曼哈顿距离最小生成树(树状数组)
转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/Anding-16/p/7367845.html
POJ-3241 Object Clustering
Dscription
We have N (N ≤ 10000) objects, and wish to classify them into several groups by judgement of their resemblance. To simply the model, each object has 2 indexes a and b (a, b ≤ 500). The resemblance of object i and object j is defined by dij = |ai - aj| + |bi - bj|, and then we say i is dij resemble to j. Now we want to find the minimum value of X, so that we can classify the N objects into K (K < N) groups, and in each group, one object is at most X resemble to another object in the same group, i.e, for every object i, if i is not the only member of the group, then there exists one object j (i ≠ j) in the same group that satisfies dij ≤ X
Input
The first line contains two integers N and K. The following N lines each contain two integers a and b, which describe a object.
Output
A single line contains the minimum X.
Sample Input
6 2
1 2
2 3
2 2
3 4
4 3
3 1
Sample Output
2
[Submit] [Status] [Discuss]
- 题意 -
曼哈顿距离最小生成树上第k大的边.
曼哈顿距离: (对于点A(x1, y1), B(x2, y2))
dis(A,B)=|x1−x2|+|y1−y2| dis(A,B)=|x1−x2|+|y1−y2| .
(下文中dis() dis() , 距离均指曼哈顿距离)
(下文中dis() dis() , 距离均指曼哈顿距离)
(下文中dis() dis() , 距离均指曼哈顿距离)
- 思路 -
参考题解: http://blog.csdn.net/huzecong/article/details/8576908
直接暴力的话会有N 2 N2 条边, 总复杂度O(N 2 logN)(N≤10000) O(N2logN)(N≤10000) .
果断爆炸.
我们可以删去一些无用边.
对于一个平面上的点 i(x i ,y i ) i(xi,yi) , 我们以它为中心把周围部分为8份.
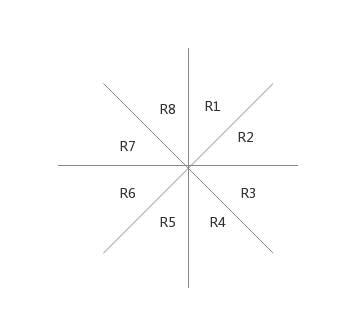
考虑每一份中最多有一个点与点 i 相连, 如 R1:
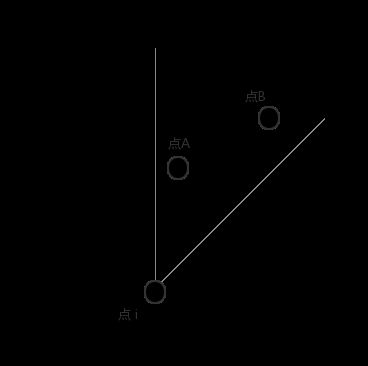
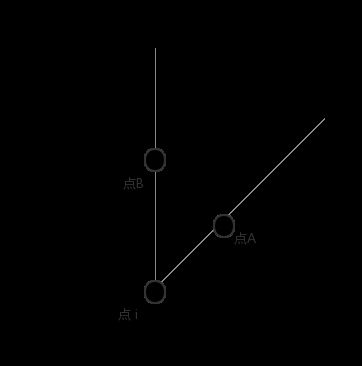
设此时点A是与点 i 距离最小的点, 则为点A, i建一条边, 考虑该部分的其它点(如点B), 它们与 A 的距离显然小于与 i 的距离(如dis(A,B)
dis(i,A)+dis(A,B)=dis(i,A)+dis(i,B) dis(i,A)+dis(A,B)=dis(i,A)+dis(i,B) 的情况如下:(A−B A−B 连线垂直于A−i A−i 连线)
所以对于每个点每一份中只需要连一条边, 由于边是无向的, 我们可以只连向右的边(也就是R1-4内的点, 点 i 向左的连线由左边的点来连), 这样就只有N*4条边了.
继续分析R1的情况, 如何找到 A 点.
发现首先 R1 区间内的点 k 满足 :
X i ≤X k Xi≤Xk
X k −X i ≤Y k −Y i Xk−Xi≤Yk−Yi 即 Y i −X i ≤Y k −X k Yi−Xi≤Yk−Xk (k为R1内任一点)
我们在满足条件的点中找到X+Y X+Y 最小的节点就行了.
于是我们可以维护一个树状数组(线段树), 底层按离散化后的Y−X Y−X 排序, 维护区间内X+Y X+Y 的最小值,
按照先从右到左, 再从上到下的顺序插入节点并查找.
对于R2-4三个部分, 我们可以对点进行旋转, 将它们转换为 R1 内的点.
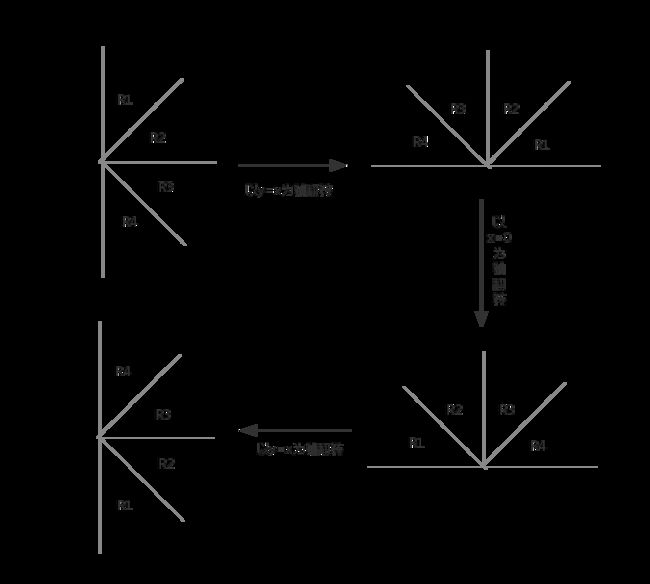
(注意看原先的R1的位置依次有R2, R3, R4的点, 这样就可以连出四个部分的边了)
细节见代码.
- 代码 -
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
struct edge
{
int x, y, v;
bool operator < (const edge &tmp) const
{
return v < tmp.v;
}
} E[N<<3];
struct point
{
int x, y, id;
bool operator < (const point &tmp) const
{
return x == tmp.x ? y < tmp.y : x < tmp.x;
}
} P[N];
struct lsh
{
int id, a;
bool operator < (const lsh &tmp) const
{
return a < tmp.a;
/* if (a == tmp.a) return id < tmp.id;
return a < tmp.a;
*/
}
} LSH[N];
int A[N], F[N];
int MI[N], ID[N];
int n, c, sz, tot, cnt;
int lowbit (int x)
{
return x&(-x);
}
int query(int x)
{
int ans = -1, mi = inf;
for (; x <= n; x += lowbit(x))
if (MI[x] < mi)
{
mi = MI[x];
ans = ID[x];
}
return ans;
}
void modify(int x, int mi, int id)
{
for (; x > 0; x -= lowbit(x))
if (MI[x] > mi)
{
MI[x] = mi;
ID[x] = id;
}
}
//BIT维护的是某数字代表的区间的X+Y最小值, 若一区间的不同位置最小值不同, 该区间则没有最小值(即MI数组维护的是其表示的区间都可以取到的最小值)
int find(int x)
{
return F[x] == x ? x : F[x] = find(F[x]);
}
void join(int x, int y)
{
int fx = find(x), fy = find(y);
if (fx == fy) return;
F[fx] = fy;
cnt++;
}
void init ()
{
sort(P + 1, P + n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
{
LSH[i].a = P[i].y - P[i].x;
LSH[i].id = i;
MI[i] = inf;
ID[i] = -1;
}
}
int abs(int x, int y)
{
return x > 0 ? x : -x;
}
int dts(int x, int y)
{
return abs(P[x].x - P[y].x) + abs(P[x].y -P[y].y);
}
void add_edge (int x, int y, int d)
{
E[++sz].x = x;
E[sz].y = y;
E[sz].v = d;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &c);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
{
scanf("%d%d", &P[i].x, &P[i].y);
P[i].id = i;
}
for (int cas = 1; cas <= 4; ++cas)
{
if (cas == 2 || cas == 4)
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
swap(P[i].x, P[i].y);
if (cas == 3)
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
P[i].x = -P[i].x;
init();
sort(LSH + 1, LSH + n + 1);//按Y-X离散化
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
A[LSH[i].id] = i; //A表示某点在BIT中的位置
for (int i = n; i >= 1; --i)
{
int tmp = query(A[i]);
if (tmp != -1)
add_edge(P[tmp].id, P[i].id, dts(tmp, i));
modify(A[i], P[i].x + P[i].y, i);
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) F[i] = i;
sort(E + 1, E + sz + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= sz; ++i)
{
join(E[i].x, E[i].y);
if (cnt == n - c)
{
printf("%d\n", E[i].v);
break;
}
}
return 0;
}