redis缓存实战
目录
redis缓存实战
redis作为二级缓存
一,搭建redis
二,讲解一下 redisTemplate
三,redis作为mybatis缓存
四,springboot cache结合redis的使用
五,redis实现分布式集群环境session共享
六,排行榜功能
redis缓存实战
如果想了解redis ,可以去看我的另一篇关于redis的文章,很全,写的不好,请多指教:
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44291453/article/details/107283384
这里说一下,window连接redis:
打开cmd ,进入 redis安装目录,然后输入"redis-cli",如图,就可以在里面操作,和看数据了:
redis作为二级缓存
让我们看看什么是一级缓存和二级缓存:
一级缓存是:sqlSession,sql建立连接到关闭连接的数据缓存
在操作数据库时会建立一个sqlSession,在对象中有一个数据结构用于存储缓存数据,第一次查询就会把数据进行缓存,第二次就会从缓存中获取,当sqlSession执行commit,即“增删改”,就会清空缓存
二级缓存是:全局
为什么要二级缓存,当spring和mybatis整合时,每次查询都要进行sqlSession关闭,关闭之后缓存会被清空,如果没有事务一级缓存没有意义
这里用spring boot来整合redis进行讲解
一,搭建redis
首先在你的pom,xml里面加上下面的依赖:
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-data-redis
然后在,*.properties添加如下配置:
# Redis数据库索引(默认为0)
spring.redis.database=0
# Redis服务器地址
spring.redis.host=localhost
# Redis服务器连接端口
spring.redis.port=6379
# Redis服务器连接密码(默认为空)
spring.redis.password=
下面是redis的配置类和简单的操做:
/**
* 实例化 RedisTemplate 对象
*
* @return
*/
//表明他是一个配置类
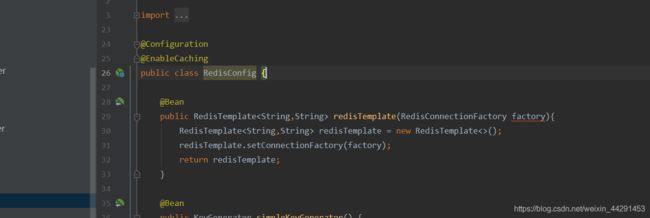
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
//交个spring容器进行管理,生成bean
@Bean
public RedisTemplate redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory){
RedisTemplate redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(factory);
return redisTemplate;
}
/**
* 设置数据存入 redis 的序列化方式,并开启事务
*
* @param redisTemplate
* @param factory
*/
private void initDomainRedisTemplate(RedisTemplate redisTemplate, RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
//如果不配置Serializer,那么存储的时候缺省使用String,如果用User类型存储,那么会提示错误User can't cast to String!
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer());
// 开启事务
redisTemplate.setEnableTransactionSupport(true);
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(factory);
}
}
//表明它是controller层,并且返回json
@RestController
public class RedisController {
//将redisTemplate注入进来
@Resource
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
//访问路径
@RequestMapping("/redis/setAndGet")
@ResponseBody
public String setAndGetValue(String name,String value){
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(name,value);
return (String) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(name);
} 二,讲解一下 redisTemplate
这是redisTemplate里面的部分源码
public SetOperations opsForSet() {
if (this.setOps == null) {
this.setOps = new DefaultSetOperations(this);
}
return this.setOps;
}
public ValueOperations opsForValue() {
if (this.valueOps == null) {
this.valueOps = new DefaultValueOperations(this);
}
return this.valueOps;
}
public ZSetOperations opsForZSet() {
if (this.zSetOps == null) {
this.zSetOps = new DefaultZSetOperations(this);
}
return this.zSetOps;
}
public ListOperations opsForList() {
if (this.listOps == null) {
this.listOps = new DefaultListOperations(this);
}
return this.listOps;
}
public HashOperations opsForHash() {
return new DefaultHashOperations(this);
} 这里介绍一下这五种api对应的用法:
opsForValue 操作String,Key,Value,包含过期key,setBit位操作等
opsForSet 操作set
opsForHash 操作hash
opsForZset 操作SortSet
opsForList 操作list队列
例如:opsForValue这个方法,他返回的DefaultValueOperations
class DefaultValueOperations extends AbstractOperations implements ValueOperations {
DefaultValueOperations(RedisTemplate template) {
super(template);
}
public V get(Object key) {
return this.execute(new AbstractOperations.ValueDeserializingRedisCallback(key) {
protected byte[] inRedis(byte[] rawKey, RedisConnection connection) {
return connection.get(rawKey);
}
}, true);
}
public V getAndSet(K key, V newValue) {
final byte[] rawValue = this.rawValue(newValue);
return this.execute(new AbstractOperations.ValueDeserializingRedisCallback(key) {
protected byte[] inRedis(byte[] rawKey, RedisConnection connection) {
return connection.getSet(rawKey, rawValue);
}
}, true);
}
public void set(K key, V value) {
final byte[] rawValue = this.rawValue(value);
this.execute(new AbstractOperations.ValueDeserializingRedisCallback(key) {
protected byte[] inRedis(byte[] rawKey, RedisConnection connection) {
connection.set(rawKey, rawValue);
return null;
}
}, true);
}
} 三,redis作为mybatis缓存
1,用户第一次访问的时候,获取数据库的值,然后将从数据库查处来的值缓存进redis数据库,并且设置过期时间,
2,再次访问时直接从缓存中获取数据
3,String类型常用于登陆,比如缓存token
用如下方法,time就是设定他的过期时间:
/**
* set值和get值的时候序列化方式必须保持一致
* @param id
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/getUserCache")
@ResponseBody
public User getUseCache(String id) {
//step1 先从redis里面取值
User user = (User)redisService.get(key + id);
//step2 如果拿不到则从DB取值
if (user == null) {
User userDB = userMapper.find(id);
System.out.println("fresh value from DB id:" + id);
//step3 DB非空情况刷新redis值
if (userDB != null) {
redisService.set(key + id, userDB,24*3600L);
return userDB;
}
}
return user;
}
/**
* 普通缓存放入并设置时间
*
* @param key 键
* @param value 值
* @param time 时间(秒) time要大于0 如果time小于等于0 将设置无限期
* @return true成功 false 失败
*/
public boolean set(String key, Object value, long time) {
try {
if (time > 0) {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, value, time, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
} else {
set(key, value);
}
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}四,springboot cache结合redis的使用
为什么要用 springboot cache:可以使用注解就能完成数据进入缓存
spring cache包含两个顶级接口,cache(缓存)和cacheManager(缓存管理器),顾名思义,cacheManager去管理一堆Cache
看一下,他支持多种缓存,如:redis,ehcache
1,首先添加如下依赖
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-cache
2,开启缓存注解: @EnableCaching,这里的注解放在配置类redisconfig里,即可
3,下面对注解的简单介绍
@CacheConfig(cacheNames="userInfoCache") 在同个redis里面必须唯一
@Cacheable(查) :
来划分可缓存的方法 - 即,结果存储在缓存中的方法,以便在后续调用(具有相同的参数)时,返回缓存中的值而不必实际执行该方法
@CachePut(修改、增加) :
当需要更新缓存而不干扰方法执行时,可以使用@CachePut注释。也就是说,始终执行该方法并将其结果放入缓存中(根据@CachePut选项)
@CacheEvict(删除) :
对于从缓存中删除陈旧或未使用的数据非常有用,指示缓存范围内的驱逐是否需要执行而不仅仅是一个条目驱逐
4,我们用简单的实例看看怎么用:
@Service
@CacheConfig(cacheNames="userInfoCache") // 本类内方法指定使用缓存时,默认的名称就是userInfoCache
public class UserService {
@Nullable
@Cacheable(key="#p0") // @Cacheable 会先查询缓存,如果缓存中存在,则不执行方法
public User findById(String id){
System.err.println("根据id=" + id +"获取用户对象,从数据库中获取");
Assert.notNull(id,"id不用为空");
return this.userMapper.find(id);
}
}第一,生成key:userInfoCache::1,过于简单,容易冲突,所以我们得配置一下
第二,无法设置过期时间,默认过期时间为永久不过期。我们也得配置一下
第三,配置序列化方式,默认的是序列化JDKSerialazable。我们根据自己的项目情况进行配置
RedisConnectionFactory 它的实现类是有两个,一个是LettuceConnectionFactory,还有一个是JedisConnectionFactory
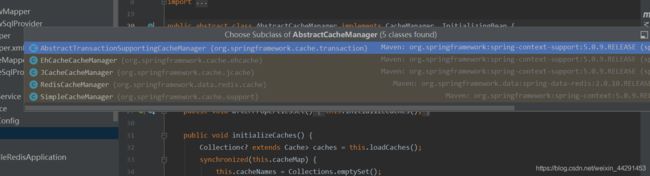
我们找到 RedisCacheManager这个类,如图,里面有个RedisCacheConfiguration配置类,那么下面的配置代码就好理解了:
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory){
RedisTemplate redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(factory);
return redisTemplate;
}
/*
* 配置key(类名+方法名+参数)"
* o(类)
* method(方法名)
* objects(参数)
*/
@Bean
public KeyGenerator simpleKeyGenerator() {
return (o, method, objects) -> {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
stringBuilder.append(o.getClass().getSimpleName());
stringBuilder.append(".");
stringBuilder.append(method.getName());
stringBuilder.append("[");
for (Object obj : objects) {
stringBuilder.append(obj.toString());
}
stringBuilder.append("]");
return stringBuilder.toString();
};
}
/**
*
* 设置过期时间
*
*/
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
return new RedisCacheManager(
RedisCacheWriter.nonLockingRedisCacheWriter(redisConnectionFactory),
this.getRedisCacheConfigurationWithTtl(600), // 默认策略,未配置的 key 会使用这个
this.getRedisCacheConfigurationMap() // 指定 key 策略
);
}
/**
*
* 给指定的key配置过期时间
*/
private Map getRedisCacheConfigurationMap() {
Map redisCacheConfigurationMap = new HashMap<>();
redisCacheConfigurationMap.put("UserInfoList", this.getRedisCacheConfigurationWithTtl(100));
redisCacheConfigurationMap.put("UserInfoListAnother", this.getRedisCacheConfigurationWithTtl(18000));
return redisCacheConfigurationMap;
}
/**
* 配置序列化方式
*默认序列化JDKSerialazable
*
*/
private RedisCacheConfiguration getRedisCacheConfigurationWithTtl(Integer seconds) {
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer 简单的案例:
@Service
@CacheConfig(cacheNames="userInfoCache") // 本类内方法指定使用缓存时,默认的名称就是userInfoCache
public class UserService {
@Nullable
@Cacheable(value = "UserInfoList", keyGenerator = "simpleKeyGenerator") // @Cacheable
//会先查询缓存,如果缓存中存在,则不执行方法
public User findByIdTtl(String id){
System.err.println("根据id=" + id +"获取用户对象,从数据库中获取");
Assert.notNull(id,"id不用为空");
return this.userMapper.find(id);
}
}步骤1,先回去看缓存里面有没有数据
步骤2,没有数据就会去数据库里面查,
步骤3,把查到的数据放入缓存
根据配置,它的缓存为100秒,它生成的key 为:UserInfoList::userService.findByIdTtl[1],这个1就是参数
五,redis实现分布式集群环境session共享
多机器部署同一套服务(代码),性能更好,更承受更高的用户并发
1、cookie与session
1)Cookie是什么? Cookie 是一小段文本信息,伴随着用户请求和页面在 Web 服务器和浏览器之间传递。Cookie 包含每次用户访问站点时 Web 应用程序都可以读取的信息,我们可以看到在服务器写的cookie,会通过响应头Set-Cookie的方式写入到浏览器
2)HTTP协议是无状态的,并非TCP一样进行三次握手,对于一个浏览器发出的多次请求,WEB服务器无法区分是不是来源于同一个浏览器。所以服务器为了区分这个过程会通过一个sessionid来区分请求,而这个sessionid是怎么发送给服务端的呢。cookie相对用户是不可见的,用来保存这个sessionid是最好不过了
2、redis实现分布式集群配置过程:
1).引入依赖:
org.springframework.session
spring-session-data-redis
2) @EnableRedisHttpSession 开启redis session缓存
maxInactiveIntervalInSeconds指定缓存的时间
下面是setSession和getsession的简单例子:
@RestController
public class SessionController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/setSession", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public Map setSession (HttpServletRequest request){
Map map = new HashMap<>();
request.getSession().setAttribute("request Url", request.getRequestURL());
map.put("request Url", request.getRequestURL());
return map;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/getSession", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public Object getSession (HttpServletRequest request){
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("sessionIdUrl",request.getSession().getAttribute("request Url"));
map.put("sessionId", request.getSession().getId());
return map;
}
} 六,redis实现排行榜功能排行榜功能
排行榜功能是一个很普遍的需求。使用 Redis 中有序集合的特性来实现排行榜是又好又快的选择。一般排行榜都是有实效性的,比如“用户积分榜”,游戏中活跃度排行榜,游戏装备排行榜等。
先看排行榜需要那些表
score_flow(积分流水表),用于排行比如:top100
user_score(用户积分表总表),查用户的排名
这是我简单建立的用户表和数据:
1、添加用户积分,这里只是部分代码
里面key是用id+name组成的,查找缓存可以看到用户的姓名
public class RangingService implements InitializingBean {
private static final String SALESCORE = "sale_score_rank:";
public void increSaleSocre(String uid, Integer score) {
//从用户表查询数据
User user = userMapper.find(uid);
if (user == null) {
return;
}
int uidInt = Integer.parseInt(uid);
long socreLong = Long.parseLong(score + "");
String name = user.getName();
String key = uid + ":" + name;
//将用户id,name,score插入score_flow(积分流水表)
scoreFlowMapper.insertSelective(new ScoreFlow(socreLong, uidInt, name));
//将用户id,name,score插入user_score(用户积分表总表)
userScoreMapper.insertSelective(new UserScore(uidInt, socreLong, name);
//将用户缓存;key:"sale_score_rank:" value: map
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().incrementScore(SALESCORE,key,score);
}
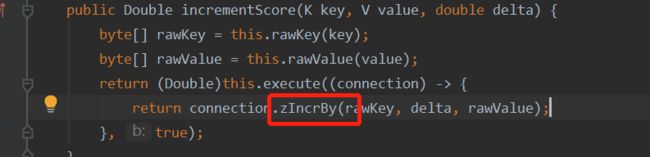
} 这里面的redisTemplate.opsForZSet().incrementScore(SALESCORE,key,score),incrementScore方法底层用的是:zIncrBy命令
Zincrby 命令对有序集合中指定成员的分数加上增量 increment,就是当对同一个对象插入分数时,他会对分数进行累加
2.根据用户ID获取排行
public Map userRank(String uid, String name) {
Map retMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
String key = uid + ":" + name;
//查找用户的排名
Integer rank =redisTemplate.opsForZSet().rank(SALESCORE, key).intValue();
//查找用户的分数
Long score = redisTemplate.opsForZSet().score(SALESCORE, key).longValue();
retMap.put("userId", uid);
retMap.put("score", score);
retMap.put("rank", rank);
return retMap;
} redisTemplate.opsForZSet().score(SALESCORE, key),score方法里用的是:zScore命令
zScore 是返回key的分数。
如图:
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().rank(SALESCORE, key),rank方法里用的是:zrank命令
zrank——返回key对应的SortSet中指定member的排名。其中member按score值递增(从小到大);
排名以0为底,也就是说,score值最小的成员排名为0,排行榜越高的,值越大,排行榜中运用
2、获取top N 排行
public List> reverseZRankWithRank(long start, long end) {
//获取指定的范围的排名,比如,获取前100的排名,成员按 score 值递减的次序排列
Set> setObj = redisTemplate.opsForZSet().reverseRangeWithScores(SALESCORE, start, end);
List> mapList = setObj.stream().map(objectTypedTuple -> {
Map map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
map.put("userId", objectTypedTuple.getValue().toString().split(":")[0]);
map.put("userName", objectTypedTuple.getValue().toString().split(":")[1]);
map.put("score", objectTypedTuple.getScore());
return map;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
return mapList;
}
有如果对你帮助,请点个赞呗