编译原理——LL(1)语法分析
编译原理——语法分析
编译原理课程上的一次实验
程序可实现:
使用自上而下的LL(1)语法分析法,分析指定txt文件中的文法。
结果显示包括:
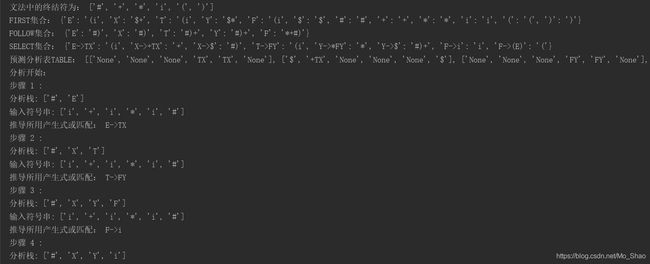
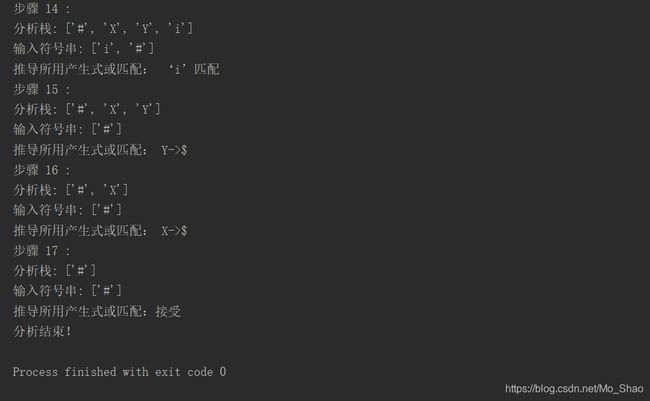
文法、终结符集、非终结符集、First集、Follow集、Select集、预测分析表Table以及分析过程(包含步骤、分析栈、输入符号串、推导所用产生式或匹配)
txt文件内容已经是左递归后的文法,“$”表示推导出空的文法的右部。含有“ ‘ ”的非终结符不方便识别,这里用其他大写英文字母(X、Y)代替该类非终结符。
文件路径改为存储路径后即可正常运行。
有问题可留言或私聊讨论~
txt文件内容:
E->TX
X->+TX
X->$
T->FY
Y->*FY
Y->$
F->i
F->(E)
源代码:
#定义终结符:
VT=['a','b','c','d','e','f','g','h','i','j','k','l','m','n','o','p','q','r','s','t','u','v','w','x','y','z','+','_','*',"/",'(',')','#']
#定义非终结符:
VN=["A","B","C","D","E","F","G","H","I","J","K","L","M","N","O","P","Q","R","S","T","U","V","W","X","Y","Z" ]
#终结符匹配函数:
def VT_matching(p):
for word in VT:
if p==word:
return 1
#非终结符匹配函数:
def VN_matching(p):
for word in VN:
if p==word:
return 1
#从文件提取文法:
with open(r'D:\PC\txt\prediction analysis.txt') as f:
predictions = [] #使用predictions来记录所有文法,以列表的形式
while True:
line=f.readline().split() #按行读取并去掉空格
predictions=predictions+line
if not line:break
print("文法为:",predictions)
#扫描非终结符:
Vn=[] #Vn是非终结符列表
Vn_copy=[]
for prediction in predictions:
p=prediction #p是一个字符串
if (VN_matching(p[0])==1):
Vn.append(p[0])
for i in Vn:
if(i not in Vn_copy):
Vn_copy.append(i)
Vn=Vn_copy
print("文法中的非终结符为:",Vn)
#扫描终结符:
Vt=["#"] #Vt是终结符列表,初始化时就有#
for prediction in predictions: #prediction是一个字符串
for t in prediction:
if (VT_matching(t)==1 ):
Vt.append(t)
set(Vt) #set语句去除Vt中的重复元素
print("文法中的终结符为:",Vt)
#建立FIRST集、FOLLOW集和SELECT集合,三者都是字典形式
FIRST={}
FOLLOW={}
SELECT={}
#初始化两个字典(非终结符的FIRST集合里为空,FOLLOW集合理为#)
def initialization():
for prediction in predictions:
left=prediction.split('->')[0]
right=prediction.split('->')[1]
FIRST[left]=""
FOLLOW[left]=""
FIRST["$"]="$"
for i in Vt:
FIRST[i]=i
FOLLOW[Vn[0]]='#' #文法开始非终结符的FOLLOW集合为#
#FIRST集合函数:
def FirstGet():
for prediction in predictions:
left=prediction.split("->")[0]
right=prediction.split("->")[1]
#FIRST集合中面向“A->bB”型解决:
if VT_matching(right[0])==1:
FIRST[left]=FIRST.get(left)+right[0]
#FIRST集合中面向“A->$”型解决:
elif right=='$':
FIRST[left]=FIRST.get(left)+right
#FIRST集合中面向“A->B”型解决:
elif VN_matching(right[0])==1:
#这一步需要手动迭代一次才能得出每个非终结符的FISRT集合
FIRST[left]=FIRST.get(left)+FIRST.get(right[0])
#去除FIRST集合中重复项函数:
def FisrtRemove():
while(1):
test=FIRST
FirstGet()
#去除重复项
for i,j in FIRST.items():
temp=""
for word in list(set(j)):
temp=temp+word
FIRST[i]=temp
if test==FIRST:
break
#初始化并建立FIRST集合:
initialization()
FirstGet()
FirstGet()
FisrtRemove()
print("FIRST集合:",FIRST)
#判断文法中非终结符能否推出空集:
def Empty(p):
a=p+'->$'
for prediction in predictions:
if prediction==a:
i=1
break
else:
i=0
continue
return i
#FOLLOW集合函数:
def FollowGet():
for prediction in predictions:
left=prediction.split('->')[0]
right=prediction.split('->')[1]
if right=='$': #如果右部为:$(空)
continue #则continue
elif VT_matching(right)==1: #如果右部为:单个终结符
continue #则continue
elif VN_matching(right)==1: #如果右部为:单个非终结符
FOLLOW[right]=FOLLOW.get(left)+FOLLOW.get(right) #则把左部非终结符的FOLLOW集,加入右部非终结符的FOLLOW集
else: #剩下的,右部复杂情况
temp=[]
for i in right:
temp.append(i)
temp.reverse() #temp里为右部字符串的倒序
if VN_matching(temp[0])==1: #如果右部最后一位字符为非终结符
FOLLOW[temp[0]]=FOLLOW.get(temp[0])+FOLLOW.get(left) #则把左部非终结符的FOLLOW集,加入右部非终结符的FOLLOW集
temp1=temp[0]
for j in temp[1:]: #依次倒序扫描右部
if VT_matching(j)==1: #若j为终结符
continue
elif Empty(temp1)==0: #若非终结符temp1无法推出空
continue
else: #剩下的,若非终结符j能推出空
FOLLOW[j]=FOLLOW.get(j)+FOLLOW.get(left)
temp1=j
#以上为处理#
c=0
while(c<len(right)-1):
# print("长度:",len(right)-1)
if VT_matching(right[c])==1: #若c为终结符
c=c+1
continue
else: #剩下的,若c为非终结符
if VT_matching(right[c+1])==1: #若c+1为终结符
FOLLOW[right[c]]=FOLLOW.get(right[c])+right[c+1] #该终结符加入FOLLOW集合
else: #剩下的,若c+1为非终结符
FOLLOW[right[c]]=FOLLOW.get(right[c])+FIRST.get(right[c+1]) #该非终结符的FIRST集合加入FOLLOW集合
c=c+1
#去除FOLLOW集合中重复项函数:
def FollowRemove():
while(1):
test=FOLLOW
FollowGet()
#去除重复项
for i,j in FOLLOW.items():
temp=""
for word in list(set(j)):
if word=="$": #去除FOLLOW集中的"$"
continue
else:
temp=temp+word
FOLLOW[i]=temp
if test==FOLLOW:
break
#建立FOLLOW集合
FollowGet()
FollowRemove()
print("FOLLOW集合:",FOLLOW)
def SelectGet():
for prediction in predictions:
SELECT[prediction]="" #初始化SELECT集合
left=prediction.split('->')[0]
right=prediction.split('->')[1]
if right=="$" or (VN_matching(right)==1 and Empty(right)==1): #右部为空或右部为单非终结符且推导出空
con=""
for i in FIRST.get(right[0]):
if i== "$": #去除FIRST集中的"$"
continue
else:
con=con+i
FIRST[right[0]]=con
SELECT[prediction]=FIRST.get(right[0])+FOLLOW.get(left) #SELECT(A->α)=FIRST(α)-"$")∪FOLLOW(A)
else:
SELECT[prediction]=FIRST.get(right[0]) #SELECT集合为FIRST(α)
SelectGet()
print("SELECT集合:",SELECT)
table_copy=[] #文法分析表、row和col字典复制版的初始化
row_copy={}
col_copy={}
def TABLE():
#初始化预测分析表table,表内全为:None
table=[["None"]*(len(Vt)) for i in range(len(Vn))]
global table_copy
table_copy=table
row={} #行字典
col={} #列字典
c=0
for i in Vn:
row[i]=c
c=c+1 #非终结符个数为表的行数
d=0
for i in Vt:
col[i]=d
d=d+1 #终结符个数为表的列数
# print("row字典:",row)
# print("col字典:",col)
global row_copy
row_copy=row.copy()
global col_copy
col_copy=col.copy()
#至此初始化预测分析表结束
for prediction in predictions: #对每一句文法进行分析
left=prediction.split('->')[0]
right=prediction.split('->')[1]
string=SELECT.get(prediction) #string记录该文法的SELECT集和中的终结符字符串
for i in Vt: #对每个终结符进行分析
if(i in string): #若该终结符在string里
a=row.get(left)
b=col.get(i)
table[a][b]=right #则把文法非左部加入预测分析表中
print("预测分析表TABLE:",table)
TABLE()
#文法匹配函数:
def Select_matching(x,y): #x,y是字符形式.x为非终结符,y为终结符
g=row_copy.get(x)
h=col_copy.get(y)
if (table_copy[g][h]!="None"):
return 1
#文法返回函数:
def Select_return(x,y): #x,y是字符形式
g=row_copy.get(x)
h=col_copy.get(y)
return (table_copy[g][h])
def PROCESS():
# string=input("请输入待分析符号串:")
string="i+i*i#"
Sstack=[] #建立输入符号串列表
for i in string:
Sstack.append(i)
#print(Sstack)
Astack=["#"] #初始化分析栈
Astack.append(Vn[0]) #文法开始符号进入分析栈
print("分析开始:")
print("步骤 1 :")
print("分析栈:", Astack)
print("输入符号串:", Sstack)
step=1
#以下为分析过程
while (Astack!=["#"] or Sstack!=["#"]): #分析结束的标志
Schar="" #用Schar存储输入符号串的待分析字符(均为非终结符)
Schar=Sstack[0] #Schar记录输入串首个字符
Achar="" #用Achar存储待分析字符(可能为终结符或非终结符)
Achar=Astack[len(Achar)-1] #Achar记录分析栈中最后一个字符
# print("分析栈中最后一个字符:",Achar)
# print("输入字符串中第一个字符:",Schar)
if ((Achar in Vn) and Select_matching(Achar,Schar)==1): #若Achar为非终结符(Achar和Schar两者能匹配)
print("推导所用产生式或匹配:",Achar+"->"+Select_return(Achar,Schar))
Astack.pop(len(Astack)-1) #删除分析栈中最后一个字符(非终结符)
selectstring=Select_return(Achar,Schar) #使用文法返回函数将非左部赋予selectstring(字符串)
temp=[]
for i in selectstring:
temp.append(i)
temp.reverse() #将selectstring倒序后赋予temp(列表)
if (temp!=["$"]): #若temp为空,则不把temp中的“空”元素加入分析栈
for i in temp:
Astack.append(i) #temp里列表元素入分析栈
# print("Astack:",Astack)
else: #剩下的,Achar为终结符
print("推导所用产生式或匹配:","‘"+Achar+"’"+"匹配")
Astack.pop(len(Astack)-1) #删除分析栈中最后一个字符(终结符)
if Sstack[0]!="#": #分析到输入字符串最后一个字符后,保留字符“#”
Sstack.pop(0) #删除输入字符串中的第一个字符
step+=1
print("步骤",step,":")
print("分析栈:",Astack)
print("输入符号串:",Sstack)
print("推导所用产生式或匹配:接受")
print("分析结束!")
PROCESS()