O - 推箱子 HDU - 1254(bfs_box + bfs_man)
O - 推箱子 HDU - 1254
推箱子是一个很经典的游戏.今天我们来玩一个简单版本.在一个M*N的房间里有一个箱子和一个搬运工,搬运工的工作就是把箱子推到指定的位置,注意,搬运工只能推箱子而不能拉箱子,因此如果箱子被推到一个角上(如图2)那么箱子就不能再被移动了,如果箱子被推到一面墙上,那么箱子只能沿着墙移动.
现在给定房间的结构,箱子的位置,搬运工的位置和箱子要被推去的位置,请你计算出搬运工至少要推动箱子多少格.
Input
输入数据的第一行是一个整数T(1<=T<=20),代表测试数据的数量.然后是T组测试数据,每组测试数据的第一行是两个正整数M,N(2<=M,N<=7),代表房间的大小,然后是一个M行N列的矩阵,代表房间的布局,其中0代表空的地板,1代表墙,2代表箱子的起始位置,3代表箱子要被推去的位置,4代表搬运工的起始位置.
Output 对于每组测试数据,输出搬运工最少需要推动箱子多少格才能帮箱子推到指定位置,如果不能推到指定位置则输出-1.
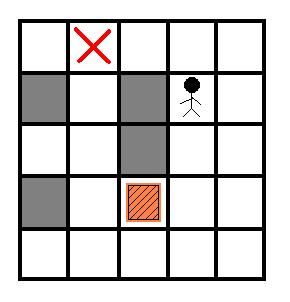
Sample Input
1
5 5
0 3 0 0 0
1 0 1 4 0
0 0 1 0 0
1 0 2 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
Sample Output
4
思路如下
此题⚠️:
- 在人不推箱子的时候,箱子也是障碍物
- 箱子可以重复走某个位置,但是这个 位置 的每个方向只能走一次(因为 在某个位置 某个方向上重复走 是浪费步数的)
- 箱子在某个位置能否被移动,要看 人 能能否从上一次移动之后人所处的位置 —> 移动到 现在箱子后面的位置(这是因为:人只有先到达箱子后面这个位置 才可以去推箱子。)
题解如下
#include