", "引兵", "大喜", "天下",
"东吴", "于是", "今日", "不敢", "魏兵", "陛下", "都督", "人马", "不知",
"孔明曰","玄德曰","刘备","云长"}
# 2.分词
words_list = jieba.lcut(words)
print(words_list)
for word in words_list:
if len(word) <= 1:
continue
else:
# 更新字典中的值
# counts[word] = 去除字典中原来键相应的值 + 1
# counts[word] = counts[word] + 1 # counts[words]如果没有就要报错
# 字典。get(k) 如果字典中没有这个键,返回NONE
counts[word] = counts.get(word, 0) + 1
print(counts)
# 3.词语过滤,删除无关词,重复词
counts['孔明'] = counts['孔明'] + counts['孔明曰']
counts['玄德'] = counts['玄德'] + counts['玄德曰'] + counts['刘备']
counts['关公'] = counts['关公'] + counts['云长']
for word in excludes:
del counts[word]
# 4.排序[(),()]
items = list(counts.items())
print(items)
def sort_by_count(x):
return x[1]
# items.sort(key=sort_by_count,reverse=True)
items.sort(key=lambda i:i[1],reverse=True)
li = [] #['孔明','','']
# 遍历
for i in range(10):
# 序列解包
role, count = items[i]
print(role, count)
# _ 是告诉看代码的人,循环里面不需要临时变量
for _ in range(count):
li.append(role)
# 5.得出结论
text = ' '.join(li)
WordCloud(
font_path='msyh.ttc',
background_color='white',
width=880,
height=600,
#两个相邻重复词之间的匹配
collocations=False
).generate(text).to_file('TOP10.png')
示例二:红楼梦TOP10人物分析
# 红楼梦 top1o人物分析
import jieba
from wordcloud import WordCloud
# 1.读取小说内容
with open('./novel/all.txt','r',encoding='utf-8') as f:
words = f.read()
counts = {}
excludes = {'什么','我们','你们','如今','说道','知道','姑娘','起来','这里','出来','众人','那里','奶奶',
'自己','太太','一面','只见','两个','没有','怎么','不是','不知','这个','听见','这样','进来',
'咱们','就是','东西','告诉','回来','回来','只是','大家','老爷','只得','丫头','这些','他们',
'不敢','出去','所以','一个','贾宝玉','王熙凤','老太太','凤姐儿','林黛玉','薛宝钗'}
# 2.分词
words_list = jieba.lcut(words)
print(words_list)
for word in words_list:
if len(word) <= 1:
continue
else:
counts[word] = counts.get(word, 0) + 1
print(counts)
# 3.词语过滤重复词
counts['宝玉'] = counts['宝玉'] + counts['贾宝玉']
counts['黛玉'] = counts['黛玉'] + counts['林黛玉']
counts['宝钗'] = counts['宝钗'] + counts['薛宝钗']
counts['贾母'] = counts['老太太'] + counts['贾母']
counts['凤姐'] = counts['凤姐'] + counts['王熙凤']+ counts['凤姐儿']
#删除无关词
for word in excludes:
del counts[word]
# 4.排序[(),()]
items = list(counts.items())
print(items)
def sort_by_count(x):
return x[1]
# items.sort(key=sort_by_count,reverse=True)
items.sort(key=lambda i:i[1],reverse=True)
li = []
# 遍历
for i in range(10):
# 序列解包
role, count = items[i]
print(role, count)
# _ 是告诉看代码的人,循环里面不需要临时变量
for _ in range(count):
li.append(role)
# 5.得出结论
text = ' '.join(li)
WordCloud(
font_path='msyh.ttc',
background_color='white',
width=880,
height=600,
# 两个相邻重复词之间的匹配
collocations=False
).generate(text).to_file('红楼梦TOP10.png')
2. 匿名函数
表达式:calc = lambda n: n*n
print(calc(数值))
关键字lambda表示匿名函数,冒号前面的n表示函数参数,可以有多个参数。匿名函数有个限制,就是只能有一个表达式,不用写return,返回值就是该表达式的结果。
sum_num = lambda x1, x2:x1+x2
print(sum_num(2, 3))
# 参数可以是无限多个,但是表达式只有一个
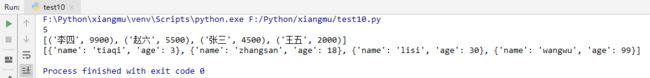
name_info_list = [
('张三',4500),
('李四',9900),
('王五',2000),
('赵六',5500),
]
name_info_list.sort(key=lambda x:x[1],reverse=True)
print(name_info_list)
stu_info = [
{"name":'zhangsan',"age":18},
{"name":'lisi',"age":30},
{"name":'wangwu',"age":99},
{"name":'tiaqi',"age":3},
]
stu_info.sort(key=lambda i:i['age'])
print(stu_info)
3. 列表推导式
1. 列表解析
- 之前我们使用普通for 创建列表
如:
li = []
for i in range(10):
li.append(i)
print(li)
使用列表推导式
格式:[表达式 for 临时变量 in 可迭代对象 可以追加条件]
# [表达式 for 临时变量 in 可迭代对象 可以追加条件]
print([i for i in range(10)])
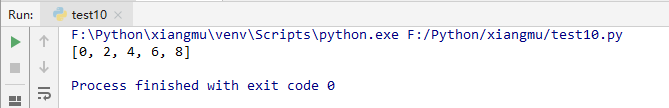
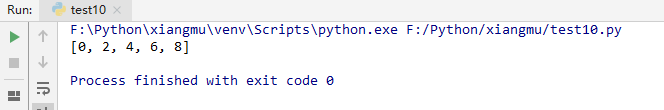
- 筛选出列表中所有的偶数
#筛选出列表中所有的偶数
li = []
for i in range(10):
if i%2 == 0:
li.append(i)
print(li)
使用列表解析
#筛选出列表中所有的偶数
print([i for i in range(10) if i%2 ==0])
- 筛选出列表中大于0的数
#筛选出列表中大于0的数
from random import randint
num_list = [randint(-10,10) for _ in range(10)]
print(num_list)
print([i for i in num_list if i>0])
2. 字典解析
# 生成100个学生的成绩
from random import randint
stu_grades = {'student{}'.format(i):randint(50,100) for i in range(1,101)}
print(stu_grades)
# 刷选大于60分的所有学生
print({k: v for k, v in stu_grades.items() if v > 60})
4. 图形绘制
1. 正弦和余弦图
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams["font.sans-serif"] = ['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
import numpy as np
# 使用100个点,绘制[0, 2∏]正弦曲线图
# .linspace 左闭右闭区间的等差数列
x = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, num=100)
print(x)
y = np.sin(x)
# 正弦和余弦在同一坐标系下
cosy = np.cos(x)
plt.plot(x, y,color='g',linestyle='--',label='sin(x)')
plt.plot(x,cosy, color='r',label='cos(x)')
plt.xlabel('时间(s)')
plt.ylabel('电压(v)')
plt.title('欢迎来到Python的世界')
2. 柱状图
# 导入
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams["font.sans-serif"] = ['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
import numpy as np
# 柱状图
import string
from random import randint
# print(string.ascii_uppercase[0,6])
# ['A','B','C',...]
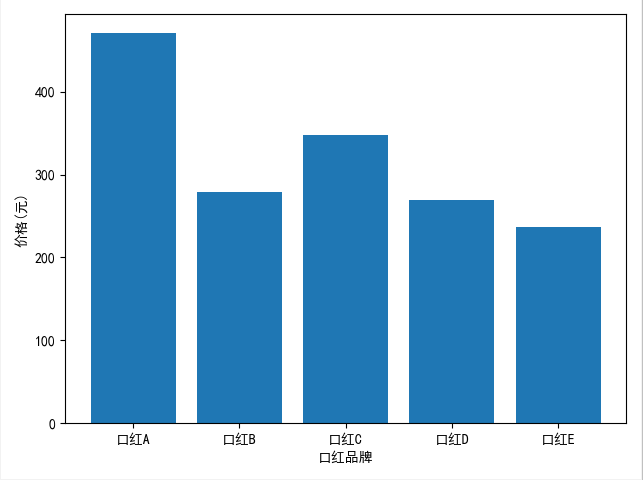
x = ['口红{}'.format(x) for x in string.ascii_uppercase[:5]]
y = [randint(200, 500) for _ in range(5)]
print(x)
print(y)
plt.xlabel('口红品牌')
plt.ylabel('价格(元)')
plt.bar(x,y)
plt.show()
3. 饼图
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams["font.sans-serif"] = ['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
import numpy as np
# # 饼图
from random import randint
import string
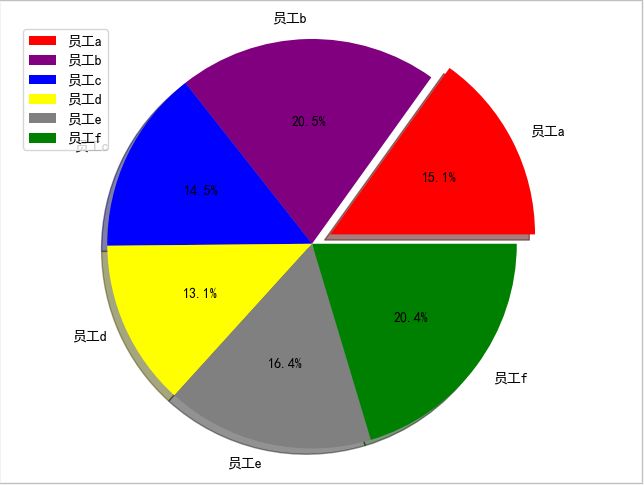
counts = [randint(3500,9000) for _ in range(6)]
labels = ['员工{}'.format(x) for x in string.ascii_lowercase[:6]]
# 距离圆心点距离
explode = [0.1,0,0,0,0,0]
colors = ['red','purple','blue','yellow','gray','green']
plt.pie(counts,explode = explode,shadow=True,labels=labels,autopct='%1.1f%%',colors=colors)
plt.legend(loc=2)
plt.axis('equal')
plt.show()
4. 散点图
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams["font.sans-serif"] = ['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
import numpy as np
x = np.random.normal(0, 1, 1000000)
y = np.random.normal(0, 1, 1000000)
# alpha透明度
plt.scatter(x, y, alpha=0.1)
plt.show()