背包问题的一些想法
原创作品,出自 “晓风残月xj” 博客,欢迎转载,转载时请务必注明出处(http://blog.csdn.net/xiaofengcanyuexj)。
由于各种原因,可能存在诸多不足,欢迎斧正!
在此说明,以下是我算法基础的节课报告,彭雷老师要求以组为单位做汇报,汇报已过,贴出思路与大家共享,并作为读书笔记存于博客。
问题描述
背包问题有很多种,一般描述为有一背包容量为maxVolume,有numOfGood件物品,对应体积、价值和数量分别为volume[i]、price[i]、number[i]。
满足以下方程
∑volume[i]*tempNumber[i]<=maxVolume
tempNumber[i]<=number[i]
使总价值:
sumPrice=∑price[i]*tempNumber[i]
sumPrice最大。
关于背包问题,有很多问题值得思考。
1、物品是否可分
(1)、若每件物品可分,即分成任意小的物品,则问题简化很多,依次直接取价值/体积大的,直到背包装满或者物品用完为止,此种情况下sumPrice最大。
(2)、若每件物品不可分,则无法通过上述贪心策略解决,这是我们组要解决的。
2、背包是否装满
背包装不装满对问题的求解起到至关重要的作用。比如:背包容积为maxVolume=4,物品numOfGood=3种,分别(体积,价值,数量)为Good[]={(1,10,1)、(2,20,1)、(4,1,1)}
在背包装满的情况下为选物品1,总价值为1;
若不要求未满,则可取物品2+物品3,总体积为1+2=3<4,总价值为10+20=30.
3、物品数量
根据物品数量,大致可分3种
(1)、Number[i]=1 0<=i
分别对应01背包、完全背包、多重背包。
4、解的准确程度
问题的规模不同,如背包容积maxVolume,物品数量numOfGood会影响得到最终解所消耗的时间、空间资源,即影响程序的效率。效率与解的准确程度往往是矛盾的,我们需要在二者之间进行折中。于是我们尝试了多种方法:搜索法与动态规划法求最优解,遗传算法与贪心算法求解可行的近似解。
解决方案
依据物品数量,可以分为01背包、完全背包、多重背包。在此我们分别给出不同的解法。
一、01背包
依据背包容积maxVolume与物品数量numOfGood的数量级,我们给出了4类解法。
1. 枚举法
当物品数量numOfGood较小的时候,可以尝试物品枚举子集,找出对应价值最大者。关于枚举,我们尝试了两种不同的方法:位操作枚举、搜索枚举。
1.1位操作枚举法
此种方法适合物品数量numOfGood较小,一般满足numOfGood<=15,总的子集数cnt=2^numOfGood,然后就是依据位操作的特点寻找符合条件的解。下面给出伪代码:
for(子集状态i从0到cnt)
{
for(枚举每件物品i)
{
挑出到目前为止对应价值最大者;
}
}
如何判断物品i是否在子集j中呢?还是举上面那个例子:背包容积为maxVolume=4,物品numOfGood=3种,分别(体积,价值,数量)为
Good[]={(1,10,1)、(2,20,1)、(4,1,1)}
此时总的子集数cnt=2^3,当j=3时,其对应二进制位00000011,只有第0、1位为1,则对应取Good[0]、Good[1].若当前子集为j(0<=j
位操作枚举法有它的局限,一来1<
1.2搜索枚举法
搜索法也是一种枚举法,但回避了位操作可能带来的溢出问题,而且可以适当的在搜索过程中进行剪枝,从而得到常数级的优化。搜索法是在一棵隐式图的基础上进行的,此图是根据问题的状态空间得到的。
对于物品i,有两个分支:取第i个物品,不取第i个物品。层层递归即可得到一棵解答树,最终求得满足条件的价值最大者。
空间复杂度为O(1),时间复杂度为O(2^n)。
2.动态规划法
特点是:每种物品仅有一件,可以选择放或不放。
用子问题定义状态:即dp[i][j]表示前i件物品恰放入一个容量为j的背包可以获得的最大价值。
则其状态转移方程便是:
dp[i][j]=max{dp[i-1][j],dp[i-1][j-Good[i].volume]+Good[i].price}
然后就是对状态转移方程的处理,一般有两种处理方法:
1.由前往后递推
2.由后往前递归
由于递归会伴随函数调用、栈资源消耗等降低效率的因素,所以我们下面给出的搜索算法都回避了递归。
2.1无优化动态规划
for i=0..numOfGood-1
for j=0..maxVolume
dp[i][j]=max{dp[i-1][j],dp[i-1][j-Good[i].volume]+Good[i].price};
空间复杂度为O(maxVolume*numOfGood),时间复杂度为O(maxVolume*numOfGood)。时间复杂度叫枚举法有较大改进。
2.2有优化动态规划
通过观察状态转移方程, dp[i][j]=max{dp[i-1][j],dp[i-1][j-Good[i].volume]+Good[i].price} 发现关于当前物品i,求dp[i][j]只与dp[i-1][j]、dp[i-1][j-Good[i].volume]+Good[i].price,前一维i-1相关,于是可以使用滚动数组。只需开辟dp[2][MAXVOLUME],然后滚动求解。
k=1;
for i=1..numOfGood-1//第一个物品单独处理
{
for j=0..maxVolume
dp[k][j]=max{dp[k^1][j],dp[k^1][j-Good[i].volume]+Good[i].price};
k^=1;
}
这样一来空间复杂度有效将至O(maxVolume)。 不过关于此问题,还有一个更为巧妙的方法。在此观察状态转移方程:
dp[i][j]=max{dp[i-1][j],dp[i-1][j-Good[i].volume]+Good[i].price}
发现第一维其实与最终要求解的价值最大无多大关系,只是为了防止当前物品使用不止一次。还是上面那个例子:背包容积为maxVolume=4,物品numOfGood=3种,分别(体积,价值,数量)为
Good[]={(1,10,1)、(2,20,1)、(4,1,1)}
若直接开辟dp[MAXVOLUME],顺序处理
for j=0..maxVolume
dp[j]=max{dp[j],dp[j-Good[i].volume]+Good[i].price};
则会带来重复使用物品,与01背包本质不符。下面是i=0时所得:
| 体积j |
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
| 价值 |
0 |
10 |
20 |
30 |
40 |
|
明显重复了,j从2开始都重复利用了前一次的值,是得物品不知被用了一次。此问题可以通过改变j的求解顺序解决,有顺序变成逆序,
| 体积j |
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
| 价值 |
0 |
10 |
10 |
10 |
10 |
从而排除了重复使用数目仅为1的物品。具体伪代码为:直接开辟dp[MAXVOLUME],顺序处理
for j=maxVolume到0
dp[j]=max{dp[j],dp[j-Good[i].volume]+Good[i].price};
空间复杂度为O(maxVolume),时间复杂度为O(maxVolume*numOfGood)。空间复杂度较无优化的动态规划有较大改进。
3.遗传算法
由上述解决方法可知,最好的解法时间复杂度为O(maxVolume*numOfGood),当maxVolume、numOfGood都很大时是无法在有限的时间范围内求出最优解的。
于是我们想到了演化计算中的遗传算法,根据物品数量numOfGood初始化若干条染色体,每条染色体代表背包的一种装法。还是上面那个例子:
背包容积为maxVolume=4,物品numOfGood=3种,分别(体积,价值,数量)为
Good[]={(1,10,1)、(2,20,1)、(4,1,1)}
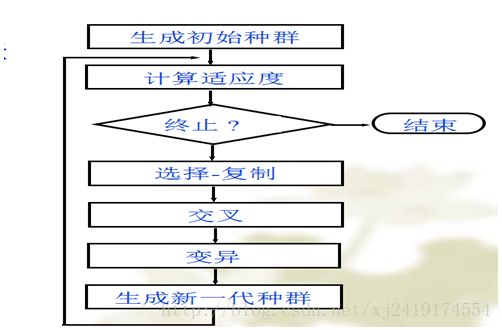
我们初始化染色体chroSingle[],若chroSingle[i]为011,则表示取第0、1个物品。然后通过遗传操作:交叉、变异、选择等不断模拟自然界适者生存的法则,最终选择出适应度较高的,对应原问题的一个可行解。当然在遗传操作中应保证所产生的染色体是合法的,即对应物品的体积和不超过背包容积。下面是我们的遗传算法框图:
通常情况下可以得到一个可行的近似解,时间复杂度为(generation*numOfGood^2)。当maxVolume、numOfGood很大尤其是maxVolume很大时,传统的方法都无法在保证效率的情况下得到准确姐,此时可以尝试人工智能的方法。
4.贪心算法
当然,当maxVolume、numOfGood达到一定程度时,不管是传统方法还是遗传算法都无法在有限的时间内求解问题,于是很自然地想到贪心算法。在前面提到过,在物品可分的情况下贪心算法是可以得到最优解的。但当物品不可分时,贪心算法在其他方法失效的情况下也是可以求解问题的。提到贪心算法,我们必须想到一个贪心策略,即选取当前最优是依据何种策略评判的。结合01背包问题本身,可以有3种贪心策略,
a、体积最小
b、价值最大
c、价值/体积最大
当然,这3种贪心策略不能说哪种绝对好,在我们的测试用例中却是也是这样的。
统计组合数+打印路径
关于01背包问题,我们基本运用了以上的4大类,8种具体不同算法。同时,我们统计了最优解的组合数并打印了路径。
(1)、位操作枚举法+遗传算法+贪心算法。统计组合数和打印路径相对简单,在此不多说。
(2)、搜索法+动态规划法。这两类方法是统计组合数+打印路径的难点所在。但由于思想相似,我们一起说说。
Int path[MAXN][MAXVOLUME];//存放路径,path[i][j]为0表示在总体积为j时不取第i个物品;path[i][j]为1表示在总体积为j时取第i个物品。当然path[i][j]可以取大于1的数值,表示不只取一个该物品,这是下面完全背包、多重背包的内容,这里先不介绍。
Int numOfCombine[MAXVOLUME];//存放总体积为j时符合条件的组合数。
下面介绍一下怎么求,怎么用上述两个数组,为了提高效率,我们求上述两个数组是糅合在求dp[][]的功能模块里的。对应伪代码为:
dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j];
if(dp[j-Good[i].volume]+Good[i].price>dp[i][j])//要i物品价值更大
{
numOfCombine[j]=numOfCombine[j-Good[i].volume];
dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j-Good[i].volume]+Good[i].price;
path[i][j]=1;
}
else if(dp[i-1][j-Good[i].volume]+Good[i].price==dp[i][j])//要与不要一样大
{
numOfCombine[j]+=numOfCombine[j-Good[i].volume];
path[i][j]=1;//此处path[i][j]可赋值可不赋值,对应路径不一样
}
当然,有些繁琐的细节在此就不说了,注意边界条件、临界状态的把握。
求得了path[][]数组,下面就是根据里面的类容打印一条路径了。由于路径很多,可能会出现组合爆炸问题,开数组代替path[][]单个值也无法保证记录所有路径,而且很可能程序运行时栈溢出,所以我们只打印了一条路径。我们由后往前推到,i=numOfGood-1,j=maxVolume;
1、.判断path[i][j]记录容积为j时第i个物品是否取。
(1)、为0表示没取,不打印第i个物品,i=i-1;
(2)、为1表示取过,打印第i个物品,i=i-1,j=j-Good[i].volume。
2、重复步骤1直到i或j其中一个小于0
上述打印模块也有地归与非递归的,为了效率,我们还是选择了非递归的程序实现。
int j=volume;
for(i从numOfGood-1减到0)
{
if(path[i][j]非0)
{
打印物品i;
调整j.
}
}
背包是否装满的处理
背包是否装满看似无关紧要,其实对问题的决策起到至关重要的作用。重复之前的例子:
背包容积为maxVolume=4,物品numOfGood=3种,分别(体积,价值,数量)为Good[]={(1,10,1)、(2,20,1)、(4,1,1)}
在背包装满的情况下为选物品1,总价值为1;
若不要求未满,则可取物品2+物品3,总体积为1+2=3<4,总价值为10+20=30.
我们此次选用的是C++,我们把背包抽象为一个类,把与之相关的所有方法都抽象为成员函数,从而实现封装与抽象。为了能同时处理背包装满与不装满问题,我们定义的接口传递了参数isFull,以此处理上述情况。其实满与不满关键在于初始值的设定。
如果要求恰好装满背包,那么在初始化为
dp[i][0]=0, 0<=i<=numOfGood-1
dp[i][j]=-1, 0<=i<=numOfGood-1且1<=j<=maxVolume
这样就可以保证最终得到的dp[numOfGood-1][maxVolume]是一种恰好装满背包的最优解
如果不要求背包装满,那么在初始化为
dp[i][j]=0, 0<=i<=numOfGood-1且0<=j<=maxVolume
为什么呢?可以这样理解:初始化的dp数组事实上就是在没有任何物品放入背包时的合法状态。
(1)、如果要求背包恰好装满,那么此时只有容量为0的背包可能被价值为0的nothing“恰好装满”,其它容量的背包均没有合法的解,属于未定义的状态,它们的值就都应该是-1了。
(2)、如果背包不要求装满,那么任何容量的背包都有一个合法解“什么都不装”,这个解的价值为0,所以初始时状态的值也就全部为0了。
二、完全背包
完全背包,即每件物品的数量无限多,
或者 Good[i].volume*Good[i].number>=maxVolume此时等价于物品数量无限多。
关于完全背包,枚举法同样可以,可以在01背包的基础上再加一层枚举,但这样时间复杂度达O(2^numOfGood*max(maxVolume/Good[i].volume)),只要numOfGood、maxVolume稍大就很难出结果。所以对于完全背包,我们放弃枚举法。
遗传算法也是可以的。只是编码上增加了一维,即原来的每一位对应一个位串,位串长度len[i],保证2^len[i]>=maxVolume/Good[i].volume),len[i]取最小(这样既能使物品i足够,又能最大限度节约空间)。由于可能长度很长超内存,不考虑这层又和01背包重复,所以我们没有用遗传算法。
1、动态规划法
特点是:每种物品足够多,可以选择不放或放多件。
用子问题定义状态:即dp[i][j]表示前i件物品恰放入一个容量为j的背包可以获得的最大价值。
则其状态转移方程便是:
dp[i][j]=max{dp[i-1][j],dp[i-1][j-k*Good[i].volume]+k*Good[i].price}
对比01背包的状态转移方程,可得多了变量k。
1.1、无优化动态规划
只需在原有01背包问题的基础上加一层数量的循环,伪代码如下:
for i=0..numOfGood-1
for j=0..maxVolume
for(k=0;k*Good[i].volume<=maxVolume;k++)
dp[i][j]=max{dp[i-1][j],dp[i-1][j-k*Good[i].volume]+k*Good[i].price};
空间复杂度为O(maxVolume*numOfGood),时间复杂度为O(maxVolume*Σ(maxVolume/Good[i].volume)),这个时间复杂度是很大的。
1.2、有优化动态规划
可以将完全背包换成01背包问题,即把每件物品看做maxVolume/Good[i].volume件体积和价值都不变的物品,于是就成了01背包,但此方法完全没有降低时间复杂度;但我们可以顺着转换为01背包的思想加以改进。
由二进制原理可知,任何整数k都能表示成二进制形式,于是尝试将完全背包问题分解为物品数为1,2,4,8,…2^e,其中e是小于等于log2(k)的最大整数。然后增加1,2,3,4,8
…2^e对应的体积和价值的物品各一件,剩下就是01背包问题了。这样一来,时间复杂度有效的降为O(maxVolume*Σ(log2(maxVolume/Good[i].volume))),这是一个比较有效的改进。
但我们还有更有效的改进方法。还记得上面顺着处理01背包带来的物品重复使用吗?在多重背包中,物品的数量是足够多的,不存在物品重复使用带来的错误。
还是那个例子:
背包容积为maxVolume=4,物品numOfGood=3种,分别(体积,价值,数量)为
Good[]={(1,10,1)、(2,20,1)、(4,1,1)}
直接开辟dp[MAXVOLUME],顺序处理
下面是i=0的情况:
| 体积 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
| 价值 |
0 |
10 |
20 |
30 |
40 |
所以顺着处理是可以的
for i=0..numOfGood-1
for j=0..maxVolume
dp[j]=max{dp[j],dp[j-Good[i].volume]+Good[i].price};
这样一来,空间复杂度为O(maxVolume),时间复杂度为O(maxVolume*numOfGood)。无优化的动态规划有较大改进。
2、贪心算法
完全背包的贪心算法基本和01背包一样,在此也就不说了。
统计组合数+打印路径+背包是否装满
在这几方面和01背包很类似,只是有些细节需要特殊处理,大家如果遇到过问题后再讨论。在此也不多说了。
三、多重背包
多重背包,即每件物品的数量有限
枚举法+遗传算法同样可以解决多重背包问题,但和完全背包一样存在很大的不足,在此也就不说了。
1、动态规划法
特点是:每种物品足够多,可以选择不放或放多件。
用子问题定义状态:即dp[i][j]表示前i件物品恰放入一个容量为j的背包可以获得的最大价值。
则其状态转移方程便是:
dp[i][j]=max{dp[i-1][j],dp[i-1][j-k*Good[i].volume]+k*Good[i].price}
对比01背包的状态转移方程,可得多了变量k;对比完全背包,可知对k又多了限制条件:K<=Good[i].number
1.1、无优化+不合并动态规划
在此说一下,这里的优化是指像完全背包那样顺着处理降低时空复杂度,提高效率。
此处基本同完全背包,只是注意
多重背包:k<=min(j/Good[i].GetVolume(),Good[i].GetNumber())
完全背包:k=j/Good[i].GetVolume()
空间复杂度为O(maxVolume*numOfGood),时间复杂度为O(maxVolume*Σ(Good[i].volume)),这个时间复杂度是很大的。
1.2、有优化+不合并动态规划
此处基本同完全背包,只是注意当Good[i].GetVolume()*Good[i].GetNumber()>=volume,对该物品来说就是完全背包; 否则,按照完全背包的思路顺着处理。这样一来,空间复杂度为O(maxVolume),时间复杂度为O(maxVolume*numOfGood)。无优化的动态规划有较大改进。
1.3、有优化+合并动态规划
这里是指顺序处理+按二进制合并。关于二进制合并在完全背包中已经有所介绍,参完全背包部分,在此不多说。
2、贪心算法
与01背包唯一不同就是物品可多选,然后就是小细节。
统计组合数+打印路径+背包是否装满
多重背包问题可以转换为01背包+完全背包,这方面基本同上述二者。
下面贴代码:
染色体类头文件Chromosome.h
#ifndef CHROMOSOME_H
#define CHROMOSOME_H
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include"Good.h"
using namespace std;
const int MAXN_LEN=100;
const int MAXN_NUM=10*MAXN_LEN;
class Chromosome
{
public:
void GetMutate(Chromosome &,int);
int GetPostion(int);
int GetVolume();
void SetPostion(int,int);
int GetFitness(vector&);
bool IsIllegal(vector&)const;
void InitiateChro(vector&,int,int);
void GetCross(Chromosome &,int,int);
void GetMutate(int);
void PrintChro(vector&);
Chromosome operator=(Chromosome);
bitset GetChro();
private:
int volume;
int length;
bitsetmyChro;
};
/***************************************************
*参数:无
*功能:返回染色体对应极限容量
****************************************************/
int Chromosome::GetVolume()
{
return volume;
}
/***************************************************
*参数:无
*功能:返回染色体
****************************************************/
bitset Chromosome::GetChro()
{
return myChro;
}
/***************************************************
*参数:tChromosome染色体基因
*功能:重载赋值操作符
****************************************************/
Chromosome Chromosome::operator=(Chromosome tChromosome)
{
length=tChromosome.length;
volume=tChromosome.volume;
for(int i=0;i& myGood)
{
for(int i=0;i& myGood)const
{
bool isIllegal=true;
int tempWei=0;
for(int i=0;ivolume)
isIllegal=false;
return isIllegal;
}
/***************************************************
*参数:无
*功能:初始化合法染色体
****************************************************/
void Chromosome::InitiateChro(vector& myGood,int tlength,int tVolume)
{
length=tlength;
volume=tVolume;
srand(unsigned(clock()));
int num=0;
do
{
for(int i=0;i=100)break;
}while(!IsIllegal(myGood));
if(num>=100)//无法在规定次数内完成染色体的初始化
{
for(int i=0;i& myGood)
{
int fitness=0;
for(int i=0;i
种群类头文件Population.h
#ifndef POPULATION_H
#define POPULATION_H
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include"Good.h"
#include"Chromosome.h"
#include"Population.h"
using namespace std;
class Population
{
public:
Population(int,int,int,int,double,double,vector&);
void GeneticAlgorithm(vector&);
int Selection(vector&);
private:
int maxTotalPrice;
int volume;
int generation;
int length;
int number;
double mutationRate;
double crossionRate;
Chromosome chroSingle[MAXN_NUM];
Chromosome bestChro;
};
/***************************************************
*参数:tGeneration,tnumber,tlength,tmutationRate,tcrossionRate
分别表示种群中进化代数,染色体数目,长度,变异率,交叉率
*功能:构造种群
****************************************************/
Population::Population(int tVolume,int tGeneration,int tnumber,int tlength,double tmutationRate,double tcrossionRate,vector& myGood)
{
volume=tVolume;
generation=tGeneration;
number=tnumber;
length=tlength;
mutationRate=tmutationRate;
crossionRate=tcrossionRate;
maxTotalPrice=-1;
for(int i=0;i& myGood)
{
int i,bestId=-1;
int ret=-1;
double sumFitness=0;
int fitness[MAXN_NUM];
double countRate[MAXN_NUM];
double selRate[MAXN_NUM];
for(i=0;irate)
break;
}
if(i==number)
--i;
TempChroSingle[num]=chroSingle[i];
++num;
}
for(i=0;i& myGood)
{
int nowGeneration=0;
int maxTotalPrice=0,tempTotalPrice=-1;
double mumCross=0,mumMutat=0;
while(nowGeneration1.0)
{
Chromosome temp1,temp2;
int id1,id2;
srand(unsigned(clock()));
do
{
id1=rand()%number;
id2=rand()%number;
int st,en;
st=rand()%length;
en=rand()%length;
if(st>en)
{
st=st^en;
en=st^en;
st=st^en;
}
temp1=chroSingle[id1];
temp2=chroSingle[id2];
temp1.GetCross(temp2,st,en);
}while(!temp1.IsIllegal(myGood)||!temp2.IsIllegal(myGood));
chroSingle[id1]=temp1;
chroSingle[id2]=temp2;
mumCross=mumCross-1;
}
while(mumMutat>1.0)
{
int bel,id;
Chromosome temp;
do
{
srand(unsigned(clock()));
bel=rand()%number;
temp=chroSingle[bel];
id=rand()%length;
temp.GetMutate(id);
}while(!temp.IsIllegal(myGood));
chroSingle[id]=temp;
mumMutat=mumMutat-1;
}
// cout<<"+++++++++++++++++++"<
物品类头文件Good.h
#ifndef GOOD_H
#define GOOD_H
#include
using namespace std;
class Good
{
public:
Good(int vol,int pri,int num)
{
price=pri;
volume=vol;
number=num;
}
Good(const Good& good)
{
price=good.price;
volume=good.volume;
number=good.number;
}
int GetPrice();
int GetVolume();
int GetNumber();
private:
int price;
int volume;
int number;
};
/***************************************************
*依次返回待处理物品价值、体积、数量
****************************************************/
int Good::GetPrice()
{
return price;
}
int Good::GetVolume()
{
return volume;
}
int Good::GetNumber()
{
return number;
}
#endif
背包类头文件Pack.h
#ifndef PACK_H
#define PACK_H
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include"Good.h"
#include"Chromosome.h"
#include"Population.h"
using namespace std;
const int MAXN=100;
const int INF=-(1<<30l);
const int MAXVOLUME=100;
int max(int a,int b)
{
return a& GetVector();
void Pack::PushBack(vector&,Good &);
int SelectGoodOfGreed(bool);
int GreedOfGetMinVolume(bool);
int GreedOfGetMaxPrice(bool);
int GreedOfGetMaxDensity(bool);
void InitateDPArrayOfNotOptimize(bool);
void InitateDPArray(bool);
int BitOperationEnum(bool);
int DFS(int,int ,bool);
int searchEnum(bool);
int SolveZeroOnePackOfNotOptimize(bool);
void SingleZeroOnePack(Good&,int,int,bool);
int SolveZeroOnePack(bool);
int SolveCompletePackOfNotOptimize(bool);
void SingleCompletePack(Good&,int,int,bool);
int SolveCompletePack(bool);
int SolveMultiplePackOfNotMergeOfNotOptimize(bool);
void SingleMultiplePackOfNotMerge(Good&,int,bool);
int SolveMultiplePackOfNotMerge(bool);
void SingleMultiplePackOfMerge(Good&,int,bool);
int SolveMultiplePackOfMerge(bool);
void PrintZeroOnePack();
void PrintCompletePack();
void PrintMultiplePack();
void PrintWhatSelected();
private:
int DFSNumOfCombine[MAXN][MAXVOLUME];
int path[MAXN][MAXVOLUME];
int dpOfNotOptimize[MAXN][MAXVOLUME];
int dp[MAXVOLUME];
int numOfCombine[MAXVOLUME];
int volume;
int maxTotalPrice;
vectormyGood;
vectormyLoadGood;
};
/***************************************************
*参数:tVolume背包容量
*功能:初始化背包
****************************************************/
void Pack::SetPack(int tVolume)
{
volume=tVolume;
}
/***************************************************
*参数:
*功能:设置种群信息
****************************************************/
void Pack::SetPackPopulation(int tVolume,int tGeneration,int tNumber,double tMutation,double tCrossion)
{
Population pop(tVolume,tGeneration,tNumber*5,tNumber,tMutation,tCrossion,myGood);
pop.GeneticAlgorithm(myGood);
}
/***************************************************
*参数:无
*功能:返回物品容器
****************************************************/
vector& Pack::GetVector()
{
return myGood;
}
/***************************************************
*返回背包的待处理物品数量
****************************************************/
int Pack::GetNumberOfGoods()
{
return myGood.size();
}
/***************************************************
*返回背包的最大容积
****************************************************/
int Pack::GetVolume()
{
return volume;
}
/***************************************************
*获得对应下标的物品
****************************************************/
Good Pack::GetPositionGood(int id)
{
if(id>=myGood.size())
{
cout<<"下标越界!"<&myVec,Good &good)
{
myVec.push_back(good);
}
/***************************************************
*参数:无
*功能:打印01背包一条路径
****************************************************/
void Pack::PrintZeroOnePack()
{
int vol=volume;
for(int id=GetNumberOfGoods()-1;id>=0;id--)
{
if(path[id][vol])
{
Good temp=GetPositionGood(id);
cout<<"("<=0&&id>=0)
{
Good temp=GetPositionGood(id);
if(path[id][vol])
{
isFirst=false;
vol-=temp.GetVolume();
++tmpNum;
}
if(!path[id][vol])
{
if(!isFirst)
{
cout<<"("<=0&&id>=0)
{
if(path[id][vol])
{
Good temp=GetPositionGood(id);
cout<<"("<::iterator iter=myLoadGood.begin();iter!=myLoadGood.end();++iter)
{
cout<<"("<GetVolume()<<","<GetPrice()<<","<GetNumber()<<")";
}
cout<=0)
{
retPri+=perNum*tmp.GetPrice();
PushBack(myLoadGood,Good(tmp.GetVolume(),tmp.GetPrice(),perNum));
}
else break;
i++;
}
}
PrintWhatSelected();
return retPri;
}
/***************************************************
*贪心法每次选体积最小物品背包最大价值
****************************************************/
bool CmpMinVolume(Good a,Good b)
{
return a.GetVolume()b.GetPrice();
}
int Pack::GreedOfGetMaxPrice(bool isInfinity)
{
sort(myGood.begin(),myGood.end(),CmpMaxPrice);
maxTotalPrice=SelectGoodOfGreed(isInfinity);
return maxTotalPrice;
}
/***************************************************
*贪心法每次选价值/体积最大物品背包最大价值
****************************************************/
bool CmpMaxDensity(Good a,Good b)
{
return (double)(a.GetPrice())/a.GetVolume()>(double)(b.GetPrice())/b.GetVolume();
}
int Pack::GreedOfGetMaxDensity(bool isInfinity)
{
sort(myGood.begin(),myGood.end(),CmpMaxDensity);
maxTotalPrice=SelectGoodOfGreed(isInfinity);
return maxTotalPrice;
}
/***************************************************
*对应01背包的位操作枚举求法
****************************************************/
int Pack::BitOperationEnum(bool isFull)
{
int numOfGoods=GetNumberOfGoods();
if(numOfGoods>15)
{
cout<<"处理物品过多,不适合位操作!"<volume)
break;
sumPrice+=temp.GetPrice();
}
}
if(j>=numOfGoods&&sumVolume<=volume&&sumPrice>=maxTotalPrice)
{
if(!isFull||(isFull&&sumVolume==volume))
{
if(sumPrice==maxTotalPrice)
{
sumNum++;
}
else
{
sumNum=1;
set=i;
maxTotalPrice=sumPrice;
}
}
}
}
myLoadGood.clear();
for(i=0;i=GetPositionGood(start).GetVolume())
{
tmp2=DFS(start-1,tvol-GetPositionGood(start).GetVolume(),isFull);//要此背包
if(-1!=tmp2)
tmp2+=GetPositionGood(start).GetPrice();
}
if(tmp1tmp2)
{
path[start][tvol]=0;
if(0==start)
DFSNumOfCombine[start][tvol]=1;
else DFSNumOfCombine[start][tvol]=DFSNumOfCombine[start-1][tvol];
return tmp1;
}
else
{
path[start][tvol]=0;
if(-1!=tmp1)
DFSNumOfCombine[start][tvol]=DFSNumOfCombine[start-1][tvol]+
DFSNumOfCombine[start-1][tvol-GetPositionGood(start).GetVolume()];
else DFSNumOfCombine[start][tvol]==0;
return tmp1;
}
}
/***************************************************
*对应01背包的搜索枚举求法主函数
****************************************************/
int Pack::searchEnum(bool isFull)
{
if(GetNumberOfGoods()>=20)
{
cout<<"物品太多,不合适枚举!"<=0;j--)
{
if(0==i)
{
if(!isFull)
{
if(j>=temp.GetVolume())
{
dpOfNotOptimize[i][j]=temp.GetPrice();
path[i][j]=1;
}
numOfCombine[j]=1;
}
else
{
if(j==temp.GetVolume())
{
dpOfNotOptimize[i][j]=temp.GetPrice();
path[i][j]=1;
numOfCombine[j]=1;
}
}
}
else
{
dpOfNotOptimize[i][j]=dpOfNotOptimize[i-1][j];
if(j>=temp.GetVolume()&&-1!=dpOfNotOptimize[i-1][j-temp.GetVolume()])
{
if(dpOfNotOptimize[i-1][j-temp.GetVolume()]+temp.GetPrice()>dpOfNotOptimize[i][j])
{
if(0==numOfCombine[j-temp.GetVolume()])
numOfCombine[j]=1;
else numOfCombine[j]=numOfCombine[j-temp.GetVolume()];
dpOfNotOptimize[i][j]=dpOfNotOptimize[i-1][j-temp.GetVolume()]+temp.GetPrice();
path[i][j]=1;
}
else if(dpOfNotOptimize[i-1][j-temp.GetVolume()]+temp.GetPrice()==dpOfNotOptimize[i][j])
{
if(0==numOfCombine[j-temp.GetVolume()])
numOfCombine[j]+=1;
numOfCombine[j]+=numOfCombine[j-temp.GetVolume()];
}
}
}
}
}
cout<<"总的组合数为:"<=temp.GetVolume();i--)
if(!isFull||(isFull&&-1!=dp[i-temp.GetVolume()]))
{
//dp[i]=max(dp[i],dp[i-temp.GetVolume()]+temp.GetPrice());
if(-1!=dp[i-temp.GetVolume()]&&dp[i-temp.GetVolume()]+temp.GetPrice()>dp[i])
{
if(0==numOfCombine[i-temp.GetVolume()])
numOfCombine[i]=1;
else numOfCombine[i]=numOfCombine[i-temp.GetVolume()];
dp[i]=dp[i-temp.GetVolume()]+temp.GetPrice();
path[id][i]=tNum;
}
else if(-1!=dp[i-temp.GetVolume()]&&dp[i-temp.GetVolume()]+temp.GetPrice()==dp[i])
{
if(0==numOfCombine[i-temp.GetVolume()])
numOfCombine[i]+=1;
numOfCombine[i]+=numOfCombine[i-temp.GetVolume()];
}
}
}
/***************************************************
*参数:isFull为真表示需装满,为假则无需装满
*功能:对应所有物品01背包的动态规划求法
****************************************************/
int Pack::SolveZeroOnePack(bool isFull)
{
InitateDPArray(isFull);
maxTotalPrice=0;
for(int i=0;i=0;j--)
// for(int j=0;j<=volume;j++)
{
if(0==i)
{
int t=j/temp.GetVolume();///
for(int k=t;k>0;k--)
//for(int k=1;j>=k*temp.GetVolume();k++)
{
if(!isFull)
{
if(j>=k*temp.GetVolume()&&dpOfNotOptimize[i][j]0;k--)
//for(int k=1;j>=k*temp.GetVolume();k++)
{
if(j>=k*temp.GetVolume()&&-1!=dpOfNotOptimize[i-1][j-k*temp.GetVolume()])
{
if(dpOfNotOptimize[i-1][j-k*temp.GetVolume()]+k*temp.GetPrice()>dpOfNotOptimize[i][j])
{
if(0==numOfCombine[j-k*temp.GetVolume()])
numOfCombine[j]=1;
else numOfCombine[j]=numOfCombine[j-k*temp.GetVolume()];
dpOfNotOptimize[i][j]=dpOfNotOptimize[i-1][j-k*temp.GetVolume()]+k*temp.GetPrice();
path[i][j]=k;
}
else if(dpOfNotOptimize[i-1][j-k*temp.GetVolume()]+k*temp.GetPrice()==dpOfNotOptimize[i][j])
{
if(0==numOfCombine[j-k*temp.GetVolume()])
numOfCombine[j]+=1;
numOfCombine[j]+=numOfCombine[j-k*temp.GetVolume()];
}
}
}
}
}
}
cout<<"总的组合数为:"<dp[i])
{
if(0==numOfCombine[i-temp.GetVolume()])
numOfCombine[i]=1;
else numOfCombine[i]=numOfCombine[i-temp.GetVolume()];
dp[i]=dp[i-temp.GetVolume()]+temp.GetPrice();
path[id][i]=tNum;
}
else if(-1!=dp[i-temp.GetVolume()]&&dp[i-temp.GetVolume()]+temp.GetPrice()==dp[i])
{
if(0==numOfCombine[i-temp.GetVolume()])
numOfCombine[i]+=1;
numOfCombine[i]+=numOfCombine[i-temp.GetVolume()];
}
}
}
/***************************************************
*参数:isFull为真表示需装满,为假则无需装满
*功能:对应所有物品完全背包的动态规划求法
****************************************************/
int Pack::SolveCompletePack(bool isFull)
{
InitateDPArray(isFull);
maxTotalPrice=0;
for(int i=0;i=0;j--)
// for(int j=0;j<=volume;j++)
{
if(0==i)
{
int t=j/temp.GetVolume();///
t=min(t,temp.GetNumber());
for(int k=t;k>0;k--)
//for(int k=1;j>=k*temp.GetVolume();k++)
{
if(!isFull)
{
if(j>=k*temp.GetVolume()&&dpOfNotOptimize[i][j]0;k--)
//for(int k=1;j>=k*temp.GetVolume();k++)
{
if(j>=k*temp.GetVolume()&&-1!=dpOfNotOptimize[i-1][j-k*temp.GetVolume()])
{
if(dpOfNotOptimize[i-1][j-k*temp.GetVolume()]+k*temp.GetPrice()>dpOfNotOptimize[i][j])
{
if(0==numOfCombine[j-k*temp.GetVolume()])
numOfCombine[j]=1;
else numOfCombine[j]=numOfCombine[j-k*temp.GetVolume()];
dpOfNotOptimize[i][j]=dpOfNotOptimize[i-1][j-k*temp.GetVolume()]+k*temp.GetPrice();
path[i][j]=k;
}
else if(dpOfNotOptimize[i-1][j-k*temp.GetVolume()]+k*temp.GetPrice()==dpOfNotOptimize[i][j])
{
if(0==numOfCombine[j-k*temp.GetVolume()])
numOfCombine[j]+=1;
numOfCombine[j]+=numOfCombine[j-k*temp.GetVolume()];
}
}
}
}
}
}
cout<<"总的组合数为:"<=volume)
SingleCompletePack(temp,id,1,isFull);
else
{
for(int i=0;i=volume)
SingleCompletePack(temp,id,1,isFull);
else
{
int k=1;
int num=temp.GetNumber();
while(k
客户端头文件
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include"Good.h"
#include"Pack.h"
using namespace std;
const int MAXNPRICE=100;
void MenuFunc(int &choice,int &subChoice,int &greedySubChoice,bool& isFull,bool& isAuto)
{
bool flag=false;
do
{
if(flag)cout<<"您的选项非法,请重新输入!"<>choice;
cout<<"+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++"<>subChoice;
cout<<"============================================="<>subChoice;
cout<<"=============================================="<>subChoice;
cout<<"==============================================="<>tmpChoice;
cout<<"==============================================="<>tmpChoice;
cout<<"==============================================="<>greedySubChoice;
cout<<"==============================================="<>maxVolOfPack;
}while(maxVolOfPack>=MAXVOLUME);
myPack.SetPack(maxVolOfPack);//实例化背包类
isInpoutCor=false;
do
{
if(isInpoutCor)
cout<<"您的物品数量过大,请重新输入!"<>nunOfGood;
}while(nunOfGood>=MAXN);
int i=1;
while(i<=nunOfGood)
{
cout<<"第"<>vol>>pri;
if(3==choice)
cin>>num;
else num=1;随便赋值
myPack.PushBack(myPack.GetVector(),Good(vol,pri,num));
++i;
}
}
FILETIME beg,end;
GetSystemTimeAsFileTime(&beg);
if(1==choice)
{
if(1==subChoice)
cout<<"位操作枚举01背包最大价值:"<
程序入口
#include
#include
#include
#include"Good.h"
#include"Pack.h"
#include"Client.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
while(true)
Process();
return 0;
}
以上是我的报告及源代码,欢迎斧正!