【Java并发】Executor框架和线程池ThreadPoolExecutor的使用
在java任务执行可以通过线程池的方式执行,java中提供了Executor框架来处理。
Executor中结构可以分为三个模块:
任务:实现Runnable接口或Callable接口
任务的执行:Executor接口以及ExecutorService接口或者ThreadPoolExecutor,ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor
异步执行结果:异步执行的结果封装进Future接口和FutureTask接口
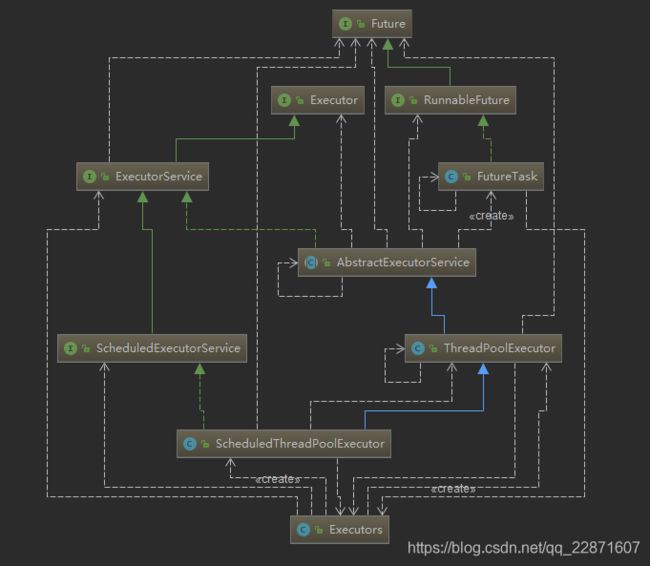
ThreadPoolExecutor:线程池的最基本实现类
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor:定时或延迟执行线程任务类
FutureTask : 存放异步结果
Executors : 线程池工具类,可以快速创建线程池
Executors工具
Executors提供了几个常用的快速创建线程池的方法:
Executors.newCachedThreadPool(无界线程池,自动线程回收)
Executors.newFixedThreadPool(固定大小的线程池);
Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(单一后台线程);
ThreadPoolExecutor
ThreadPoolExecutor有四个构造函数,看其中构造参数最多的一个:
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
if (corePoolSize < 0 ||
maximumPoolSize <= 0 ||
maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize ||
keepAliveTime < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (workQueue == null || threadFactory == null || handler == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize;
this.maximumPoolSize = maximumPoolSize;
this.workQueue = workQueue;
this.keepAliveTime = unit.toNanos(keepAliveTime);
this.threadFactory = threadFactory;
this.handler = handler;
}
其中参数的意思分别是:
corePoolSize : 核心线程池大小
maximumPoolSize : 最大线程池大小
keepAliveTime : 线程最大空闲时间
unit : 时间单位
workQueue : 线程等待队列
threadFactory : 线程创建工厂
handler : 拒绝策略
通过ThreadPoolExecutor定义一个我们自己的线程池:
1、首先写一个自定义的线程池类,目的是为了记录每个线程的执行执行时间:
public class CommonThreadPoolExecutor extends ThreadPoolExecutor {
private static final Log logger = LogManager.getLogger(CommonThreadPoolExecutor.class);
private final static ThreadLocal local = new ThreadLocal();
private final AtomicLong finishTime = new AtomicLong();
public long getFinishTime() {
return finishTime.get();
}
@Override
protected void beforeExecute(Thread t, Runnable r) {
local.set(System.currentTimeMillis());
logger.info("线程before执行,线程名="+t.getName()+", 线程ID="+t.getId()+",threadGroup="+t.getThreadGroup()+",state=" + t.getState());
super.beforeExecute(t, r);
}
@Override
protected void afterExecute(Runnable r, Throwable t) {
Long lastTime = local.get();
local.remove();
finishTime.addAndGet(System.currentTimeMillis() - lastTime);
logger.info("线程after执行, 线程名:"+ Thread.currentThread().getName() + ", 线程ID:" + Thread.currentThread().getId() + ",线程执行任务花费时间:" + finishTime.get() + "毫秒!");
super.afterExecute(r, t);
}
public CommonThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue workQueue) {
super(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue);
}
public CommonThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue workQueue, ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
super(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue, threadFactory);
}
public CommonThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue workQueue, RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
super(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue, handler);
}
public CommonThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue workQueue, ThreadFactory threadFactory, RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
super(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue, threadFactory, handler);
}
}
2、定义一个线程管理工厂来创建线程池
@Component
public class CommonThreadPoolManager {
private static final ILog logger = LogManager.getLogger(CommonThreadPoolManager.class);
private static final String TITLE = "CommonThreadPoolManager";
private static final int CORE_POOL_SIZE = 10;
private static final int MAX_POOL_SIZE = 30;
private static final int KEEP_ALIVE_TIME = 0;
private static final int WORK_QUEUE_SIZE = 3000;
public CommonThreadPoolManager() {
logger.info(TITLE, "通用线程池init......");
}
private final CommonThreadPoolExecutor statQueryPool = new CommonThreadPoolExecutor(CORE_POOL_SIZE, MAX_POOL_SIZE, KEEP_ALIVE_TIME, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue(WORK_QUEUE_SIZE), new DefThreadFactory(),new RejectExecutionHandlerPolicy());
final class RejectExecutionHandlerPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler{
@Override
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
logger.warn("当前任务被拒绝,线程ID:"+Thread.currentThread().getId()+",线程名称:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
throw new InvokeServiceException("500", "拒绝服务! " + executor.toString());
}
}
public CommonThreadPoolExecutor getStatQueryPool() {
return statQueryPool;
}
}
3、自定义创建线程工厂
public class DefThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory {
private static final AtomicInteger poolNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
private final ThreadGroup group;
private final AtomicInteger threadNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
private final String namePrefix;
public DefThreadFactory() {
SecurityManager s = System.getSecurityManager();
group = (s != null) ? s.getThreadGroup() :
Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();
namePrefix = "fltdata-thread-pool-" + poolNumber.getAndIncrement() + "-thread-";
}
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread t = new Thread(group, r,
namePrefix + threadNumber.getAndIncrement(),
0);
if (t.isDaemon())
t.setDaemon(false);
if (t.getPriority() != Thread.NORM_PRIORITY)
t.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);
return t;
}
}
4、根据业务需求定义线程任务
public class QueryTask implements Callable {
private static final Log logger = LogManager.getLogger(QueryTask .class);
private QueryDao dao;
public QueryTask (QueryDao dao){
this.dao= dao;
}
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
try{
logger.info("当前线程:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+", 执行查询!");
return dao.query();
}catch (Exception e){
logger.error("查询失败, e : " + e);
throw new CommonException("500", "查询失败!");
}
}
}
5、使用
@Autowired
private CommonThreadPoolManager commonThreadPoolManager;
// 在业务方法内使用
Future submit = commonThreadPoolManager.getStatQueryPool().submit(new QueryTask(dao));