卷积自编码器
卷积自编码器利用了传统自编码器的无监督的学习方式,结合了卷积神经网络的卷积和池化操作,从而实现特征提取,最后通过stack,实现一个深层的神经网络。
具体文章可以参考:
Masci J, Meier U, Cireşan D, et al. Stacked convolutional auto-encoders for hierarchical feature extraction[C]//International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2011: 52-59.
无监督学习
无监督学习可以在没有标记的情况下去学习样本的特征
The main purpose of unsupervised learning method is to extract generally useful features from unlabelled, to detect and remove input redundancies and to preserve only essential aspects of the data in robust and discriminative representations.
而卷积自编码器创建的目的就在于,利用卷积神经网络的卷积和池化操作,实现特征不变性提取(invariant feature)的无监督特征提取。
卷积神经网络和传统自编码器
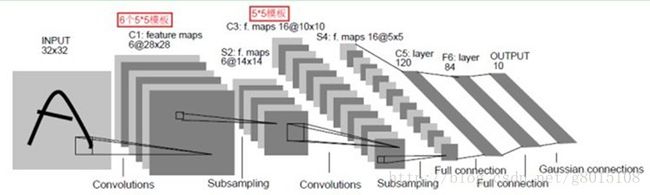
卷积神经网络由一个由卷积和池化组成的神经网络。卷积的作用相当于一个滤波器,而池化则是提取不变特征。其网络结构如下图所示:
自编码器则是一个由输入层,隐含层,输出层所构成的神经网络,其结构如下图所示:

通过利用输入层与输出层之间的映射关系,实现样本重构,从而提取特征。
卷积自编码器
假设我们有k个卷积核,每个卷积核由参数 wk 和 bk 组成,用和 hk 表示卷积层,则
代码
这个是在github找到的一个基于keras的代码:
def getModel():
input_img = Input(shape=(48, 48, 1))
x = Convolution2D(16, 3, 3, activation='relu', border_mode='same', dim_ordering='tf')(input_img)
x = MaxPooling2D((2, 2), border_mode='same', dim_ordering='tf')(x)
x = Convolution2D(32, 3, 3, activation='relu', border_mode='same', dim_ordering='tf')(input_img)
x = MaxPooling2D((2, 2), border_mode='same', dim_ordering='tf')(x)
x = Convolution2D(64, 3, 3, activation='relu', border_mode='same', dim_ordering='tf')(x)
encoded = MaxPooling2D((2, 2), border_mode='same', dim_ordering='tf')(x)
#6x6x32 -- bottleneck
x = UpSampling2D((2, 2), dim_ordering='tf')(encoded)
x = Convolution2D(32, 3, 3, activation='relu', border_mode='same', dim_ordering='tf')(x)
x = UpSampling2D((2, 2), dim_ordering='tf')(x)
x = Convolution2D(16, 3, 3, activation='relu', border_mode='same', dim_ordering='tf')(x)
decoded = Convolution2D(3, 3, 3, activation='relu', border_mode='same', dim_ordering='tf')(x)
#Create model
autoencoder = Model(input_img, decoded)
return autoencoder
# Trains the model for 10 epochs
def trainModel():
# Load dataset
print("Loading dataset...")
x_train_gray, x_train, x_test_gray, x_test = getDataset()
# Create model description
print("Creating model...")
model = getModel()
model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop', loss='binary_crossentropy',metrics=['accuracy'])
# Train model
print("Training model...")
model.fit(x_train_gray, x_train, nb_epoch=10, batch_size=148, shuffle=True, validation_data=(x_test_gray, x_test), callbacks=[TensorBoard(log_dir='/tmp/tb', histogram_freq=0, write_graph=False)])
# Evaluate loaded model on test data
print("Evaluating model...")
score = model.evaluate(x_train_gray, x_train, verbose=0)
print "%s: %.2f%%" % (model.metrics_names[1], score[1]*100)
# Serialize model to JSON
print("Saving model...")
model_json = model.to_json()
with open("model.json", "w") as json_file:
json_file.write(model_json)
# Serialize weights to HDF5
print("Saving weights...")
model.save_weights("model.h5")