解决mFactorySet在Android Q中被非SDK接口限制的问题
mFactorySet问题由来
mFactorySet这个值如果熟悉的同学一定知道,通常我们在使用换肤框架的时候,需要使用我们自定义的LayoutInflater.Factory类,这时候就需要调用LayoutInflater的setFactory方法。而我之前编写的一个基于Factory去给原生控件增加shapre xml属性的框架也是同样的原理(无需自定义View,彻底解放shape,selector吧)。
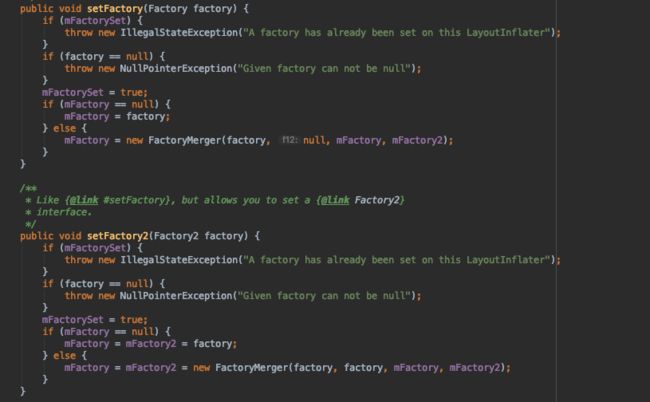
我们来看一下setFactory方法的源码:
通过源码得知,我们在调用setFactory方法的时候,首先会判断mFactorySet的值,如果mFactorySet为true,则代表该LayoutInflater已经设置了factory,而系统一般会在Activity的onCreate方法中设置自己的factory类。
如果这时候我们想要通过替换自己的factory类来实现换肤功能的话,我们会通过反射去修改mFactorySet的值为false,这样就可以调用setFactory方法。
下面就是在android q之前常用的方法:
try {
Field field = LayoutInflater.class.getDeclaredField("mFactorySet");
field.setAccessible(true);
field.setBoolean(inflater, false);
BackgroundFactory factory = new BackgroundFactory();
inflater.setFactory2(factory);
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
然而android Q更新之后,将mFactorySet加入来非SDK接口限制的黑名单,如果在q上我们再通过这种方法去setFactroy,会报如下错误:
java.lang.NoSuchFieldException: No field mFactorySet in class Landroid/view/LayoutInflater; (declaration of 'android.view.LayoutInflater' appears in /system/framework/framework.jar!classes3.dex)
这就是这个问题的由来,接下来就来探讨一下如何解决这个问题。
解决android Q上无法二次setFactroy的问题。
google官方提供的方法
虽然google已经将这个字段放在sdk限制名单里,但是它也给我们提供来解决方案:
# mFactorySet is being modified by app developers to reset the factory
# on an existing LayoutInflater. Instead, a developer should use the
# existing LayoutInflater#cloneInContext() to create a new LayoutInflater
# and set the factory on it instead.
#
# This is often desired at the Activity level, so that any part of
# the application getting a LayoutInflater using the Activity as
# a Context will get the LayoutInflater with a custom factory. To
# do this, the Activity has to replace the returned LayoutInflater.
# Something like this should work:
#
# private LayoutInflater mLayoutInflater;
#
# @Override
# public Object getSystemService(String name) {
# if (Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE.equals(name)) {
# if (mLayoutInflater == null) {
# mLayoutInflater =
# ((LayoutInflater)super.getSystemService(name)).cloneInContext(this);
# mLayoutInflater.setFactory(new CustomLayoutFactory());
# }
# return mLayoutInflater;
# }
# return super.getSystemService(name);
# }
谷歌官方建议方法为,先调用LayoutInflater的cloneInContext的方法,然后setFactory,这样就可以重新设置factroy,因此我们按照谷歌的方法可以这么用:
LayoutInflater inflater = LayoutInflater.from(context).cloneInContext(context);
inflater.setFactory(factory);
但是通过调试发现,这种方法对我们来说是无效的,原因如下:
- cloneInContext返回的LayoutInflater是一个新的LayoutInflater对象,和LayoutInflater.from(context)并不是同一个对象
- 新返回的inflater进行setFactory是没有问题的,但是Activity以及Fragment创建View的时候还是通过LayoutInflater.from(context)获取的,所以cloneInContext并不能直接对原inflater进行修改。
通过反射LayoutInflaterCompat去修改factory
之所以想到LayoutInflaterCompat,是因为LayoutInflaterCompat也提供来setFacttory方法,它属于supportv4包,google应该不会随随便便让自己是support包被加入sdk限制接口,我们来看一下LayoutInflaterCompat的源码:
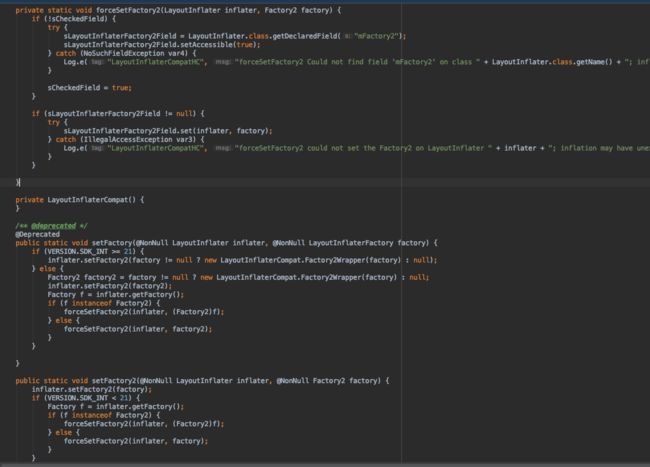
LayoutInflaterCompat提供了setFactory2方法,那我们能否直接通过这个方法来设置factory呢,显然是不能的,因为该方法内有api的限制:
if (VERSION.SDK_INT < 21) {
Factory f = inflater.getFactory();
if (f instanceof Factory2) {
forceSetFactory2(inflater, (Factory2)f);
} else {
forceSetFactory2(inflater, factory);
}
}
只有api小于21才会去调用forceSetFactory2,顾名思义,强制去设置factory。通过forceSetFactory2源码可得,它是通过反射去设置inflater的factory。
但是我们开发app不可能只是适配api21以下版本,所以这个方法并不可用。但是它给了我们思路,我们可以直接通过反射去设置factory的值。因此我们可以通过如下代码去强制设置factory的值:
private static void forceSetFactory2(LayoutInflater inflater) {
Class compatClass = LayoutInflaterCompat.class;
Class inflaterClass = LayoutInflater.class;
try {
Field sCheckedField = compatClass.getDeclaredField("sCheckedField");
sCheckedField.setAccessible(true);
sCheckedField.setBoolean(inflater, false);
Field mFactory = inflaterClass.getDeclaredField("mFactory");
mFactory.setAccessible(true);
Field mFactory2 = inflaterClass.getDeclaredField("mFactory2");
mFactory2.setAccessible(true);
BackgroundFactory factory = new BackgroundFactory();
if (inflater.getFactory2() != null) {
factory.setInterceptFactory2(inflater.getFactory2());
} else if (inflater.getFactory() != null) {
factory.setInterceptFactory(inflater.getFactory());
}
mFactory2.set(inflater, factory);
mFactory.set(inflater, factory);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
总结
如何绕过mFactorySet的限制去设置factory的方法已经给出,但是有一点要注意:尽量同时设置factory和factory2,这样才能尽可能保证view创建的时候使用我们自定义的factory类。