快速沃尔什变换(FWT)
问题
FWT用来解决这样的一个问题:
给出多项式A(x),B(x),求C(x),其中
C(k)=∑i⊕j=kA(i)B(j) C ( k ) = ∑ i ⊕ j = k A ( i ) B ( j )
(也可以换成and/or)
要求在 O(nlogn) O ( n log n ) 的复杂度内求出C(x)
定义
定义 tf(A) t f ( A ) 操作表示(A是一个长度为2的幂的多项式,k表示A的长度,A0A1分别表示A的左半边和右半边)
则
tf(A)={A(tf(A0)+tf(A1),tf(A0)−tf(A1))k=1else t f ( A ) = { A k=1 ( t f ( A 0 ) + t f ( A 1 ) , t f ( A 0 ) − t f ( A 1 ) ) else
其中”,”表示物理顺序拼接
性质
然后有一条性质 tf(A)+tf(B)=tf(A+B) t f ( A ) + t f ( B ) = t f ( A + B )
证明略,可以用数学归纳法来证
因为C=A⊕B,所以可以得出 C=(A0⊕B0+A1⊕B1,A0⊕B1+A1⊕B0) C = ( A 0 ⊕ B 0 + A 1 ⊕ B 1 , A 0 ⊕ B 1 + A 1 ⊕ B 0 )
等于把异或第一位为0的数加到左边,异或第一位为1的数加到右边
然后xjb证出tf(A)tf(B)=tf(C) (当C=A⊕B时)
所以可以先求出tf(A)和tf(B),之后相乘求逆
逆运算
定义tf(A)的逆运算utf(A),表示utf(tf(A))=A
则
utf(A)={A(utf(A0)+utf(A1)2,utf(A0)−utf(A1)2)k=1else u t f ( A ) = { A k=1 ( u t f ( A 0 ) + u t f ( A 1 ) 2 , u t f ( A 0 ) − u t f ( A 1 ) 2 ) else
证明还是数学归纳法
所以这样对tf(C)做utf操作,就可以得出C了
而tf和utf操作都是 O(nlogn) O ( n log n ) 的
其它
关于三种运算的tf和utf
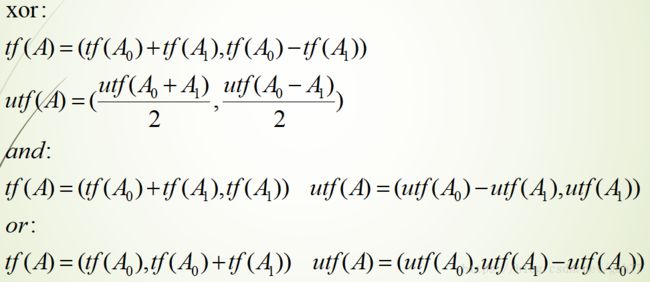
其中异或的utf是可以拆的,也就是说utf(A)+utf(B)=utf(A+B)
证明和tf基本一样(就是多了个/2)
例题
codeforces662CBinary Table 二进制表
C. Binary Table
time limit per test6 seconds
memory limit per test256 megabytes
inputstandard input
outputstandard output
You are given a table consisting of n rows and m columns. Each cell of the table contains either 0 or 1. In one move, you are allowed to pick any row or any column and invert all values, that is, replace 0 by 1 and vice versa.
What is the minimum number of cells with value 1 you can get after applying some number of operations?
Input
The first line of the input contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n ≤ 20, 1 ≤ m ≤ 100 000) — the number of rows and the number of columns, respectively.
Then n lines follows with the descriptions of the rows. Each line has length m and contains only digits ‘0’ and ‘1’.
Output
Output a single integer — the minimum possible number of ones you can get after applying some sequence of operations.
Example
inputCopy
3 4
0110
1010
0111
outputCopy
2
C.二进制表
每次测试的时间限制6秒
每次测试的内存限制256兆字节
输入标准输入
产量标准输出
您将获得一个由n行和m列组成的表。表的每个单元格包含0或1。在一个步骤中,您可以选择任何行或任何列并反转所有值,即将0替换为1,反之亦然。
在应用一些操作后,您可以获得值为1的最小单元格数是多少?
输入
输入的第一行包含两个整数Ñ和米(1≤ Ñ ≤20,1≤ 米 ≤100 000) -行的,分别的数量和列的数量。
然后n行跟随行的描述。每行的长度为m,仅包含数字“ 0 ”和“ 1 ”。
产量
输出一个整数 - 应用一系列操作后可以获得的最小数量。
例
输入复制
3 4
0110
1010
0111
产量复制
2
题解
就是给出一个01矩阵,每次可以把一行或一列取反
求所有可能的矩阵中最小的1个数
因为n很小,所以考虑状压n
如果行的方案确定了,那么答案就是每一列异或行后取反与否的最大值之和
设f(s)表示当行选取的状态为s时的答案
设ans(s)表示某一列状态为s时的答案
要考虑整列取反的情况
设g(s)表示初始列状态为s的列数
则
f(s)=∑s⊕s′=kans(k)g(s′) f ( s ) = ∑ s ⊕ s ′ = k a n s ( k ) g ( s ′ )
等于是枚举每一种可能的列,然后进行列的取反,答案就是所有列之和
可以变成
f(s)=∑s=k⊕s′ans(k)g(s′) f ( s ) = ∑ s = k ⊕ s ′ a n s ( k ) g ( s ′ )
就是FWT的形式了
code
// codeforces 662C Binary Table
// start:25/08/17
#include
using namespace std;
typedef long long AA[1048576];
int A[100001];
AA s,a,b,c;
int n,m,i,j,k,l,Len;
char ch;
long long ans;
void tf(long long *a)
{
int i,j,k,l;
int S=1,s1=1,s2=Len+1;
fo(i,1,n)
{
S<<=1;
s2>>=1;
fo(j,0,s2-1)
{
fo(k,0,s1-1)
{
l=j*S+k;
s[l]=a[l]+a[l+s1];
s[l+s1]=a[l]-a[l+s1];
}
}
memcpy(a,s,sizeof(long long)*(Len+1));
s1<<=1;
}
}
void utf(long long *a)
{
int i,j,k,l;
int S=1,s1=1,s2=Len+1;
fo(i,1,n)
{
S<<=1;
s2>>=1;
fo(j,0,s2-1)
{
fo(k,0,s1-1)
{
l=j*S+k;
s[l]=(a[l]+a[l+s1])>>1;
s[l+s1]=(a[l]-a[l+s1])>>1;
}
}
memcpy(a,s,sizeof(long long)*(Len+1));
s1<<=1;
}
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); Len=pow(2,n)-1;
fo(i,1,n)
{
scanf("\n");
fo(j,1,m)
{
scanf("%c",&ch);
A[j]=(A[j]<<1)+(ch-'0');
}
}
fo(i,1,m)
b[A[i]]++;
fo(i,0,Len)
{
j=i;
k=0;
while (j)
{
k+=j&1;
j>>=1;
}
a[i]=min(k,n-k);
}
tf(a);
tf(b);
fo(i,0,Len)
c[i]=a[i]*b[i];
utf(c);
ans=233333333;
fo(i,0,Len)
ans=min(ans,c[i]);
printf("%I64d\n",ans);
}