版本记录
| 版本号 | 时间 |
|---|---|
| V1.0 | 2018.07.15 |
前言
我们做APP界面,也就是布局UI,那么关于布局,我们有很多方法,苹果也都提供了支持,市场上我们用的并不是系统提供原生的layout,对于OC语言一般都是使用一个第三方的布局框架 —— Masonry。接下来几篇我们就一起深入看一下这个框架。
Masonry概览
Masonry利用简化,链式和富有表现力的语法,利用AutoLayout NSLayoutConstraints的强大功能。 支持iOS和OSX自动布局。
关于布局,我们一般很少直接用苹果的原生API进行布局和适配,市场上使用很多的就是OC使用Masonry,如果是swift语言,那么就使用SnapKit。他们是同一个作者,感兴趣的可以点击这里SnapKit/Masonry,可以fork回去自己慢慢研究。
题外话:我工作这几年唯一的一次见过的就是前两年在一家小公司工作的时候,leader是百度T6出来的,他就不让用三方Masonry布局,他让我们所有人布局都使用Frame,当时就很疑惑不知道他就是不习惯使用三方,认为三方隐患比较多,还是他就是个Low B,我是Get不到他的点。直到后来我去另外一家大厂工作,我问一些其他同事,他们也是很不理解,每个VC里面,打开代码视图实例化和布局那个方法里面就最少一二百行,说实话我感觉很恶心,弄的跟Shi一样,还不让我们用xib,实在不明白,题外话就说这么多。
框架其中的一个作者如下所示,感兴趣的可以Follow他。
Masonry目前仍在积极维护,致力于修复错误并合并来自更广泛社区的优质PR。 但是,如果您在项目中使用Swift,建议使用**SnapKit **,因为它通过更简单的API提供更好的类型安全性。
Masonry是一个轻量级的布局框架,它使用更好的语法包装AutoLayout。 Masonry有自己的布局DSL,它提供了一种描述NSLayoutConstraints的可链接方式,从而使布局代码更简洁,更易读。 Masonry支持iOS和Mac OS X。
有关示例,请查看Masonry workspace中的Masonry iOS Examples项目,下载后您需要运行pod install。
What's wrong with NSLayoutConstraints? - NSLayoutConstraints怎么了
Auto Layout是一种强大而灵活的组织和布局视图的方式。 但是,从代码创建约束是冗长的,并不是非常具有描述性。 想象一个简单的例子,你想要一个视图填充其父视图,但每边插入10个像素间隔。
UIView *superview = self.view;
UIView *view1 = [[UIView alloc] init];
view1.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = NO;
view1.backgroundColor = [UIColor greenColor];
[superview addSubview:view1];
UIEdgeInsets padding = UIEdgeInsetsMake(10, 10, 10, 10);
[superview addConstraints:@[
//view1 constraints
[NSLayoutConstraint constraintWithItem:view1
attribute:NSLayoutAttributeTop
relatedBy:NSLayoutRelationEqual
toItem:superview
attribute:NSLayoutAttributeTop
multiplier:1.0
constant:padding.top],
[NSLayoutConstraint constraintWithItem:view1
attribute:NSLayoutAttributeLeft
relatedBy:NSLayoutRelationEqual
toItem:superview
attribute:NSLayoutAttributeLeft
multiplier:1.0
constant:padding.left],
[NSLayoutConstraint constraintWithItem:view1
attribute:NSLayoutAttributeBottom
relatedBy:NSLayoutRelationEqual
toItem:superview
attribute:NSLayoutAttributeBottom
multiplier:1.0
constant:-padding.bottom],
[NSLayoutConstraint constraintWithItem:view1
attribute:NSLayoutAttributeRight
relatedBy:NSLayoutRelationEqual
toItem:superview
attribute:NSLayoutAttributeRight
multiplier:1
constant:-padding.right],
]];
即使有这样一个简单的例子,所需的代码也非常冗长,当你有超过2或3个视图时很快变得不可读。 另一种选择是使用视觉格式语言(VFL),这种语言有点不长。 然而,ASCII类型语法有其自身的缺陷,并且它也有点难以动画,因为NSLayoutConstraint constraintsWithVisualFormat:返回一个数组。
Prepare to meet your Maker! - 看一下Maker
这里使用MASConstraintMaker创建同样的约束。
UIEdgeInsets padding = UIEdgeInsetsMake(10, 10, 10, 10);
[view1 mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.top.equalTo(superview.mas_top).with.offset(padding.top); //with is an optional semantic filler
make.left.equalTo(superview.mas_left).with.offset(padding.left);
make.bottom.equalTo(superview.mas_bottom).with.offset(-padding.bottom);
make.right.equalTo(superview.mas_right).with.offset(-padding.right);
}];
或者,可以更短和简洁
[view1 mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.edges.equalTo(superview).with.insets(padding);
}];
另请注意,在第一个示例中,我们必须将约束添加到superview [superview addConstraints:....但是Masonry会自动将约束添加到适当的视图中。
Masonry也会为你调用view1.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = NO;。
Not all things are created equal - 并不是所有的约束都使用equal
-
.equalTo相当于NSLayoutRelationEqual -
.lessThanOrEqualTo相当于NSLayoutRelationLessThanOrEqual -
.greaterThanOrEqualTo相当于NSLayoutRelationGreaterThanOrEqual
这三个等式约束接受一个可以是以下任何一个的参数:
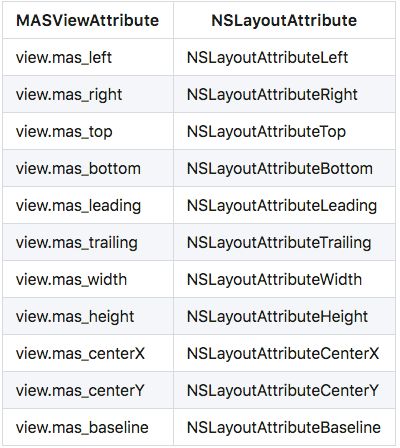
1. MASViewAttribute
make.centerX.lessThanOrEqualTo(view2.mas_left);
2. UIView/NSView
如果你想view.left大于或等于label.left:
//these two constraints are exactly the same
make.left.greaterThanOrEqualTo(label);
make.left.greaterThanOrEqualTo(label.mas_left);
3. NSNumber
自动布局允许将宽度和高度设置为常量值。 如果要将视图设置为具有最小和最大宽度,则可以将数字传递给equality block:
//width >= 200 && width <= 400
make.width.greaterThanOrEqualTo(@200);
make.width.lessThanOrEqualTo(@400)
但是,“自动布局”不允许将对齐属性(如left,right,centerY等)设置为常量值。 因此,如果您为这些属性传递NSNumber,Masonry会将这些变为相对于视图的父视图的约束,即:
//creates view.left = view.superview.left + 10
make.left.lessThanOrEqualTo(@10)
您可以使用基元和结构来构建约束,而不是使用NSNumber,如下所示:
make.top.mas_equalTo(42);
make.height.mas_equalTo(20);
make.size.mas_equalTo(CGSizeMake(50, 100));
make.edges.mas_equalTo(UIEdgeInsetsMake(10, 0, 10, 0));
make.left.mas_equalTo(view).mas_offset(UIEdgeInsetsMake(10, 0, 10, 0));
默认情况下,支持autoboxing的宏以mas_为前缀。 通过在导入Masonry之前定义MAS_SHORTHAND_GLOBALS,可以使用未加前缀的版本。
4. NSArray
任何先前类型的混合阵列
make.height.equalTo(@[view1.mas_height, view2.mas_height]);
make.height.equalTo(@[view1, view2]);
make.left.equalTo(@[view1, @100, view3.right]);
Learn to prioritize - 学习优先级
-
.priority允许您指定确切的优先级 -
.priorityHigh相当于UILayoutPriorityDefaultHigh -
.priorityMedium介于高低之间 -
.priorityLow相当于UILayoutPriorityDefaultLow
优先级可以固定到约束链的末尾,如下所示:
make.left.greaterThanOrEqualTo(label.mas_left).with.priorityLow();
make.top.equalTo(label.mas_top).with.priority(600);
Composition, composition, composition
Masonry还为您提供了一些方便的方法,可以同时创建多个约束。 这些被称为MASCompositeConstraints
edges
// make top, left, bottom, right equal view2
make.edges.equalTo(view2);
// make top = superview.top + 5, left = superview.left + 10,
// bottom = superview.bottom - 15, right = superview.right - 20
make.edges.equalTo(superview).insets(UIEdgeInsetsMake(5, 10, 15, 20))
size
// make width and height greater than or equal to titleLabel
make.size.greaterThanOrEqualTo(titleLabel)
// make width = superview.width + 100, height = superview.height - 50
make.size.equalTo(superview).sizeOffset(CGSizeMake(100, -50))
center
// make centerX and centerY = button1
make.center.equalTo(button1)
// make centerX = superview.centerX - 5, centerY = superview.centerY + 10
make.center.equalTo(superview).centerOffset(CGPointMake(-5, 10))
您可以链接视图属性以提高可读性:
// All edges but the top should equal those of the superview
make.left.right.and.bottom.equalTo(superview);
make.top.equalTo(otherView);
Hold on for dear life
有时您需要修改现有约束以设置动画或删除/替换约束。 在Masonry中,有一些不同的方法来更新约束。
1. 引用
您可以通过将约束生成表达式的结果分配给局部变量或类属性来保留特定约束的引用。 您还可以通过将它们存储在数组中来引用多个约束。
// in public/private interface
@property (nonatomic, strong) MASConstraint *topConstraint;
...
// when making constraints
[view1 mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
self.topConstraint = make.top.equalTo(superview.mas_top).with.offset(padding.top);
make.left.equalTo(superview.mas_left).with.offset(padding.left);
}];
...
// then later you can call
[self.topConstraint uninstall];
2. mas_updateConstraints
或者,如果您只更新约束的常量值,则可以使用便利方法mas_updateConstraints而不是mas_makeConstraints
// this is Apple's recommended place for adding/updating constraints
// this method can get called multiple times in response to setNeedsUpdateConstraints
// which can be called by UIKit internally or in your code if you need to trigger an update to your constraints
- (void)updateConstraints {
[self.growingButton mas_updateConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.center.equalTo(self);
make.width.equalTo(@(self.buttonSize.width)).priorityLow();
make.height.equalTo(@(self.buttonSize.height)).priorityLow();
make.width.lessThanOrEqualTo(self);
make.height.lessThanOrEqualTo(self);
}];
//according to apple super should be called at end of method
[super updateConstraints];
}
3. mas_remakeConstraints
mas_updateConstraints对于更新一组约束很有用,但除了更新常量值之外做任何事情都会让人筋疲力尽。 这就是mas_remakeConstraints的用武之地。
mas_remakeConstraints类似于mas_updateConstraints,但它不是更新常量值,而是在再次安装之前删除所有约束。 这使您可以提供不同的约束,而不必保留对要删除的引用的引用。
- (void)changeButtonPosition {
[self.button mas_remakeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.size.equalTo(self.buttonSize);
if (topLeft) {
make.top.and.left.offset(10);
} else {
make.bottom.and.right.offset(-10);
}
}];
}
您可以在Masonry iOS Examples项目中找到所有三种方法的更详细示例。
When the ^&*!@ hits the fan!
布置您的视图并不总是顺利。 因此,你不想像这样看控制台输出:
Unable to simultaneously satisfy constraints.....blah blah blah....
(
"=5000)]>",
"",
"",
""
)
Will attempt to recover by breaking constraint
=5000)]>
Masonry为NSLayoutConstraint添加了一个类别,它覆盖了- (NSString *)描述的默认实现。 现在,您可以为视图和约束提供有意义的名称,还可以轻松选择由Masonry创建的约束。
这意味着你的控制台输出现在看起来像这样:
Unable to simultaneously satisfy constraints......blah blah blah....
(
"",
"= 5000>",
"",
""
)
Will attempt to recover by breaking constraint
= 5000>
有关如何设置,请查看Masonry工作区中的Masonry iOS Examples项目。
Where should I create my constraints?
@implementation DIYCustomView
- (id)init {
self = [super init];
if (!self) return nil;
// --- Create your views here ---
self.button = [[UIButton alloc] init];
return self;
}
// tell UIKit that you are using AutoLayout
+ (BOOL)requiresConstraintBasedLayout {
return YES;
}
// this is Apple's recommended place for adding/updating constraints
- (void)updateConstraints {
// --- remake/update constraints here
[self.button remakeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.width.equalTo(@(self.buttonSize.width));
make.height.equalTo(@(self.buttonSize.height));
}];
//according to apple super should be called at end of method
[super updateConstraints];
}
- (void)didTapButton:(UIButton *)button {
// --- Do your changes ie change variables that affect your layout etc ---
self.buttonSize = CGSize(200, 200);
// tell constraints they need updating
[self setNeedsUpdateConstraints];
}
@end
Installation - 安装
使用orsome CocoaPods
在Podfile中
pod 'Masonry'
如果你想使用masonry而没有那些讨厌的mas_前缀。 在导入Masonry之前,将#define MAS_SHORTHAND添加到您的prefix.pch中
#define MAS_SHORTHAND
Code Snippets - 代码块
将包含的代码片段复制到〜/ Library / Developer / Xcode / UserData / CodeSnippets,以闪电般的速度编写masonry块!
mas_make -> [<#view#> mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) { <#code#> }];
mas_update -> [<#view#> mas_updateConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) { <#code#> }];
mas_remake -> [<#view#> mas_remakeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) { <#code#> }];
Features - 特点
- 不限于自动布局的子集。
NSLayoutConstraint可以做的任何事情,Masonry也可以做! - 出色的调试支持,为您的视图和约束提供有意义的名称
- 约束读起来像句子。
- 没有疯狂的宏观魔法。 Masonry不会用宏污染全局命名空间。
- 不基于字符串或字典,因此您可以获得编译时检查。
后记
本篇主要讲述了Masonry框架一些基本了解和信息,感兴趣的给个赞或者关注~~~~