HashMap的一些自己的理解
HashMap的一些自己的理解
HashMap是继承了AbstractMap, 实现Map接口, 底层是采用了哈希表(散列表)结构,
既然说道了哈希表, 那就说下哈希表的结构
我们都知道, 数组的特点是占用空间连续, 查询效率高, 增删效率低;链表结构占用空间不连续, 查询效率低, 增删效率高, 我们能不能既查询效率高, 又增删效率也高呢? 为此我们就有了哈希表
哈希表就是结合了数组和链表的优点, 增删查效率高的一种数据结构
HashMap中的结构中含有key和value(键值对), 通过源码我们可以知道
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;//哈希码
final K key;//键
V value;//值
Node<K,V> next;//下一个节点
}
一个Node节点里面包含了4部分, 该位置的哈希码, 键, 值, 以及下一个节点对象, 正是因为以上的结构, 才有了哈希表的优点. 下面说下HashMap一些方法:
- put(key, value): 该方法是向Map集合中中添加元素,当向集合中添加一个元素的时候, 首先, 通过hashCode()(该函数底层是通过c语言编写, 在java中通过关键字native来修饰)函数计算该key值的哈希码, 将计算出来的哈希码, 再通过一种散列函数将该hash散列到一个数组中, 散列到到对应的数组下标下, 将其添加到对应的位置下, 判断该位置是否有元素, 如果没有就直接将该节点放在这个位置, 当该位置已有元素时, 就调用equals()方法进行比较该位置和当前的元素是否相同,相同就不添加(保证了HashMap集合的key的唯一性), 不相等就在位置的以链的方式来添加到该位置的末尾, 实现HashMap集合的添加操作.
补充: 在jdk1.8之前是插入链表的头部的,在jdk1.8中是插入链表的尾部的。 - get(key): 获取集合中的元素, 首先计算key对应的hash值, 接着通过一系列的方法来找到该节点对象node, 而该节点node对象中的value值就是需要查找到值.
get()方法的源码:
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;//计算key的hash码,再通过getNode()来获指定的节点Node对象
}
final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) {//通过hash值和对应的key值来查找对应Node对象
Node<K,V>[] tab;
Node<K,V> first, e;
int n; K k;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
return null;
}
接着再说下, HashMap的扩容机制, HashMap位桶的概念, 初始值是16. 在使用过程中该值是可变的. 如果位桶数组中的元素长度达到填充因子的最大值(0.75*数组length), 就会将数组进行扩容.
从JDK1.8开始引入了红黑树, 即当集合中的链表中的节点个数大于8时,就会将链表改为红黑树结构,目的是为了减少查询比较的次数, 下面是java源码定义的中红黑树TreeNode对象.
static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> {
TreeNode<K,V> parent; // 父节点
TreeNode<K,V> left;//左节点
TreeNode<K,V> right;//右节点
TreeNode<K,V> prev; // 该节点的前一个节点
boolean red;//树的颜色
TreeNode(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, val, next);
}
以上是都是自己的理解, 有不足之处还请大家指出.
-----------------------------------------------------------华丽的分割线-----------------------------------------------------------------
20191228更新
手写hashMap, 这次主要是实现HashMap中的put(), get(), size(), isEmpty()
首先定义一个接口MyMap:
public interface MyMap {
public void put(Object key,Object value);
public Object get(Object key);
public int size();
public boolean isEmpty();
interface Entry{
public Object getKey();
public Object getValue();
}
}
实现类:
package com.wxx.hashmap;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
public class MyHashMap implements MyMap {
//默认的数组的长度
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16
//键值对的数量,Entry的数量
transient int size;
//数组的引用,用来指向一个数据,数组的元素都是Entry
transient Entry[] table = null;
//无参构造方法
public MyHashMap() {
table = new Entry[DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY];//构造方法中,默认新建一个长度为16的数组
}
@Override
public void put(Object key, Object value) {
//1.计算hash值
int hash = key.hashCode();
//2.计算存储位置,计算需要存到数组中的那个位置
int index = hash % table.length;
//3.存储到指定的位置,如果当前的table没有对象就存到数组上
if (table[index] == null) {
table[index] = new Entry(key, value, null, hash);//将entry对象放入到数组中
size++;
} else {//该数组的位置已经存在了元素, 检查下面的链表是否存在相同的key的Entry对象
Entry entry = table[index];
while (entry != null) {
//比较,找到了就将旧value覆盖,并返回
if (entry.hash == hash && entry.getKey().equals(key)) {
entry.value = value;
return;
}
//指向下一个节点
entry = entry.next;
}
//如果上面的循环完后都没有找到,那就将这个新节点添加到最前面,不是添加到末尾
Entry firstEntry = table[index];//原来的第一个节点
size++;//数量++
table[index] = new Entry(key, value, firstEntry, hash);//将新节点添加最前面,下一个节点就是原来的第一个节点
}
}
@Override
public Object get(Object key) {
//1.计算hash值
int hash = key.hashCode();
//2.j计算存储位置
int index = hash % table.length;
//这个就是数组某个索引的头节点
Entry entry = table[index];
//遍历链表
while (entry != null) {
//判断key是否一样,找到了就返回value
if (entry.hash == hash && entry.key.equals(key)) {
return entry.value;
}
//指向下一个节点
entry = entry.next;
}
//直到最后都没有查到, 就返回null
return null;
}
//打印hashMap
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder("{");
for (Entry entry : table) {
if (entry != null) {
while (entry != null) {
//追加
builder.append(entry.key + "=" + entry.value + ",");
//指向下一个节点
entry = entry.next;
}
}
}
//将最后一个","删除,先判断是否有元素
if (builder.length() > 2) {
builder.deleteCharAt(builder.length() - 1);
}
builder.append("}");
return builder.toString();
}
@Override
public int size() {
return size;
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
class Entry implements MyMap.Entry {
final Object key;
Object value;
Entry next;
int hash;
public Entry(Object key, Object value, Entry next, int hash) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
this.hash = hash;
}
@Override
public Object getKey() {
return key;
}
@Override
public Object getValue() {
return value;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Entry{" +
"key=" + key +
", value=" + value +
", next=" + next +
", hash=" + hash +
'}';
}
}
}
测试:
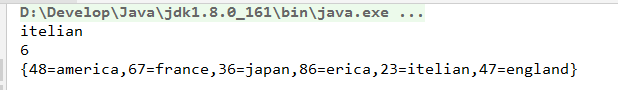
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyMap map = new MyHashMap();
map.put(23,"china");
map.put(36,"japan");
map.put(48,"america");
map.put(86,"erica");
map.put(67,"france");
map.put(23,"itelian");
map.put(47,"england");
System.out.println( map.get(23));
System.out.println(((MyHashMap) map).size);
System.out.println(map.toString());
}
}