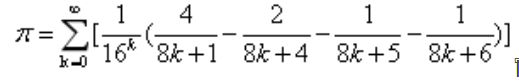Python语言程序设计(北京理工大学)第四周_Python Programming week04
整数的加减和
描述
编写程序计算如下数列的值:
1-2+3-4...966
其中,所有数字为整数,从1开始递增,奇数为正,偶数为负
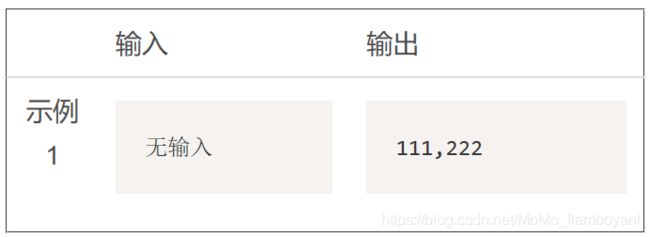
输入输出示例
sum = 0
flag = 1
for i in range(1, 967, 1):
sum += flag * i
flag = -flag
print(sum)
三位水仙花数
描述
"水仙花数"是指一个三位整数,其各位数字的3次方和等于该数本身。
例如:ABC是一个"3位水仙花数",则:A的3次方+B的3次方+C的3次方 = ABC。
请按照从小到大的顺序输出所有的3位水仙花数,请用"逗号"分隔输出结果。
输入输出示例
输出仅表示格式,不表示对错。
flag = 0
for i in range(100, 1000, 1):
hundred = i//100
ten = i%100//10
unit = i%10
if unit**3 + ten**3 + hundred**3 == i:
if flag == 1:
print(",", end="")
print(i, end="")
if flag == 0:
flag = 1
用户登录的三次机会
描述
给用户三次输入用户名和密码的机会,要求如下:
1)如输入第一行输入用户名为‘Kate’,第二行输入密码为‘666666’,输出‘登录成功!’,退出程序;
2)当一共有3次输入用户名或密码不正确输出“3次用户名或者密码均有误!退出程序。”。
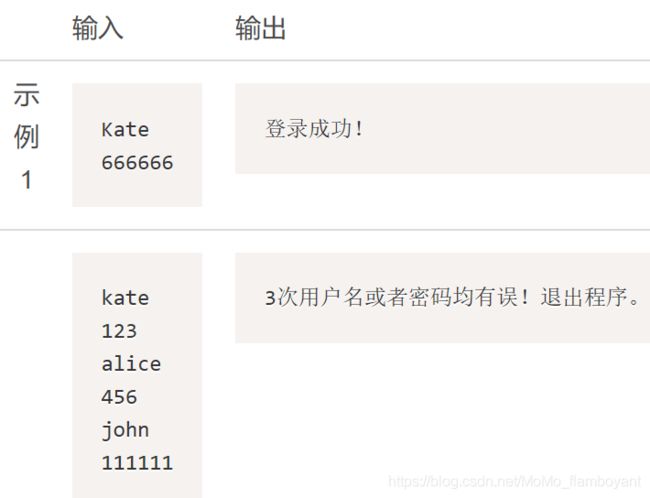
输入输出示例
cnt = 0
while 1:
name = input(); psw = input()
if name == 'Kate' and psw == '666666':
print("登录成功!")
break
else:
cnt += 1
if cnt == 3:
print("3次用户名或者密码均有误!退出程序。")
break
实例5:身体质量指数BMI
描述
BMI :Body Mass Index 国际上常用的衡量人体肥胖和健康程度重要标准,主要用于统计分析
定义:BMI = 体重 (kg) /身高2(m2)
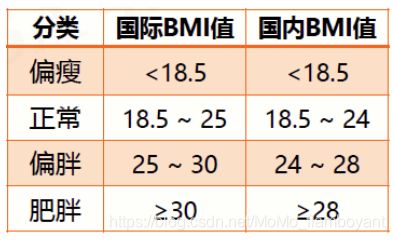
获取用户输入的体重和身高值,计算并给出国际和国内的 BMI 分类
要求如下:
(1) 混合计算并给出国际和国内的 BMI 分类;
(2) 使用input()获得测试用例输入时,不要增加提示字符串。
输入
示例1:1.68,41
示例2:1.72,80
输出
示例1:
BMI 数值为:14.53
BMI 指标为:国际'偏瘦', 国内'偏瘦'
示例2:
BMI 数值为:27.04
BMI 指标为:国际'偏胖', 国内'偏胖'
height, weight = eval(input())
bmi = weight / pow(height, 2)
print("BMI数值为:{:.2f}".format(bmi))
who, nat = "", ""
if bmi < 18.5:
who, nat = "偏瘦", "偏瘦"
elif 18.5 <= bmi < 24:
who, nat = "正常", "正常"
elif 24 <= bmi < 25:
who, nat = "正常", "偏胖"
elif 25 <= bmi < 28:
who, nat = "偏胖", "偏胖"
elif 28 <= bmi < 30:
who, nat = "偏胖", "肥胖"
else:
who, nat = "肥胖", "肥胖"
print("BMI指标为:国际'{0}',国内'{1}'".format(who, nat))
实例6:圆周率的计算
描述
圆周率的近似计算公式:
# CalPiV1.py
pi = 0
N = 100
for k in range(N):
pi += 1/pow(16,k)*( \
4/(8*k+1) - 2/(8*k+4) - \
1/(8*k+5) - 1/(8*k+6) )
print("圆周率值是: {}".format(pi))
利用蒙特卡罗方法解 π 值:
# CalPiV2.py
from random import random
from time import perf_counter
DARTS = 1000*1000
hits = 0.0
start = perf_counter()
for i in range(1, DARTS+1):
x, y = random(), random()
dist = pow(x**2 + y**2, 0.5)
if dist <= 1.0:
hits += 1
pi = 4 * (hits/DARTS)
print("圆周率值是:{}".format(pi))
print("运行时间是:{:.5f}s".format(perf_counter()-start))
# exceptions.py
try:
num = eval(input("请输入一个整数:"))
print(num**2)
except NameError:
print("输入不是整数")
=================== RESTART: D:\2018\python\exceptions.py ===================
请输入一个整数:123
15129
>>>
=================== RESTART: D:\2018\python\exceptions.py ===================
请输入一个整数:abc
输入不是整数# random.py
import random
print("1".center(20,'='))
print(random.random())
print(random.random())
print("2".center(20,'='))
random.seed(10)
print(random.random())
print(random.random())
print("3".center(20,'='))
random.seed(10)
print(random.random())
random.seed(10)
print(random.random())
===================== RESTART: D:\2018\python\random.py =====================
=========1==========
0.37170965930088506
0.25296994260039385
=========2==========
0.5714025946899135
0.4288890546751146
=========3==========
0.5714025946899135
0.5714025946899135
>>>
===================== RESTART: D:\2018\python\random.py =====================
=========1==========
0.17335124288255233
0.030127742109735678
=========2==========
0.5714025946899135
0.4288890546751146
=========3==========
0.5714025946899135
0.5714025946899135>>> import random
>>> random.randint(10, 100)
68
>>> random.randint(10, 100)
88
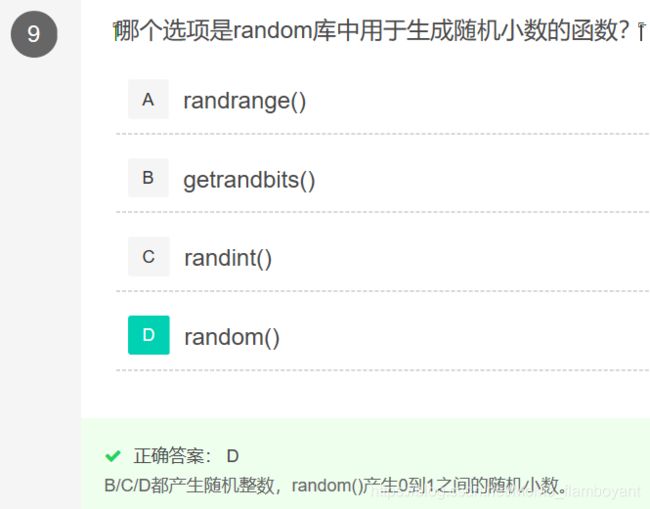
>>> random.randrange(10, 100, 10)
60
>>> random.randrange(10, 100, 10)
90
>>> random.getrandbits(16)
24568
>>> random.getrandbits(16)
36211
>>> random.uniform(10, 100)
39.17072665841261
>>> random.uniform(10, 100)
17.89261875127591
>>> random.choice([1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9])
9
>>> random.choice([1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9])
2
>>> s = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
>>> random.shuffle(s)
>>> print(s)
[5, 4, 1, 3, 6, 8, 2, 9, 7]
>>> s = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]; random.shuffle(s); print(s)
[3, 4, 8, 6, 1, 2, 5, 9, 7]