Android OpenGL相机视角
Android OpenGL相机视角
首先申明下,本文为笔者学习《OpenGL ES应用开发实践指南》的笔记,并加入笔者自己的理解和归纳总结。
1、矩阵层次结构
(1) 模型矩阵
模型矩阵是用来把物体放在世界控件坐标系的。比如模型初始的中心点都在(0, 0, 0),如果想要移动它们,可以使用一个模型矩阵,把那些顶点与这个矩阵相乘来变换它们。
(2) 视图矩阵
视图矩阵是出于同模型矩阵一样的原因被使用的,但是它平等地影响场景中的每一个物体。
(3) 投影矩阵
投影矩阵帮助创建三维幻象,当屏幕变换方位时,它才会变化。
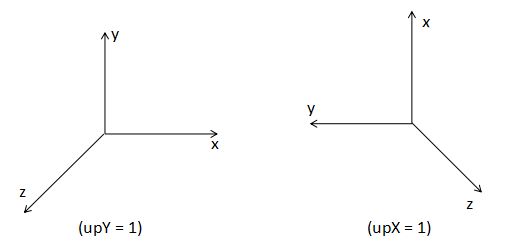
2、定义相机视角
Matrix.setLookAtM(float[] rm, int rmOffset, float eyeX, float eyeY, float eyeZ,
float centerX, float centerY, float centerZ, float upX, float upY, float upZ)| rm | 存储视图矩阵 |
| rmOffset | 偏移量 |
| eyeX,eyeY,eyeZ | 眼睛所在的位置 |
| centerX,centerY,centerZ | 眼睛正在看的位置,这个位置出现在场景的中心 |
| upX,upY,upZ | 这个是你头指向的地方,upY的值为1意味着你的头笔直指向上方 |
3、绘制着色器
(1) 视图矩阵,创建透视投影,并把视角移动到(0, 1.2f, 2.5f),头指向上方。private float[] projectionMatrix = new float[16];
private float[] viewMatrix = new float[16];
private float[] viewProjectMatrix = new float[16];
// 创建透视投影
Matrix.perspectiveM(projectionMatrix, 0, 45, (float)width / (float)height, 1, 10);
// 移动视角,等同于模型矩阵沿z轴移动2.8
Matrix.setLookAtM(viewMatrix, 0, 0f, 0f, 2.8f, 0f, 0f, 0f, 0f, 1f, 0f);
// 生成新的视图工程模型
Matrix.multiplyMM(viewProjectMatrix, 0, projectionMatrix, 0, viewMatrix, 0);private float[] modelMatrix = new float[16];
private float[] modelViewProjectionMatrix = new float[16];
// 定义模型矩阵
Matrix.setIdentityM(modelMatrix, 0);
Matrix.rotateM(modelMatrix, 0, -60, 1f, 0f, 0f);
// 生成工程模型矩阵
Matrix.multiplyMM(modelViewProjectionMatrix, 0, viewProjectMatrix,
0, modelMatrix, 0);
class OpenGLEyeTextureShaderRender implements GLSurfaceView.Renderer {
private float[] projectionMatrix = new float[16];
private float[] modelMatrix = new float[16];
private float[] viewMatrix = new float[16];
private float[] viewProjectMatrix = new float[16];
private float[] modelViewProjectionMatrix = new float[16];
private TextureProgram mTextureProgram;
private ColorProgram mColorProgram;
private Table mTable;
private Mallet mMallet;
@Override
public void onSurfaceCreated(GL10 gl, EGLConfig config) {
GLES20.glClearColor(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f);
mTable = new Table();
mMallet = new Mallet();
mTextureProgram = new TextureProgram(OpenGLEyeTextureShaderActivity.this,
R.drawable.air_hockey_surface);
mColorProgram = new ColorProgram(OpenGLEyeTextureShaderActivity.this);
}
@Override
public void onSurfaceChanged(GL10 gl, int width, int height) {
GLES20.glViewport(0, 0, width, height);
// 创建透视投影
Matrix.perspectiveM(projectionMatrix, 0, 45, (float)width / (float)height, 1, 10);
// 移动视角
Matrix.setLookAtM(viewMatrix, 0, 0f, 0f, 2.8f, 0f, 0f, 0f, 0f, 1f, 0f);
// 生成新的视图工程模型
Matrix.multiplyMM(viewProjectMatrix, 0, projectionMatrix, 0, viewMatrix, 0);
// 定义模型矩阵
Matrix.setIdentityM(modelMatrix, 0);
Matrix.rotateM(modelMatrix, 0, -60, 1f, 0f, 0f);
// 生成工程模型矩阵
Matrix.multiplyMM(modelViewProjectionMatrix, 0, viewProjectMatrix,
0, modelMatrix, 0);
}
@Override
public void onDrawFrame(GL10 gl) {
GLES20.glClear(GLES20.GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
mTextureProgram.setUniform(modelViewProjectionMatrix);
mTable.bindData(mTextureProgram);
mTable.draw();
mColorProgram.setUniform(modelViewProjectionMatrix);
mMallet.bindData(mColorProgram);
mMallet.draw();
}
}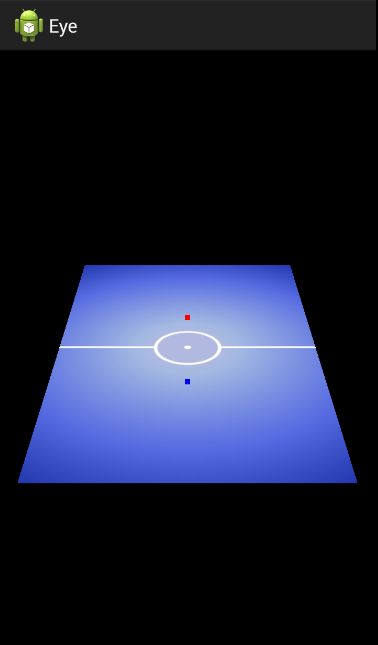
(4) 合并操作
Matrix.perspectiveM(projectionMatrix, 0, 45, (float)width / (float)height, 1, 10);
// 移动视角,代替模型翻转
Matrix.setLookAtM(viewMatrix, 0, 0f, -2.4f, 1.4f, 0f, 0f, 0f, 0f, 1f, 0f);
Matrix.multiplyMM(viewProjectMatrix, 0, projectionMatrix, 0, viewMatrix, 0);
Matrix.setIdentityM(modelMatrix, 0);
Matrix.multiplyMM(modelViewProjectionMatrix, 0, viewProjectMatrix,
0, modelMatrix, 0);参考资料:http://blog.csdn.net/kkae8643150/article/details/52805738